Fundamentals of AI and ML
Fundamentals of AI and ML
This article explores Fundamentals of AI and ML providing a clear overview of their definitions, Difference, Types of AI and ML, and How to Use AI and ML in Business.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are rapidly transforming how we interact with the world, driving innovation across industries like healthcare, transportation, finance, and education. These groundbreaking technologies power everything from voice assistants and recommendation systems to self driving cars and advanced medical diagnostics.

What are the basics of AI and ML?
What is AI (Artificial Intelligence)?
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. The goal of AI is to create systems that can perform tasks that usually require human intelligence. These tasks include:
- Understanding natural language (like voice commands)
- Recognizing images and speech
- Making decisions
- Playing games
- Driving cars
Examples of AI:
- Chatbots
- Self-driving cars
- Face recognition on smartphones
- Smart assistants (Siri, Google Assistant)
- Artificial Intelligence is a broad concept focused on creating smart systems, while Machine Learning is a subset that enables systems to learn from data.
- There are three main types of learning in ML supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
- Common machine learning algorithms include Decision Trees, K Nearest Neighbors, Support Vector Machines, and Neural Networks.
- Data preprocessing, such as cleaning and transforming raw data, is essential for improving model accuracy and performance.
What is ML (Machine Learning)?
ML is a subset of AI that focuses on teaching machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed for every single task.
Instead of writing rules for every scenario, we give the machine lots of data, and it learns patterns to make decisions or predictions.
Examples of ML:
- Spam email filters
- Product recommendations (Amazon, Netflix)
- Predicting house prices based on features
- Language translation
Differences Between AI and ML
| Feature | AI | ML |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broad field aiming to simulate human intelligence | Subfield of AI focused on learning from data |
| Focus | Decision-making, problem-solving | Pattern recognition, learning from data |
| Examples | Chess-playing bots, Siri | Spam detection, recommendation engines |
| Techniques Used | Rule-based systems, ML, DL | Regression, classification, clustering |
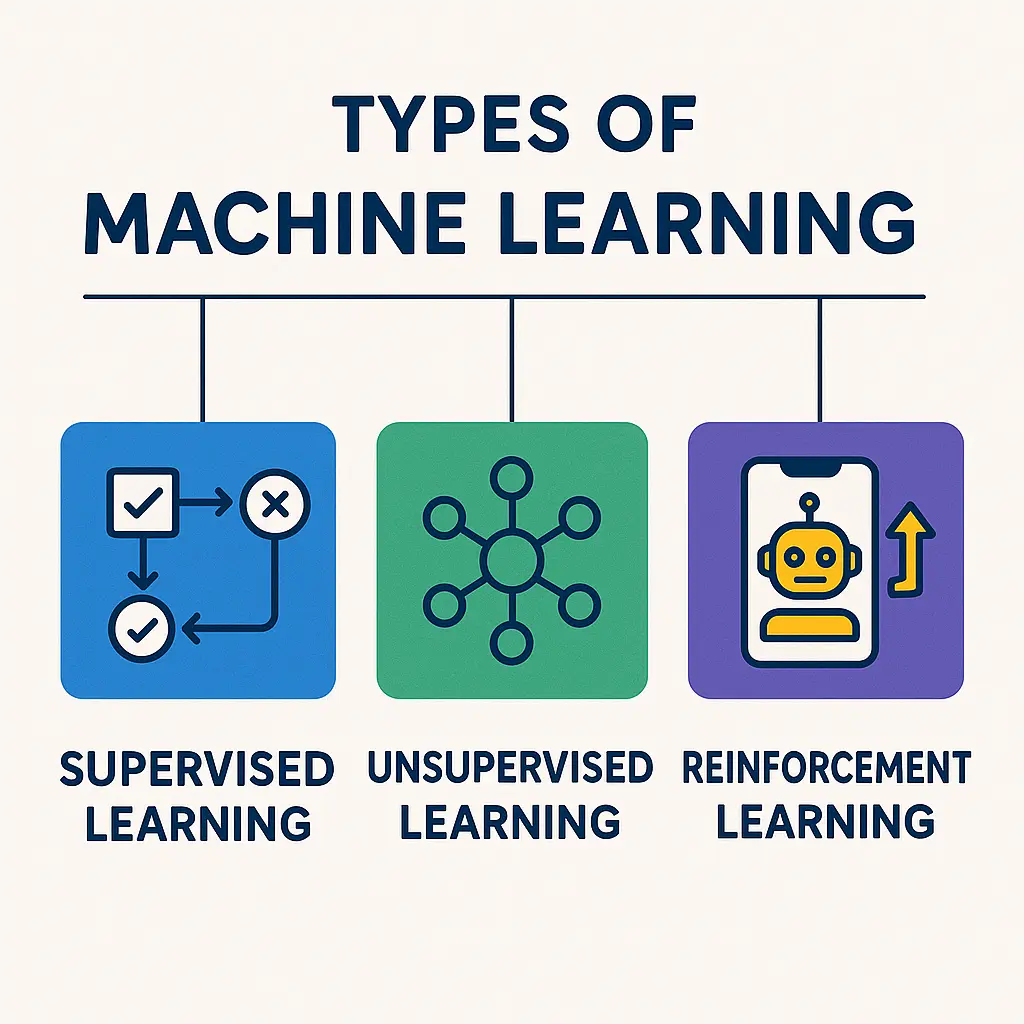
Types of Machine Learning
1. Supervised Learning
- Definition: Supervised learning involves training a model on a labeled dataset, where both the input and the desired output are provided.
- How it works: The model learns the relationship between input data and output labels to make future predictions.
- Email spam detection
- Predicting house prices
- Image classification
- Linear Regression
- Decision Trees
- Support Vector Machines (SVM)
- Neural Networks
2. Unsupervised Learning
- Definition: In unsupervised learning, the model is given data without explicit labels or outputs. It tries to find patterns or groupings within the data.
- How it works: The algorithm explores the structure of the data and identifies relationships or clusters on its own.
- Customer segmentation
- Market basket analysis
- Anomaly detection
- K Means Clustering
- Hierarchical Clustering
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Autoencoders
3. Semi Supervised Learning
- Definition: This type combines both labeled and unlabeled data, often using a small amount of labeled data with a large pool of unlabeled data.
- How it works: The model first learns from the labeled data and then applies that learning to structure the unlabeled data.
Common use cases:
- Medical imaging
- Speech analysis
- Text classification with limited labeled examples
Advantages:
- Reduces the need for large amounts of labeled data
- Often more cost-effective than supervised learning
4. Reinforcement Learning
- Definition: Reinforcement learning involves training an agent to make decisions by rewarding it for correct actions and penalizing it for wrong ones.
- How it works: The model learns by interacting with an environment and adjusting its strategy based on feedback.
Common use cases:
- Game playing (e.g., AlphaGo)
- Robotics
- Autonomous vehicles
Popular algorithms:
- Q-Learning
- Deep Q-Networks (DQN)
- Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)
- AI is used in chatbots and virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to provide automated responses and assistance.
- Machine Learning powers recommendation systems that personalize content on platforms such as Netflix, Amazon, and Spotify.
- In healthcare, AI helps detect diseases early and supports the creation of personalized treatment plans.
- Banks and financial institutions use ML models to detect fraudulent transactions and reduce risks.
What Are the 4 Types of AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the way we interact with technology. From voice assistants to self driving cars, AI is all around us. But to understand its capabilities and limitations,
Here’s a simple breakdown in point format:
1. Reactive Machines
Definition: These are the most basic form of AI. Reactive machines can only react to specific inputs with predefined outputs. They don’t have memory or the ability to learn from past experiences.
Key Characteristics:
- No memory based functionality
- Operates only in the present moment
- Doesn’t improve over time
Examples:
- IBM’s Deep Blue (chess-playing computer)
- Basic recommendation systems
2. Limited Memory
Definition: This type of AI can use past experiences to make better decisions. Limited memory AI systems are trained using historical data and improve over time.
Key Characteristics:
- Has short term memory
- Learns from past data
- Common in today’s AI applications
Examples:
- Self-driving cars (use data from previous trips)
- Chatbots and virtual assistants
- Fraud detection systems
3. Theory of Mind
Definition: A more advanced type of AI, theory of mind AI refers to machines that can understand emotions, beliefs, and thought processes something humans do naturally.
Key Characteristics:
- Recognizes and responds to human emotions
- Interacts socially with humans
- Still under development and largely theoretical
Potential Uses:
- Emotional AI in healthcare and education
- Human-robot interactions
- Personalized customer service
4. Self-Aware AI
Definition: This is the most advanced and futuristic type of AI. Self-aware AI will not only understand emotions and thoughts but also have its own consciousness and self awareness.
Key Characteristics:
- Has a sense of self
- Possesses consciousness and awareness
- Can make independent decisions
Status:
- Still theoretical and not yet developed
- Subject of ethical and philosophical debates
How to Use AI and ML in Business?
In today’s fast paced digital world, businesses that want to stay ahead of the curve must embrace emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). These tools can significantly enhance operations, reduce costs, and provide deep insights into customer behavior. Here’s a practical guide on how to use AI and ML in business, broken down into actionable points:
1. Enhance Customer Experience
- Use AI-powered chatbots for 24/7 customer support.
- Implement recommendation engines (like Netflix or Amazon) to personalize product or content suggestions.
- Leverage sentiment analysis tools to understand customer feedback and improve satisfaction.
2. Automate Routine Tasks
- Streamline repetitive processes like data entry, scheduling, and invoice processing with AI automation.
- Use ML algorithms to handle customer inquiries through automated ticketing systems.
- Reduce human error and free up employee time for higher value tasks.
3. Improve Marketing Strategy
- Analyze customer data to predict buying behavior and personalize marketing campaigns.
- Use AI to optimize ad placements and bidding strategies in real-time.
- Implement ML tools to segment audiences and target the right users more accurately.
4. Boost Sales and Lead Generation
- Use AI to identify high quality leads based on past behavior and engagement.
- Employ predictive analytics to forecast sales trends and close more deals.
- Automate follow ups and email campaigns with AI-driven tools.
5. Optimize Supply Chain and Inventory
- Forecast demand more accurately using machine learning models.
- Automate inventory management to reduce waste and prevent stockouts.
- Use AI to optimize logistics and delivery routes for faster and cheaper shipping.
6. Enhance Security and Fraud Detection
- Monitor transactions in real time to detect fraudulent activity using ML algorithms.
- Use AI to identify anomalies in user behavior and trigger alerts.
- Improve cybersecurity with AI based threat detection systems.
7. Data Driven Decision Making
- Use AI to gather and analyze large datasets faster than traditional methods.
- Implement ML models to forecast trends and support strategic decisions.
- Generate actionable insights from business data without needing advanced technical skills.
8. Human Resources and Recruitment
- Use AI to scan resumes and shortlist candidates based on job requirements.
- Analyze employee performance and predict attrition with machine learning.
- Implement AI chatbots to handle basic HR queries and onboarding.
9. Product Development and Innovation
- Use AI to simulate product designs and predict performance.
- Collect and analyze user feedback automatically to iterate faster.
- Identify gaps in the market using data-driven insights.
If you’re wondering how to use AI and ML in business, start small identify one or two pain points and experiment with AI tools tailored to those needs. As you grow more confident, scale up your efforts across departments. The key is to align AI/ML solutions with your business goals for maximum impact.
Conclusion
Understanding the Fundamentals of AI and ML is essential for anyone looking to thrive in today’s tech driven world. These technologies are shaping industries and transforming the way we solve problems. A strong grasp of the Fundamentals of AI and ML empowers individuals to innovate and stay competitive. As AI continues to evolve, foundational knowledge remains key. Investing time in learning these concepts can open doors to countless opportunities.
FAQs
They provide the base knowledge needed to understand how intelligent systems work and how they can be applied across industries. Mastery of these fundamentals enables smarter decision-making and innovation.
From personalized recommendations to smart assistants and fraud detection, AI and ML are embedded in daily technology. Their presence is growing, making it crucial to understand their core principles.
Yes, with the right resources and dedication, beginners can build a strong foundation. Many platforms now offer structured, beginner-friendly courses.
Skills in AI and ML open doors to roles like data scientist, machine learning engineer, and AI researcher. These fields are in high demand and offer lucrative, future proof careers.


