Bool() in Python
Bool
Bool() is an built-in function in python. It returns the boolean value of a speciified object i.e is True or False using standard truth testing procedure. Booleans are essential for making decisions in your Python programs, as they are often used in conditional statements (e.g., if, elif, else) to control the flow of your code based on logical conditions.
Bool :
- It generally takes one value as parameter.
- If no values passed it will return default value which is False.
- If value passed is true it will True else False.
- In some of cases it will always return False
- If None is passed.
- If an empty list , set or any sequence is passed .
- If zero is passed .
- If and function inside bool function returns zero i.e len() or count().
- Syntax: bool(x)
- Example: x = bool(1) #return the boolean value of 1
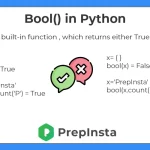
Example :
Run
# Python program
# built-in method bool()
# Returns True as x is True
x = True
print(bool(x))
# Returns False as x is False
x = False
print(bool(x))
# Returns False as x is not equal to y
x = 4
y = 14
print(bool(x==y))
# Returns False as x is None
x = None
print(bool(x))
# Returns False as x is an empty sequence
x = []
print(bool(x))
# Returns False as x is an empty mapping
x = {}
print(bool(x))
# Returns False as x is 0
x = 0.0
print(bool(x))
# Returns True as x is a non empty string
x = 'Prepinsta'
print(bool(x))
#Returns True as length of x > 1
x=(1,2)
print(bool(len(x)))Output:
True False False False False False False True True
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment