Linked List in Java
Understanding Linked List in Java Programming
Linked List in Java is a dynamic linear data structure that efficiently manages and stores large amounts of data. Unlike arrays, the elements in a linked list are not stored in contiguous memory locations.
Instead, each node contains data and a reference (or link) to the next node, allowing for flexible memory allocation and easy insertion or deletion of elements without requiring data reorganization.
This structure enables efficient memory usage and provides quick access to data based on the node references.

Explore the fundamentals of Linked Lists in Java through this article. We’ve covered key types and comparisons to build a strong foundation:
How to Make a Linked List in Java ?
A Linked List is a linear data structure composed of multiple nodes, each containing data and a link to the next node. Here’s how to implement it in Java:
Define the Node Class:
Create a class named
Nodewith two fields:Data: Stores the value.
Link/Next: Stores the reference to the next node.
Create the Linked List Class:
Implement a class named
LinkedListwith a reference to theheadnode.Include methods to insert, delete, and traverse nodes.
Insert Nodes:
To insert a node, create a new node, set its data, and link it to the existing list by updating the
nextpointer of the previous node.
Traverse the List:
Start from the
headnode and follow the links to access each node sequentially until reaching the end (null).
Manage Edge Cases:
Handle scenarios like inserting at the beginning, end, or at a specific position.

Structure of Linked List Node in Java
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head
// Linked list Node
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// constructor to initialize
Node(int d) {
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
} Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Types of Linked Lists
There are many variations but below are the most important ones:
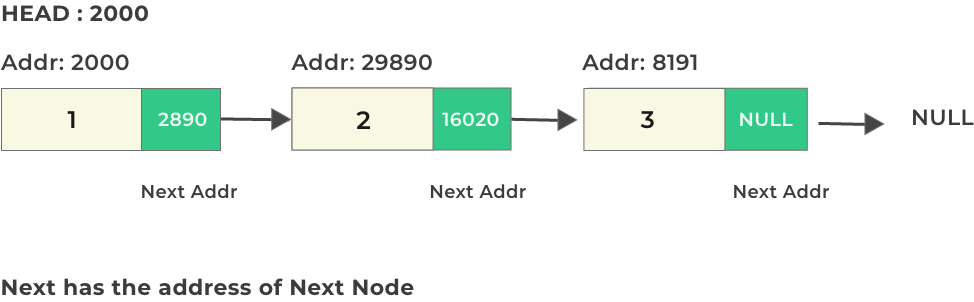
1. Singly Linked List
Singly Linked List is a linear data structure in which each node contains two parts:
Data: Stores the value.
Next: A pointer/reference to the next node in the list.
The last node’s
nextpointer points tonull, indicating the end of the list.Traversal is unidirectional — from the head to the last node.
Each node is connected to one another as the next value for each node holds the address to the next node in the sequence.
The first node is called as head and the last node is called as tail, where the last node’s next value is null.
2. Doubly Linked List
Doubly Linked List is similar to a singly linked list but with an additional pointer. Each node contains:
Data: Stores the value.
Next: A pointer/reference to the next node.
Prev: A pointer/reference to the previous node.
Traversal is bidirectional — we can move forward or backward through the list.
The main advantage is we can traverse in any direction forwards and backwards.

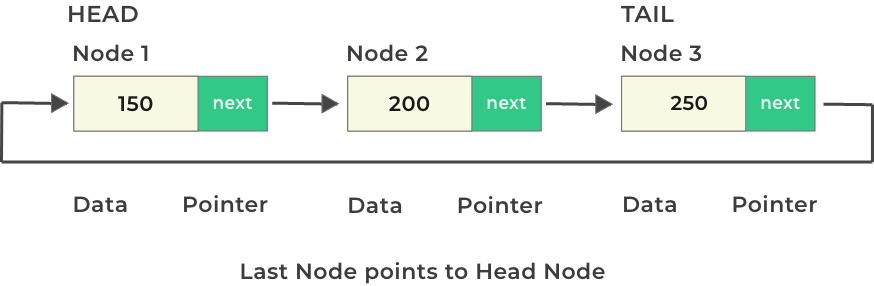
3. Circular Linked List
Circular Linked List can be either singly or doubly linked, but the last node points back to the first node, forming a circle.
There is no
nullat the end, making traversal continuous.
Types:
Singly Circular Linked List: The last node points to the head node, allowing traversal in one direction.
Doubly Circular Linked List: The last node points to the head, and the head points back to the last node, allowing traversal in both directions.
Insertion and Deletion in Linked List in Java
Insertion and Deletion in Linked List in Java
Runimport java.lang.*; class LinkedList { Node head; // not using parameterized constructor would by default // force head instance to become null // Node head = null; // can also do this, but not required // Node Class class Node{ int data; Node next; Node(int x) // parameterized constructor { data = x; next = null; } } public Node insert(int data) { // Creating newNode memory & assigning data value Node newNode = new Node(data); // assigning this newNode's next as current head node newNode.next = head; // re-assigning head to this newNode head = newNode; return head; } public void display() { Node node = head; //as linked list will end when Node reaches Null while(node!=null) { System.out.print(node.data + " "); node = node.next; } System.out.println(""); } public void delete() { if (head == null){ System.out.println("List is empty, not possible to delete"); return; } System.out.println("Deleted: " + head.data); // move head to next node head = head.next; } } class Main{ public static void main(String args[]) { LinkedList ll = new LinkedList(); ll.insert(6); ll.insert(5); ll.insert(3); ll.insert(4); ll.insert(2); ll.insert(1); ll.display(); ll.delete(); ll.delete(); ll.display(); } }
Output
1 2 4 3 5 6 Deleted: 1 Deleted: 2 4 3 5 6
Runimport java.lang.*; // Node Class class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) // parameterized constructor { data = x; next = null; } } class Main { static Node insertStart(Node head, int data) { // Creating newNode memory & assigning data value Node newNode = new Node(data); // assigning this newNode's next as current head node newNode.next = head; // re-assigning head to this newNode head = newNode; return head; } public static Node delete(Node head) { if (head == null){ System.out.println("List is empty, not possible to delete"); return head; } System.out.println("Deleted: " + head.data); // move head to next node head = head.next; return head; } static void display(Node node) { //as linked list will end when Node is Null while (node != null) { System.out.print(node.data + " "); node = node.next; } System.out.println("\n"); } public static void main(String args[]) { Node head = null; head = insertStart(head,6); head = insertStart(head,5); head = insertStart(head,4); head = insertStart(head,3); head = insertStart(head,2); head = insertStart(head,1); display(head); head = delete(head); head = delete(head); display(head); } }
Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 Deleted: 1 Deleted: 2 3 4 5 6
Linked List as a part of Collection:
There are various different frameworks in Java which we can use for storing and operating efficiently on our data. Such is a framework known as Collection framework in Java.
In this framework there are various different classes and interfaces are present using which we can code Linked List in Java in a very easy manner as it has a pre-defined class LinkedList stored in it, which has functions like:
- add()
- delete()
- search()
- reverse(), etc
which we can use for operating on a linked list.
Linked List vs Array
| Linked List | Array |
|---|---|
| Operation like insertion and deletion are easier. | Operation like searching and traversing are easier. |
| Data is stored in a continuous manner. | Data is stored in a contiguous manner. |
| No need for pre-allocating the size of the list. | User need to define the size before inserting the data. |
| Memory loss is comparatively low. | Memory loss is comparatively high. |
Some of the pre defined function of LinkedList class
| Method Name | Method Description |
|---|---|
| void addFirst(E e) | This method inserts an element at the beginning of the list |
| void addLast(E e) | This method inserts an element at the end of the list |
| void add(int index, E element) | This method inserts an element at the specific position of the list |
| void clear() | It is used to clear all the elements from the list |
| boolean contains(Object o) | This method returns true if the specific element is present in the list, otherwise return false |
| element() | This element let us view the first element of the list |
| getLast () | This method gives us the last element of the list |
| lastIndexOf(Object o) | This method returns the index of the last occurrence of a specified element |
| size() | This method returns the size of the list |
| toArray() | This method converts the list into an array |
Conclusion
- Linked lists in Java are versatile data structures that provide dynamic memory allocation and flexible data management.
- Singly linked lists allow one way traversal, while doubly linked lists enable navigation in both directions but consume more memory.
- Circular linked lists form a continuous loop, making them ideal for cyclic data processing.
- Understanding these types and their Java implementations helps in choosing the right structure based on memory usage, traversal needs, and insertion or deletion complexity.
Learn DSA
FAQ's related to Linked List In Java Programming
Answer:
In Java, a linked list can be implemented using a custom class for the node, containing data and a reference to the next node (
Node next). Java also provides theLinkedListclass in thejava.utilpackage, which is a doubly linked list by default.
Answer:
LinkedListclass in Java is a doubly linked list, allowing bidirectional traversal withnextandprevpointers. A custom singly linked list only has anextpointer, making it less memory intensive but limited to forward traversal.
Answer:
In a circular linked list, the last node’s
nextpointer is set to the head node, creating a loop. In Java, we manually set thenextpointer of the last node to the head node after node insertion.
Answer:
add()method in Java’sLinkedListclass has a time complexity of O(n) because it needs to traverse the list to locate the specified index before insertion. If inserting at the beginning or end, the complexity is O(1).
Answer:
Java’s LinkedList class provides a built-in method toArray() that converts the linked list to an array.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment