C Program to move the last n node of a linked list to the beginning of the list
Move the last node of a linked list to the beginning of the list
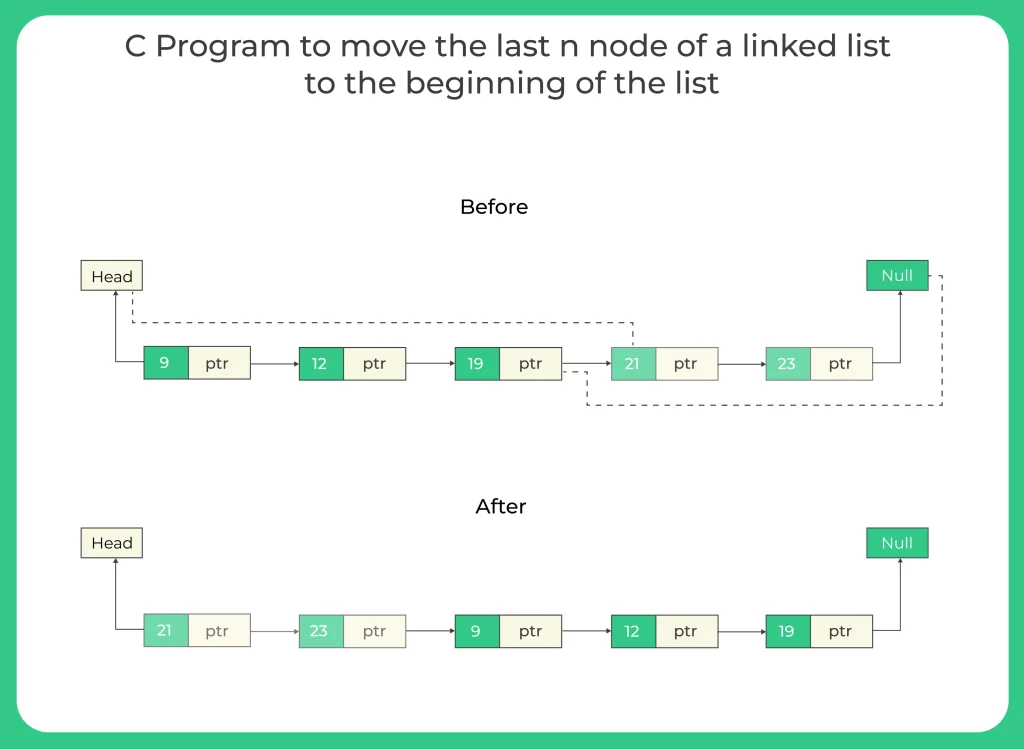
C Program to move the last node of a linked list to the beginning of the list.Today we will learn how to put last node in the beginning of the linked list that is not so tough to do in the data structures.
For Example:-
Input:- Enter Linked list elements :
21 -> 20 -> 7 -> 45 -> 50
Output:- List after put last element of the node in the beginning of the linked list :
50 -> 21 -> 20 -> 7 -> 45

Working required for move the last node of a linked list to the front of the list:-
- Move to the last node of the linked list.
- Use two pointers first to store the address of last node and second to store the address of second last node.
- Make a loop and do some operations after it.
- Make the second last node as last means put sec_Last -> next = NULL
- Then set next of last node as head such as last->next = *head_ref
- Make last as head that is *head_ref = last
- Return
Structure of the node in the Singly Linked List:-
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
C Program to move the last node of a linked list to the beginning of the list :-
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node // Structure of node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void move_Front (struct Node **head_ref, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (*head_ref == NULL || (*head_ref)->next == NULL)
return;
struct Node *sec_Last = NULL;
struct Node *last = *head_ref;
while (last->next != NULL)
{
sec_Last = last;
last = last->next;
}
sec_Last->next = NULL;
last->next = *head_ref;
*head_ref = last;
}
}
void Display (struct Node *node) //print function of the list
{
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
void
insert (struct Node **head_ref, int new_data)
{
//allocate memory
struct Node *new_node = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int main ()
{
int n = 2; // number of node from end to be appended
struct Node *start = NULL; //insert the data
insert (&start, 91);
insert (&start, 58);
insert (&start, 17);
insert (&start, 45);
insert (&start, 53);
insert (&start, 1);
insert (&start, 8);
insert (&start, 64);
insert (&start, 15);
insert (&start, 20);
printf ("The linked list is: \n");
Display (start);
move_Front (&start, n);
printf
("\nAppend the last nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list: \n");
Display (start);
return (0);
}
Output :- The linked list is: 20 15 64 8 1 53 45 17 58 91 Append the last nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list: 58 91 20 15 64 8 1 53 45 17



Login/Signup to comment