Hash Function in Python

Introduction to Hash Function in Python
Hash function in Python are fundamental components in computer science and cryptography. They are used to map data of arbitrary size to a fixed-size string of characters. This process is known as hashing.
Let’s jump into the article to know more about Hash Function in Python and also you will get to know about Hashing.
Understanding Python Hash Function
In Python, A hash function is a mathematical algorithm that takes an input (or ‘message’) and returns a fixed-size string of characters, which is typically a hexadecimal number. The output, often referred to as the ‘hash value’ or ‘digest,’ is unique to the input data. Even a slight change in the input data results in a significantly different hash value.
Python’s Built-in ‘hash’ Method
Python provides a built-in function called ‘hash’ that allows you to generate hash values for various data types, including strings, numbers, and more. The ‘hash’ method uses a cryptographic hash function under the hood to ensure the uniqueness and security of generated hash values.
Components of Hashing in Python
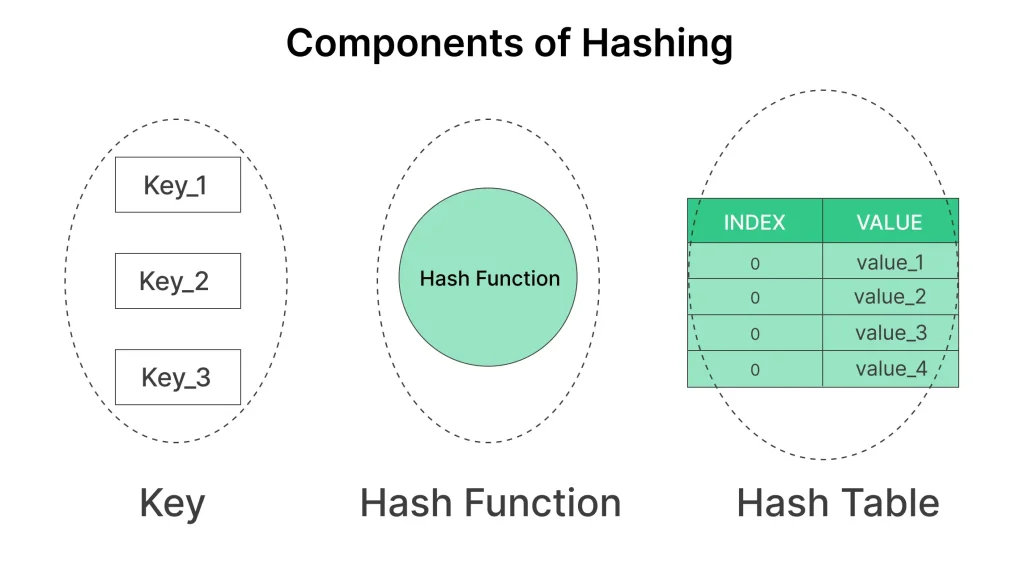
The Components of Hashing
Key: Key refers to the input data that is provided to a hash function to generate a hash value. The key is the information you want to transform into a fixed-size string of characters, which is the hash value
Hash Function: When you need to retrieve a specific data element, you simply use the key as an index to access the corresponding slot in the array. This direct access ensures rapid retrieval, making Direct Address Tables highly efficient for applications that require frequent data lookups.
Hash Value:
The hash value is the output of the hash function. It’s a unique string of characters that represents the input data. Hash values are typically in hexadecimal format and are of a fixed length, regardless of the size or complexity of the input data.
How to Use Python's 'hash' Method
Hashing Strings
text = "Hello, World!"
hash_value = hash(text)
print(f"Hash value of '{text}': {hash_value}")
Hashing Numbers
number = 42
hash_value = hash(number)
print(f"Hash value of {number}: {hash_value}")
Implementation of Hash Function in Python
hashlib module that offers various hash functions like MD5, SHA-1, and SHA-256. import hashlib # Create a new hash object hash_object = hashlib.sha256() # Update the hash with data data = b'Hello, World!' hash_object.update(data) # Get the hexadecimal digest hash_value = hash_object.hexdigest()
Dealing with Hash Function Collisions
A collision in hash functions occurs when two different inputs produce the same hash value or key. In other words, the hash function maps these distinct inputs to the same location in the hash table, resulting in a collision.
Why Do Hash Function Collisions Occur?
Limited Hash Space: Hash functions map data from an infinite space to a finite hash space. Collisions are inevitable when mapping many inputs to a smaller output space.
Poorly Designed Hash Functions: Inadequate hash functions can exhibit clustering behavior, where inputs with similar characteristics produce similar hash values, increasing the likelihood of collisions.
Hashing of Arbitrary Data: Hash functions can be used for any type of data, including arbitrary data. This diversity of inputs can lead to collisions.
Hashing Strings in Python
String hashing is the process of taking an input string and transforming it into a fixed-size string, typically a hexadecimal number. The output, known as a hash value, is unique to each unique input.
Why Hash Strings in Python?
Data Security: Hashing is crucial for securely storing passwords, ensuring that plain-text passwords are never stored.
Data Deduplication: Hashing is used to identify duplicate data efficiently, saving storage space.
Data Integrity: Hashing verifies data integrity during transmission or storage by comparing hash values.
Common Hashing Algorithms
- MD5 (Message Digest 5)
- SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1)
- SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256)
SHA-256 Hashing in Python
SHA-256 is a cryptographic hashing algorithm that takes an input message and produces a 256-bit (32-byte) hash value. It’s designed to be highly secure and is widely used in various applications, including password storage, digital signatures, and data integrity verification.
SHA-256 Hashing in Python
- Using the
hashlibLibrary : Python’s'hashlib'library provides a simple and efficient way to perform SHA-256 hashing.
import hashlib
# Create a new SHA-256 hash object
sha256 = hashlib.sha256()
# Update the hash object with the string you want to hash
data = "Hello, World!"
sha256.update(data.encode())
# Get the hexadecimal representation of the hash
hashed_string = sha256.hexdigest()
# Print the hashed string
print("SHA-256 Hash:", hashed_string)
MD5 Hashing in Python
MD5 is a cryptographic hashing algorithm that takes an input message and produces a 128-bit (16-byte) hash value. It’s fast and efficient, making it suitable for non-security-critical applications.
MD5 Hashing in Python
- Using the
hashlibLibrary : Python’s'hashlib'library provides a straightforward way to perform MD5 hashing.
import hashlib
# Create a new MD5 hash object
md5 = hashlib.md5()
# Update the hash object with the string you want to hash
data = "Hello, World!"
md5.update(data.encode())
# Get the hexadecimal representation of the hash
hashed_string = md5.hexdigest()
# Print the hashed string
print("MD5 Hash:", hashed_string)
Common Use Cases of Hash Function in Python
Conclusion :
We explored the fundamental concepts of hash function in Python are versatile tools with a wide range of applications. Understanding their properties, use cases, and best practices is essential for any programmer. Whether you’re working on data retrieval, cryptography, or data integrity verification, hash functions are indispensable.
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
FAQs
Yes, it’s possible but rare, and collision avoidance techniques can mitigate this risk.
No, hash functions are one-way transformations and cannot be reversed.
You can define your custom hash function using Python’s hashlib library.
To explore advanced hashing techniques, consider PrepInsta courses to learn more about DSA in Python.

Question 1.
Can two different inputs ever produce the same hash value?
Yes, it’s possible but rare, and collision avoidance techniques can mitigate this risk.

Question 2.
Are hash functions reversible?
No, hash functions are one-way transformations and cannot be reversed.

Question 3.
How can I create a custom hash function in Python?
You can define your custom hash function using Python’s hashlib library.

Question 4.
Where can I learn more about advanced hashing techniques?
To explore advanced hashing techniques, consider PrepInsta courses to learn more about DSA in Python.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment