Packages in Java
Packages in Java Language
The packages in Java Language is nothing more than directories that gathers related classes, interfaces,
and sub-packages based on their functional relationships in java.
There are many built-in packages for the Java language.

Overview of Packages :
- Encapsulation is a key Java OOP principle that is implemented mostly through packages.
- A large project’s classes can be organised using Java packages, which can aid in the implementation of encapsulation.
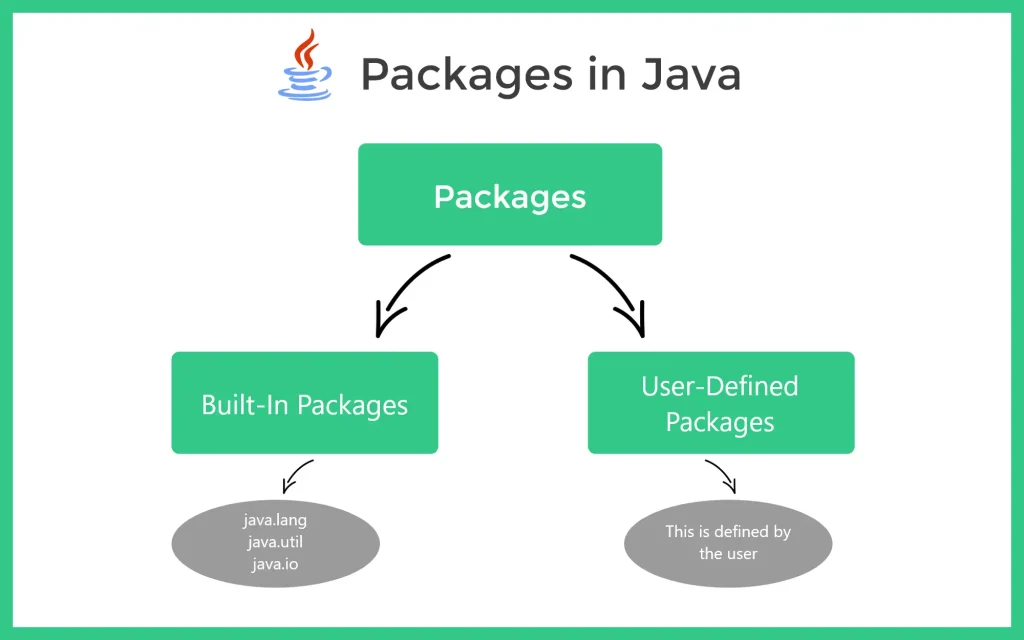
There exist two different kinds of packages :
- Build-in packages
- User-defined packages
Creating User -Defined Packages :
In java, we already have a number of pre-defined packages that contain a large number of classes and interfaces. These packages are known as Built-in packages and we can directly import them in our code.
Some commonly used built-in packages are:
- java.io Data streams, serialisation, and the file system are all supported by this package for system input and output.
- java.lang contains classes that are essential to the design of the Java programming language.
- java.math Classes in this package perform arbitrary-precision integer arithmetic (BigInteger) and arbitrary-precision decimal arithmetic (BigDecimal).
- java.util The collections framework, some internationalisation support classes, and a few utility classes are included.
import java.util.*; or import java.util.Scanner;
Creating Packages in Java Command Line :
javac -d PrepInsta java
Creating User -Defined Packages :
Java also allows you to make your own packages.These are referred to as user-defined packages.
package demoPackage;
public class demoClass
{
public void getMessage(String m)
{
System.out.println(m);
}
}
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
After creating our own package we can use its classes in our program.
public class Main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String message = "This is how User-Definded Packages work";
demoClass object = new demoClass();
object.getMessage(message);
}
} Points to Remember:
- Either import the class or use the fully qualified class name in order to access code that is located outside the current package.
- Using packages while coding provides code reusability benefit.
- Packages allow us to uniquely identify a class.
- Access control features include protected classes, default classes, and private classes.
- They enable the hiding of classes, preventing other programmes from accessing classes intended for internal use only.
- You can better organise your project and find related classes by using packages.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment