Spiral Traversal of a Matrix in Python
Spiral Traversal of a Matrix in Python
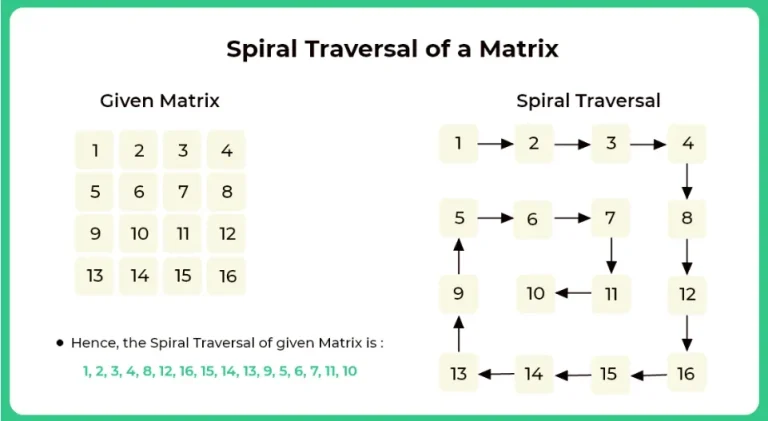
Here, on this page, we will discuss the program to print the Spiral Traversal of the Matrix in Python programming language. We are given the elements of the array in two-dimensional form and we need to traverse the entire matrix in spiral form and print the corresponding element.

Method discussed :
- Method 1: Using Brute force.
- Method 2: Using DFS
Method 1 :
- Declare a 2-d array of size rXc.
- Now, create variable top and initialize it with 0 denotes starting of row, and variable bottom initialized it with (r-1) denotes the end of row, another variable say left set it to 0, it indicate the starting of the column and last variable is right that will be declared with value c-1 which indicate the end of the column.
- Run a loop until all the squares of loops are printed.
- Print the top row, i.e. Print the elements of the top-th row from column index left to right, and increase the count of top.
- Print the right column, i.e. Print the last column or right-th column from row index top to bottom and decrease the count of right.
- Print the bottom row, i.e. if top < bottom, then print the elements of bottom-th row from column right to left and decrease the count of bottom
- Print the left column, i.e. if left < right, then print the elements of left-th column from bottom-th row to top-th row and increase the count of left.
Time and Space Complexities :
- Time-Complexity :O(r*c)
- Space-Complexity : O(1)
Python Code
Run
r = 4
c = 4
a = [[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9, 10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15, 16]]
left = 0
right = c - 1
top = 0
bottom = r - 1
while left <= right and top <= bottom:
""" Print the first row from the remaining rows"""
for i in range(left, right + 1):
print(a[top][i], end=" ")
top += 1
""" Print the last column from the remaining columns"""
for i in range(top, bottom - 1, -1):
print(a[i][right], end=" ")
right -= 1
"""Print the last row from the remaining rows"""
if top <= bottom:
for i in range(right, left - 1, -1):
print(a[bottom][i], end=" ")
bottom -= 1
"""Print the first column from the remaining columns"""
if left <= right:
for i in range(bottom, top - 1, -1):
print(a[i][left], end=" ")
left += 1
Output
1 2 3 4 8 12 16 15 14 13 9 5 6 7 11 10
Method 2 :
- Create a DFS function that takes matrix, cell indices, and direction.
- Now, we will check the cell indices pointing to a valid cell (that is, not visited and in bounds), if not, skip this cell
- Print the value of the cell.
- And Mark matrix cell pointed by indicates as visited by changing it to a value not supported in the matrix
- Now, check the surrounding cells are valid. If not stop the algorithm, else continue.
- If the direction given is right then check if the cell to the right is valid. If so, DFS to the right cell given the steps above, else change the direction to down and DFS downwards given the steps above.
- Else, if the direction given is down then check, if the cell to the down is valid. If so, DFS to the cell below given the steps above else, change the direction to left and DFS leftwards given the steps above.
- Else, if the direction given is left then check, if the cell to the left is valid. If so, DFS to the left cell given the steps above, else change the direction to up and DFS was upwards given the steps above.
- Else, if the direction given is up then check, if the cell to the up is valid. If so, DFS to the upper cell given the steps above, else, change the direction to right and DFS rightwards given the steps above.
Time and Space Complexities :
- Time-Complexity: O(r*c)
- Space-Complexity: O(1)
Run
R = 4
C = 4
def isInBounds(i, j):
global R
global C
if i < 0 or i >= R or j < 0 or j >= C:
return False
return True
# Check if the position is blocked
def isBlocked(matrix, i, j):
if not isInBounds(i, j):
return True
if matrix[i][j] == -1:
return True
return False
# DFS code to traverse spirally
def spirallyDFSTravserse(matrix, i, j, Dir, res):
if isBlocked(matrix, i, j):
return
allBlocked = True
for k in range(-1, 2, 2):
allBlocked = allBlocked and isBlocked(
matrix, k + i, j) and isBlocked(matrix, i, j + k)
res.append(matrix[i][j])
matrix[i][j] = -1
if allBlocked:
return
# dir: 0 - right, 1 - down, 2 - left, 3 - up
nxt_i = i
nxt_j = j
nxt_dir = Dir
if Dir == 0:
if not isBlocked(matrix, i, j + 1):
nxt_j += 1
else:
nxt_dir = 1
nxt_i += 1
elif Dir == 1:
if not isBlocked(matrix, i + 1, j):
nxt_i += 1
else:
nxt_dir = 2
nxt_j -= 1
elif Dir == 2:
if not isBlocked(matrix, i, j - 1):
nxt_j -= 1
else:
nxt_dir = 3
nxt_i -= 1
elif Dir == 3:
if not isBlocked(matrix, i - 1, j):
nxt_i -= 1
else:
nxt_dir = 0
nxt_j += 1
spirallyDFSTravserse(matrix, nxt_i, nxt_j, nxt_dir, res)
def spirallyTraverse(matrix):
res = []
spirallyDFSTravserse(matrix, 0, 0, 0, res)
return res
a = [[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9, 10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15, 16]]
res = spirallyTraverse(a)
print(*res)
Output
1 2 3 4 8 12 16 15 14 13 9 5 6 7 11 10
For similar Questions click on the given button






# SPIRAL TRAVERSAL PROGRAM
spiral= []
rows, cols = [int(x) for x in input(“Enter the no. of rows and columns: “).split()]
A = [[int(input()) for c in range (cols)] for r in range(rows)] #Getting inputs from user
def transpose(A): #Transpose function
A = [[A[j][i] for j in range(len(A))] for i in range(len(A[0]))]
return A
def insertandrotate(A): #Function for inserting & rotating matrix
spiral.extend(A.pop(0))
A = transpose(A)
A = A[::-1]
return A
return spiral
while len(A) >= 1:
A = insertandrotate(A) #Performing insertion & rotating till the min len
spiral.extend(A.pop(0))
print(*spiral) #Printing the inserted elements #Coded by Arjun M