C++ Program for Balanced Parenthesis problem
Balanced parenthesis problem
Today in this article we will learn how to solve Balanced Parenthesis problem.
Lets understand this with the help of an example:-
- Input: str = “[{}]”
Output: balanced

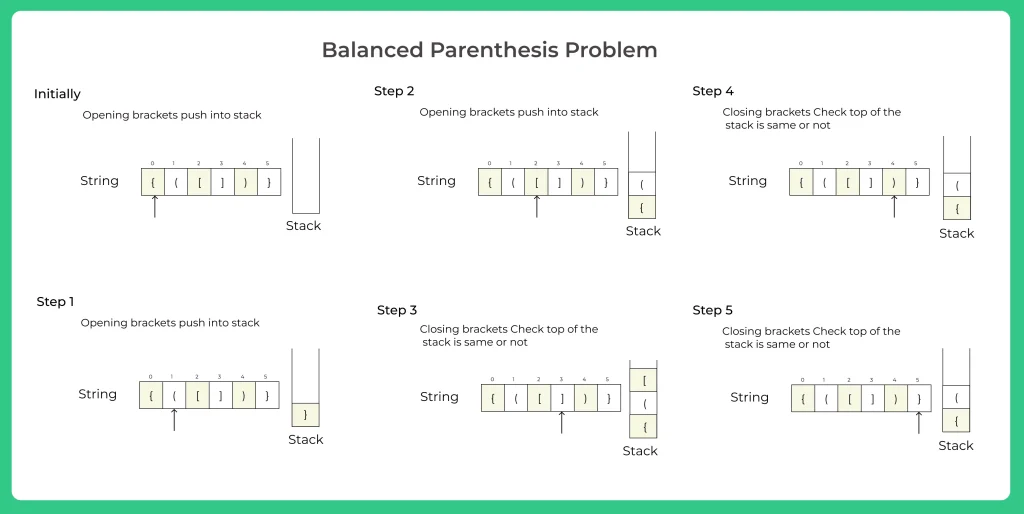
Algorithm
- Initialize a character stack st
- Now traverse the string s
- If the current character is a starting bracket (‘(‘ or ‘{‘ or ‘[‘) then push it to stack st.
- If the current character is a closing bracket (‘)’ or ‘}’ or ‘]’) then check if the st is empty or not and also check if the top of the stack is the same opening brackets if it’s true then pop from stack otherwise put ans = false and break.
- At last check if stack is empty or not if its not empty return false
- At the end of the function return ans.
- In the main function inside if function check the string and print if the string is balanced or not
C++ Code :-
Run
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool areBracketsBalanced (string expr)
{
stack < char >s;
char x;
// Traversing the Expression
for (int i = 0; i < expr.length (); i++)
if (expr[i] == '(' || expr[i] == '[' ||expr[i] == '{')
{
// Push the element in the stack
s.push (expr[i]);
continue;
}
// IF current current character is not opening
// bracket, then it must be closing. So stack
// cannot be empty at this point.
if (s.empty ())
return false;
switch (expr[i])
{
case ')': // Store the top element in a
x = s.top ();
s.pop ();
if (x == '{' || x == '[')
return false;
break;
case '}': // Store the top element in b
x = s.top ();
s.pop ();
if (x == '(' || x == '[')
return false;
break;
case ']': x = s.top ();
s.pop ();
if (x == '(' || x == '{')
return false;
break;
}
}
return (s.empty ());
}
// Driver code
int main ()
{
string expr = "{()}[]";
// Function call
if (areBracketsBalanced (expr))
cout << "Balanced";
else
cout << "Not Balanced";
return 0;
}Output:-
Enter the brackets to check if its balanced or not : [{}]
BalancedEnter the brackets to check if its balanced or not : {]
Not Balanced



Login/Signup to comment