Process Scheduling in Operating System
What is Process scheduling in Operating System
Process scheduling in Operating System – Have you ever wondered how your computer runs so many programs at the same time without crashing? Whether you’re browsing the internet, listening to music, or downloading a file — everything runs smoothly. That’s possible because of something called Process Scheduling in the operating system.
The decision to move different parallel processes competing with one another for execution, to different states like Ready to running or running to exit state based on a certain decision strategy is known as Process Scheduling in Operating System.
Handled by – Process Manager

What is Process Scheduling in Operating System?
In simple words, Process Scheduling is the way your computer decides which task (or process) should run first, and which one can wait.
- Since your system can’t run all programs at the exact same time, it quickly switches between them — giving each a fair share of the processor’s time.
- This helps all your apps work properly and smoothly, without delay or lag.
Simple Example:
Imagine you’re the only cook in a kitchen and you have 4 dishes to prepare. You can’t make them all at once, right? So you spend a few minutes on one, then move to the next, and so on. You keep rotating until all dishes are ready. This is how your computer also works — by quickly switching between tasks so that all of them get done, and nothing is left behind.
Why CPU Scheduling?
One or more processes may be in the running state at the same time and they all share the CPU time using multiplexing.
Focus for Intelligent Scheduling is to –
- Keep CPU busy as much as possible if processes are waiting for execution
- Decrease the time of execution of critical processes
- Intelligently prioritise processes for execution
- Keep the response time minimum.
Types of Process Scheduling
We divided Process Scheduling into following two
- Preemptive Scheduling –The scheduling in which a running process can be interrupted if a high priority process enters the queue and is allocated to the CPU is called preemptive scheduling. In this case, the current process switches from the running queue to ready queue and the high priority process utilizes the CPU cycle.
- Non Preemptive Scheduling – The scheduling in which a running process cannot be interrupted by any other process is called non-preemptive scheduling. Any other process which enters the queue has to wait until the current process finishes its CPU cycle
Meaning of Prempt – take action in order to prevent (an anticipated event) happening; forestall.
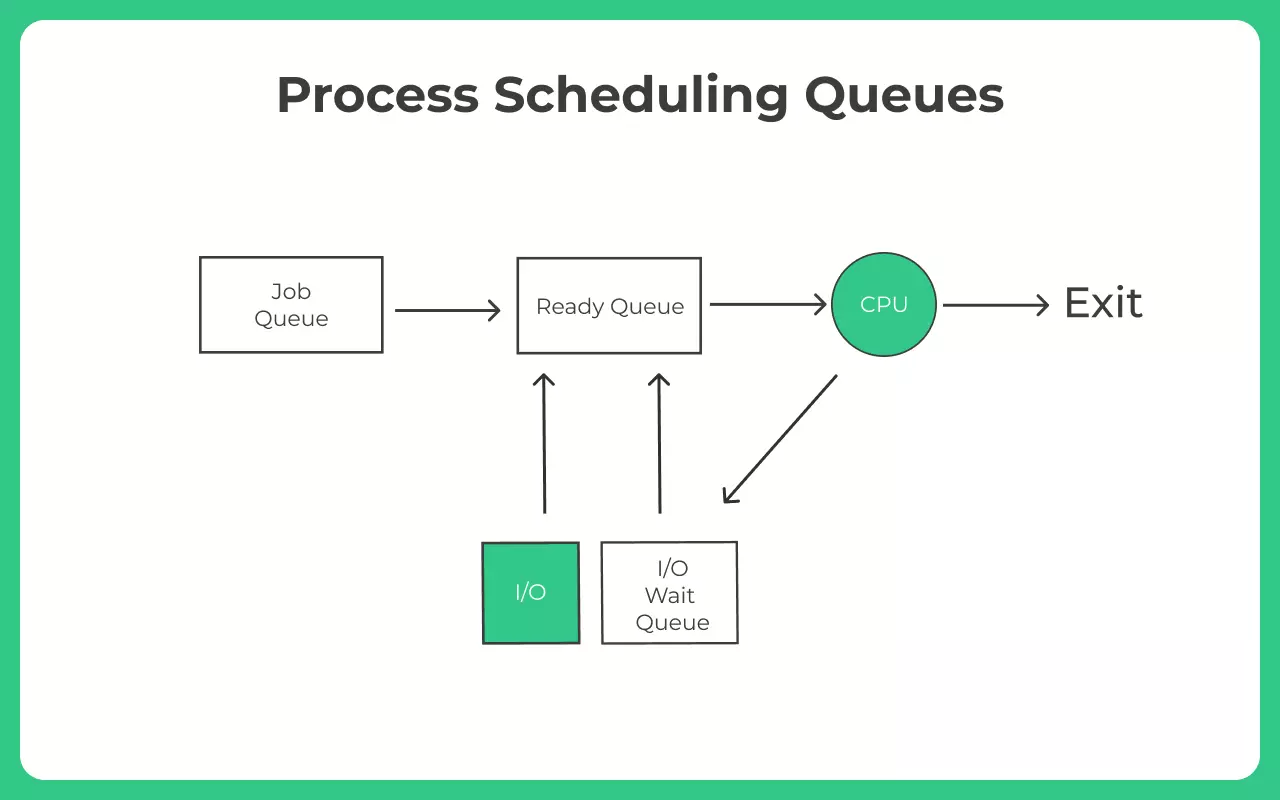
Process Scheduling Queues
There are the following types of queues –
- Job Queue – Whenever any process enters the system its there in job Queue
- Ready Queue – Processes in the ready queue waiting for run time are in the ready queue.
- Device Queue – Some processes may be waiting some I/O operation, such processes are in the device queue.
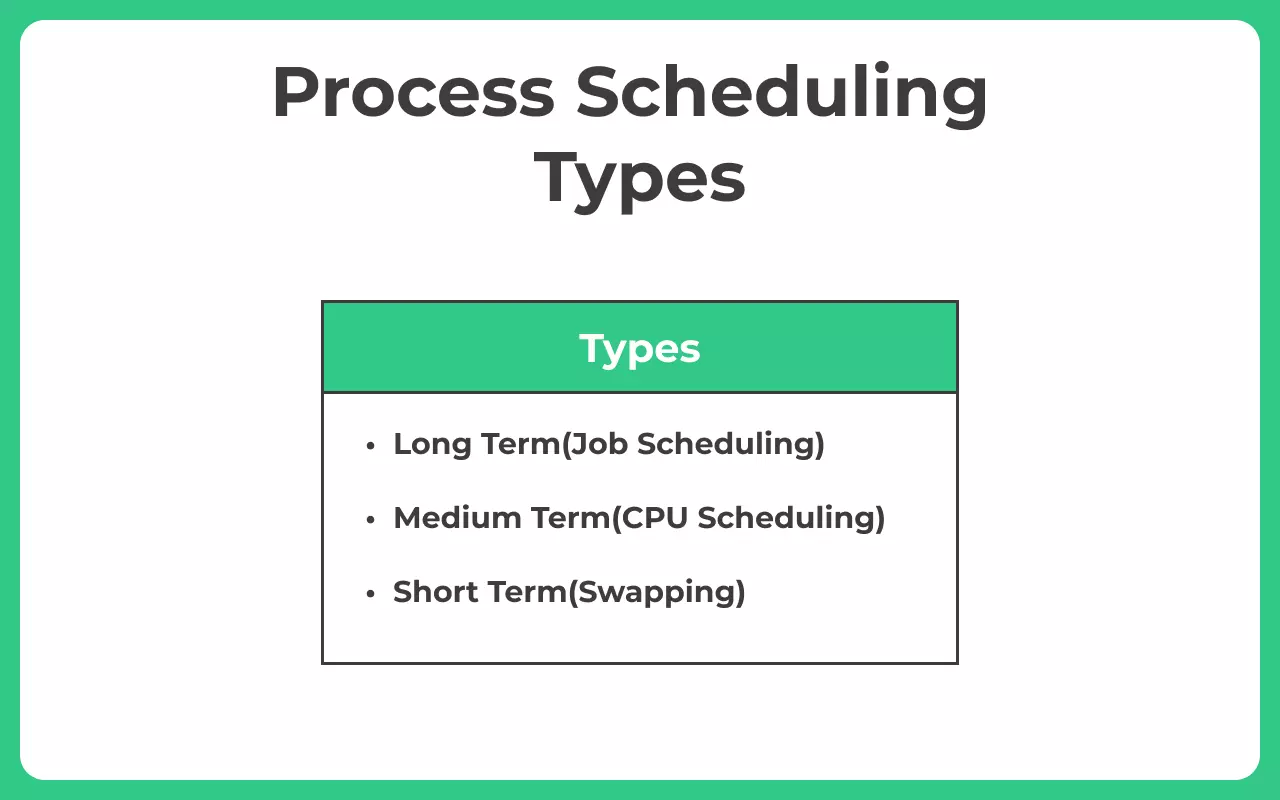
Different Types of Schedulers
There are three type of schedulers categorically –
- Long-term Scheduler
- Short-term Scheduler
- Medium-term Scheduler
Long Term Scheduler
Also knowns as Job Scheduler. It selects the process that are to be placed in ready queue. The long term scheduler basically decides the priority in which processes must be placed in main memory. Processes of long term scheduler are placed in the ready state because in this state the process is ready to execute waiting for calls of execution from CPU which takes time that’s why this is known as long term scheduler.
Medium-Term Scheduler
It places the blocked and suspended processes in the secondary memory of a computer system. The task of moving from main memory to secondary memory is called swapping out. The task of moving back a swapped out process from secondary memory to main memory is known as swapping in. The swapping of processes is performed to ensure the best utilisation of main memory.
Short-Term Scheduler
Also knowns as CPU Scheduler. It decides the priority in which processes is in the ready queue are allocated the central processing unit (CPU) time for their execution. The short term scheduler is also referred as central processing unit (CPU) scheduler.
Context Switch
A context switch is a procedure that a computer’s CPU (central processing unit) follows to change from one task (or process) to another while ensuring that the tasks do not conflict. Effective context switching is critical if a computer is to provide user-friendly multitasking.
Read more about Context Switch here.
Final Thoughts:
Process scheduling is how your computer decides which task gets to use the CPU and when. Imagine it like a traffic controller who makes sure all cars (tasks) take turns and move smoothly, so nothing gets stuck or delayed.
Thanks to process scheduling, you can watch videos, play games, and work on documents at the same time without your computer slowing down. The operating system uses different methods to pick which task should run next, helping everything work faster and more smoothly for you.
In simple words, process scheduling is the reason your computer can handle many things at once without problems, making your experience easy and efficient
FAQs
A process is simply a program that is currently running. For example, when you open a browser or a game, it becomes a process. The operating system manages all these processes and uses scheduling to decide which one should get CPU time. So, in process scheduling, each process is like a task waiting in line to be served by the CPU.
Process scheduling improves system performance by:
- Ensuring each process gets enough time to run.
- Reducing the time a user has to wait (response time).
- Maximizing CPU usage by avoiding idle time.
- Handling both background and foreground tasks efficiently. In short, it makes the system faster, more responsive, and prevents any single process from taking over the CPU for too long.
Some common process scheduling algorithms are:
- First Come First Serve (FCFS): Tasks are handled in the order they arrive.
- Shortest Job Next (SJN): The task that will take the least time is done first.
- Round Robin (RR): Each task is given a fixed time slot and is rotated in a cycle.
- Priority Scheduling: Tasks with higher priority are done before others. Each of these has its own way of managing processes to make the system efficient and fair.
Without proper process scheduling:
- Some programs might get stuck waiting forever (called starvation).
- The CPU may remain idle even when tasks are waiting.
- Some apps may freeze or crash.
- The overall system will become slow and unresponsive. So, scheduling is like the brain behind the multitasking magic – it keeps things running smoothly and avoids confusion



Login/Signup to comment