SQL Inner Join
Introduction to SQL Inner Join
SQL (Structured Query Language) stands as the cornerstone. SQL allows us to interact with relational databases efficiently, and one of its most potent features is the “INNER JOIN.”
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of the SQL Inner Join, its syntax, equipping you with the knowledge and skills needed to harness the full potential of your database queries.
Understanding the SQL INNER JOIN
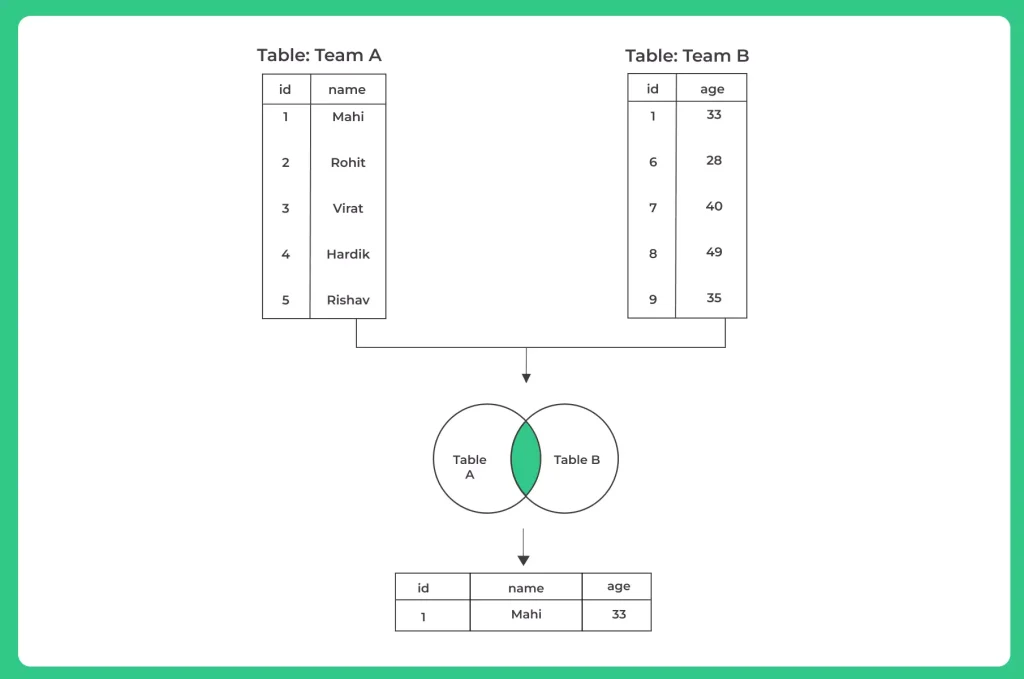
An SQL INNER JOIN is a powerful tool that enables you to combine data from two or more tables based on a related column between them. This operation forms the core of relational databases, allowing you to extract valuable insights and create meaningful connections within your data.
This technique is invaluable for consolidating information, from customer and order data to inventory and suppliers.
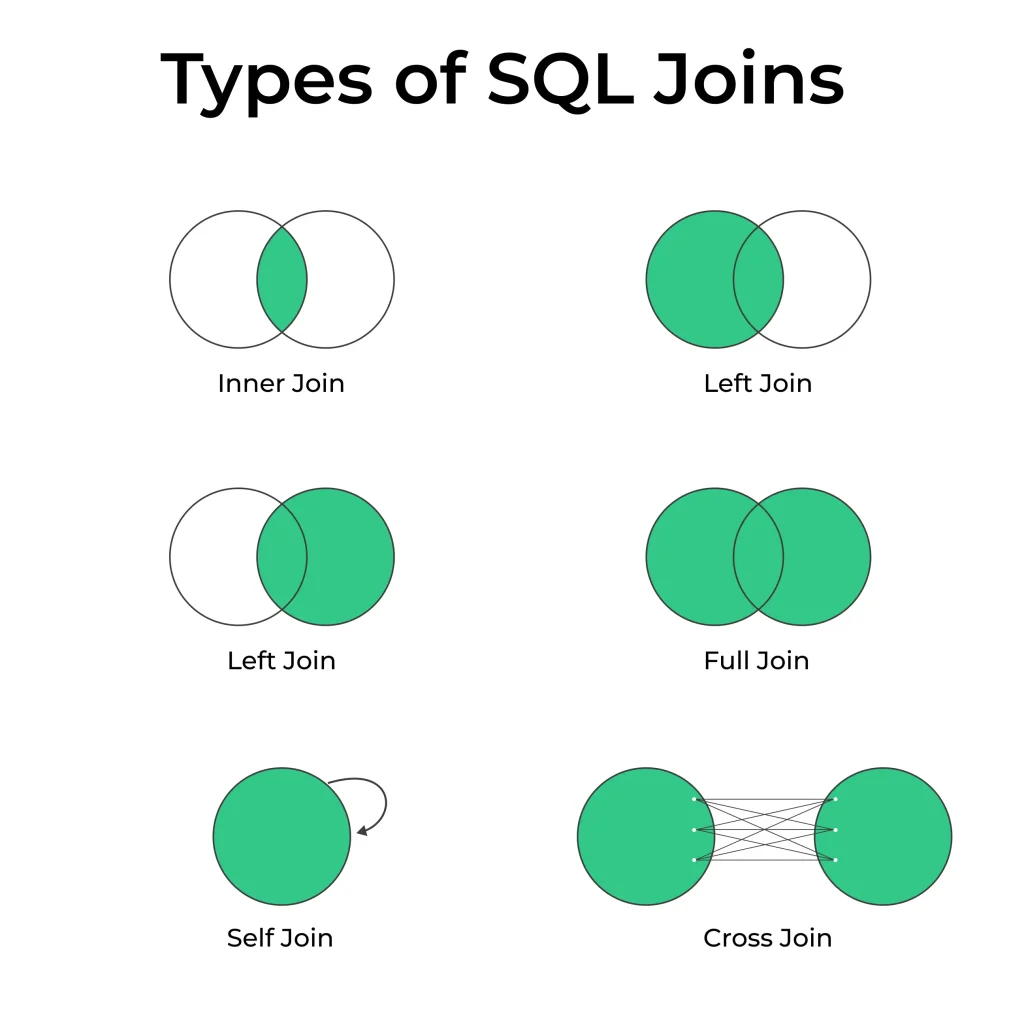
Exploring Types of SQL Inner Joins :
Equi Join : The most common type, the Equi Join, matches rows where values in the specified columns are equal. It’s the foundation of INNER JOIN operations.
Non-Equi Join : In cases where you need to compare columns using operators other than equality (e.g., greater than or less than), the Non-Equi Join comes into play.
- Self Join : A Self Join is used when you want to combine rows from a single table based on a related column. It’s often employed in hierarchical data structures.
- Cross Join : A Cross Join combines all rows from one table with all rows from another, creating a Cartesian product. While less common, it has its applications.
SQL Inner Join Syntax Explained
- This statement combines rows from ‘table1’ and ‘table2’ where the values in ‘table1.column’ match those in ‘table2.column’.
SELECT columns FROM table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column;
Why SQL Inner Join Matters
Mastering INNER JOINs is crucial because it empowers you to:
- Retrieve Precise Data: INNER JOINs help you extract specific information by linking related tables, ensuring that you obtain only the relevant data you need.
- Enhance Data Analysis: With INNER JOINs, you can merge data from multiple sources, enabling more in-depth analysis and smarter decision-making.
- Optimize Database Performance: By efficiently querying related data, you reduce the load on your database, resulting in faster and more responsive applications.
Example 1: Employee-Department Relationship
SELECT employees.name, departments.name FROM employees INNER JOIN departments ON employees.department_id = departments.department_id;
Example 2: Sales and Products
SELECT sales.transaction_date, products.product_name, sales.amount FROM sales INNER JOIN products ON sales.product_id = products.product_id;
Click below to access free SQL quizzes which will be helpful in your placement exams
Advantages of Using SQL Inner Join
Leveraging SQL JOINs in Real-World Scenarios
SQL JOINs are not confined to theoretical applications; they hold immense practical significance. Consider the following real-world scenarios:
E-Commerce Analytics
- For e-commerce businesses, SQL JOINs are instrumental in analyzing customer behavior and purchase history. An INNER JOIN can be employed to connect customer profiles with their order history, facilitating targeted marketing campaigns.
Inventory Management
- In inventory management, LEFT JOINs are often utilized to combine inventory data with supplier information. This ensures that even if certain suppliers have no corresponding inventory records, their information is still retained.
Conclusion
SQL Inner Join is a powerful tool that unlocks the potential of relational databases, allowing businesses to extract valuable insights from their data. By mastering Inner Join and adhering to best practices, organizations can make informed decisions, drive efficiency, and stay competitive in today’s data-driven world.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription

Question 1.
What is the main difference between Inner Join and Outer Join?
Inner Join returns only matching rows, whereas Outer Join returns all rows from at least one table, including non-matching rows with NULL values.

Question 2.
Can Inner Join be used with more than two tables?
Yes, Inner Join can be used with multiple tables to retrieve data from related tables in a single query.

Question 3.
What are the performance considerations when using Inner Join?
To optimize performance, ensure that the columns used in join conditions are indexed, and use query analyzers to identify and resolve bottlenecks.

Question 4.
How can SQL Inner Join benefit e-commerce businesses?
E-commerce businesses can use Inner Join to track inventory, match orders with products, and analyze sales data for better decision-making and inventory management
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Inner Join in DBMS
About Inner Join in DBMS
In this article, we will learn about inner join in DBMS.
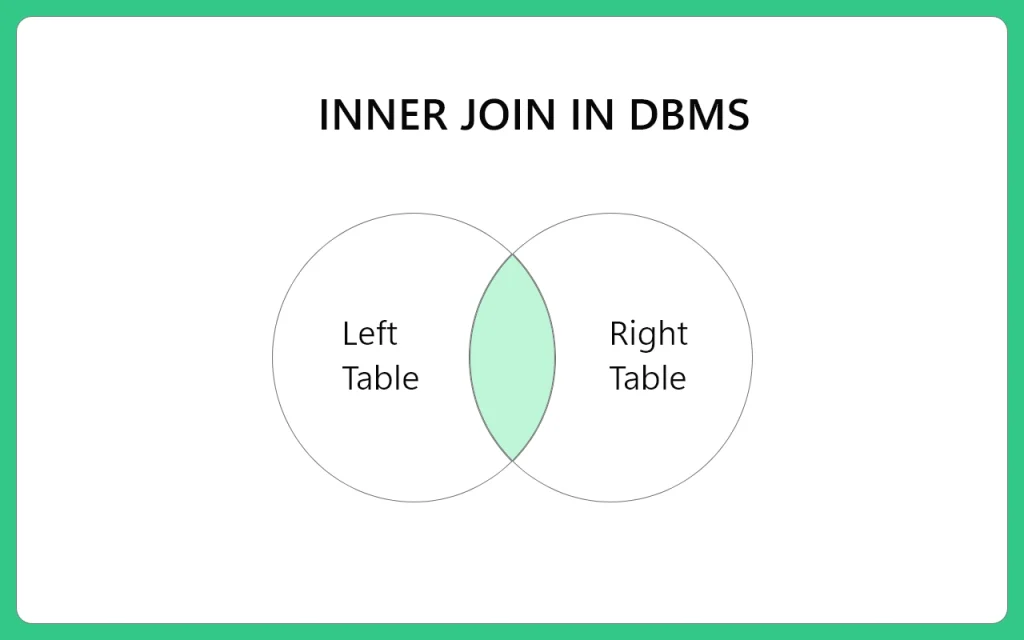
Inner Join between two tables helps to retrieve data that will be common to both the tables and thus also referred to as equi
join or simple join.

Inner join Definition
- Tables are joined based on equality condition
- Only matching records are displayed
- Joining tables must have at least one common same data type and the same values.
Syntax
select col1,col2,col3.... from table1,table2 where table1.common col name = table2.common col name;
Example for Inner Join
Consider two tables emp and dept with the following data
Emp table
| EMPNO | ENAME | JOB | MGR | HIREDATE | SAL | COMM | DEPTNO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7839 | KING | PRESIDENT | – | 17-NOV-81 | 5000 | – | 10 |
| 7698 | BLAKE | MANAGER | 7839 | 01-MAY-81 | 2850 | – | 30 |
| 7782 | CLARK | MANAGER | 7839 | 09-JUN-81 | 2450 | – | 10 |
| 7566 | JONES | MANAGER | 7839 | 02-APR-81 | 2975 | – | 20 |
| 7788 | SCOTT | ANALYST | 7566 | 19-APR-87 | 3000 | – | 20 |
| 7902 | FORD | ANALYST | 7566 | 03-DEC-81 | 3000 | – | 20 |
| 7369 | SMITH | CLERK | 7902 | 17-DEC-80 | 800 | – | 20 |
| 7499 | ALLEN | SALESMAN | 7698 | 20-FEB-81 | 1600 | 300 | 30 |
| 7521 | WARD | SALESMAN | 7698 | 22-FEB-81 | 1250 | 500 | 30 |
| 7654 | MARTIN | SALESMAN | 7698 | 28-SEP-81 | 1250 | 1400 | 30 |
| 7844 | TURNER | SALESMAN | 7698 | 08-SEP-81 | 1500 | 0 | 30 |
| 7876 | ADAMS | CLERK | 7788 | 23-MAY-87 | 1100 | – | 20 |
| 7900 | JAMES | CLERK | 7698 | 03-DEC-81 | 950 | – | 30 |
| 7934 | MILLER | CLERK | 7782 | 23-JAN-82 | 1300 | – | 10 |
Dept table
| DEPTNO | DNAME | LOC |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | ACCOUNTING | NEW YORK |
| 20 | RESEARCH | DALLAS |
| 30 | SALES | CHICAGO |
| 40 | OPERATIONS | BOSTON |
Write SQL Query to display data from two tables emp and dept wherever there is common dept no and from the sales department
select rownum,Empno,Ename,Emp.Deptno,Dname, sal*12 annsal,loc from Emp,Dept where Emp.Deptno=Dept.deptno and dname='SALES';
O/P
| ROWNUM | EMPNO | ENAME | DEPTNO | DNAME | ANNSAL | LOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7698 | BLAKE | 30 | SALES | 34200 | CHICAGO |
| 2 | 7499 | ALLEN | 30 | SALES | 19200 | CHICAGO |
| 3 | 7521 | WARD | 30 | SALES | 15000 | CHICAGO |
| 4 | 7654 | MARTIN | 30 | SALES | 15000 | CHICAGO |
| 5 | 7844 | TURNER | 30 | SALES | 18000 | CHICAGO |
| 6 | 7900 | JAMES | 30 | SALES | 11400 | CHICAGO |
We are having 6 rows in emp table from the sales department, with dept no=30 and matches with deptno=30 which is appended with the data in dept table as a result total of 6 rows are displayed
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others








Login/Signup to comment