View Serializability in DBMS

View Serializability
DBMS View Serializability in DBMS is a technique to find out that a detailed schedule is either view serializable or now not. To prove whether a special schedule is view serializable, the consumer includes trying out whether or not the agreed time table is View equivalent to its serial schedule. considering there is no synchronized transactions execution, we are able to affirm that a serial schedule will simply now not go away the database unpredictable.
View Serializability in DBMS
In this article, we will learn about View Serializability in DBMS.
- A schedule is view serializable when it is view equivalent to a serial schedule.
- All conflict serializable schedules are view serializable.
- The view serializable which is not a conflict serializable contains blind writes.
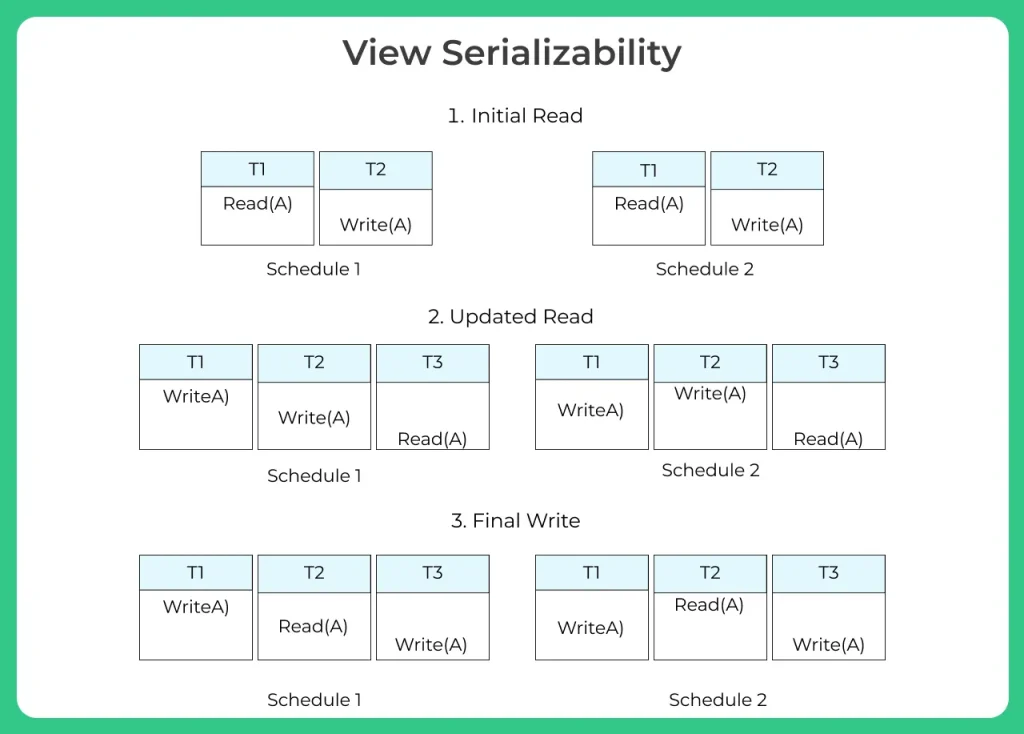
View Equivalent
Two view equivalent schedules S1 and S2 should satisfy the following conditions:
1.Initial Read
- The initial read of both the schedules must be in the same transaction.
- Suppose two schedule S1 and S2. In schedule S1, if a transaction T1 is reading the data item A, then in S2, transaction T1 should also read A.
- The two schedules S1 and S2 are view equivalent because Initial read operation in S1 is done by T1 and in S2 also it is done by T1.
2.Updated Read
- Suppose in schedule S1, if transaction Tm is reading A which is updated by transaction Tn then in S2 also, Tm should read A which is updated by Tn.
- The two schedules are not view equal because, in S1,transaction T3 is reading A updated by transaction T2 and in S2, transaction T3 is reading A which is updated by transaction T1.
3.Final Write
- A final write must be the same in both the schedules.
- Suppose in schedule S1, if a transaction T1 updates A in the last, then in S2 final write operation should also be done by transaction T1.
- The two schedules is view equal because Final write operation in S1 is done by T3 and in S2 also the final write operation is done by T3.
Example:
Consider a schedule S with 3 transactions.
The total number of possible schedules is 3!=6.They are
S1, S2 , S3 , S4, S5, S6
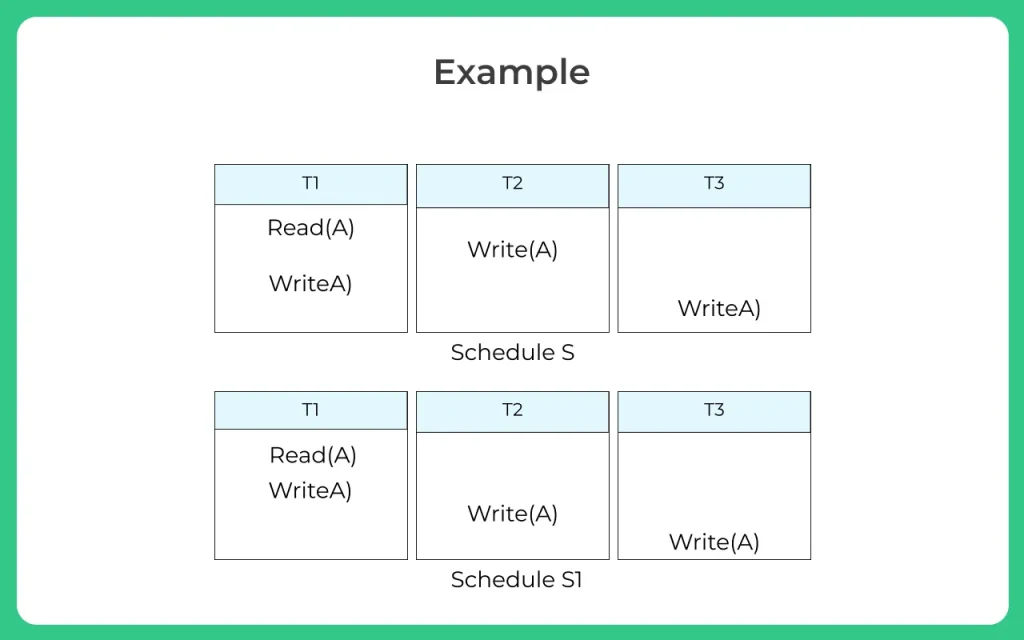
Considering the first schedule
Schedule S1
- Step 1: Final updation on data items
In both schedules S and S1, there is no read except the initial read that’s why we don’t need to check that condition.
- Step 2: Initial Read
The initial read operation in S is done by T1 and in S1, it is also done by T1.
- Step 3: Final Write
The final write operation in S is done by T3 and in S1, it is also done by T3. So, S and S1 are view Equivalent.
- The first schedule S1 satisfies all three conditions, so we don’t need to check another schedule.Hence, view equivalent serial schedule is
T1 → T2 → T3
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others





Login/Signup to comment