Set Operations in DBMS
What are Set Operators?
Set operators combine the results of two component queries into a single result. Queries containing set operators are called compound queries.
In this article, we will learn about Set Operations in DBMS.
Set Operations in DBMS
SQL set operations are used for combining data from one or more tables
There are 3 set operations in SQL. They are
UNION/UNION ALLINTERSECTMINUS
General Syntax for all SET operators
SELECT column name(s) FROM table1 UNION/UNION ALL/INTERSECT/MINUS SELECT column name(s) FROM table2
Each SELECT statement that is used this set operators must follow these conditions
- The same number of columns
- The columns must also have similar data types
- The columns in each SELECT statement must also be in the same order
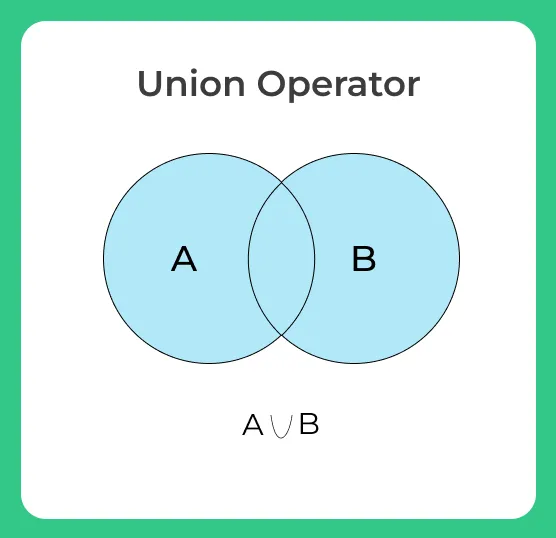
UNION/UNION ALL
Union clause used to combine the result-set of two or more select queries
Customers table:
| City | Country |
|---|---|
| Thimpu | Germany |
| Hyderabad | India |
| Hyderabad | India |
Suppliers table:
| City | Country |
|---|---|
| London | UK |
| California | USA |
| Texas | USA |
Example for UNION
SELECT City FROM Customers UNION SELECT City FROM Suppliers ORDER BY City;
Output:
| City |
|---|
| Texas |
| Thimpu |
| London |
| Hyderabad |
| California |
UNION all in SQL
The only difference between UNION and UNION all Clause is that UNION removes duplicate values while comparing where UNION ALL allows duplicate values while combining
Example for UNION ALL
SELECT City, Country FROM Customers; UNION ALL SELECT City, Country FROM Suppliers
Output:
| City | Country |
|---|---|
| Texas | USA |
| Thimpu | Germany |
| Londona | UK |
| Hyderabad | India |
| California | USA |
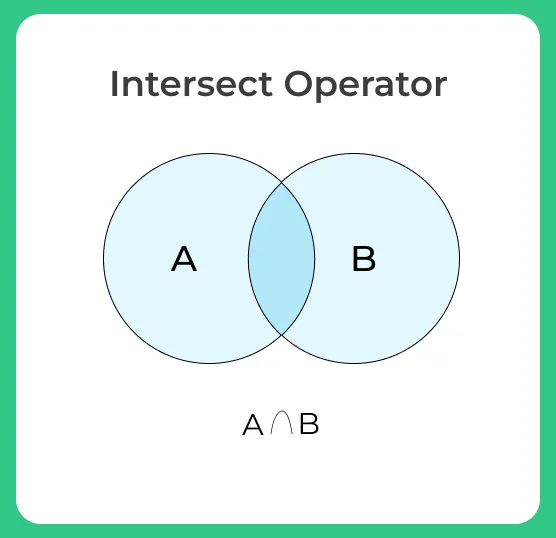
INTERSECT
- Intersect statement combines result-set of two or more select queries and returns only those values that are common in both the result set
- Simply INTERSECT returns the common rows are values common in both the data sets and will not consider duplicate values
Example of INTERSECT
The First table,| ID | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | rishi |
| 2 | trish |
| 3 | mahi |
| ID | Name |
|---|---|
| 2 | trish |
| 3 | Chester |
| 4 | mahi |
SELECT name FROM First INTERSECT SELECT name FROM Second;The result set table will look like
| Name |
|---|
| trish |
| mahi |
MINUS
- Minus operator is used to subtract the result set obtained by the first SELECT query from the result set obtained by the second SELECT query.
- Simply, we can say that MINUS operator will return only those rows which are unique in only first SELECT query and not those rows which are common to both first and second SELECT queries.
Table1
| Name | Address | Age | Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Priya | Hyderabad | 19 | A |
| Rahul | Chennai | 20 | B |
| Karthik | Mumbai | 21 | A |
| Payal | Delhi | 20 | B |
Table2
| Name | Course | Age | Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divya | Java | 22 | B |
| Amitha | C++ | 19 | A |
| Harshitha | Python | 21 | A |
| Payal | Java | 20 | B |
Example
SELECT Name FROM Table1 MINUS SELECT Name FROM Table2;
Output:
| Name |
|---|
| Priya |
| Rahul |
| Karthik |
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment