Functional dependency and Attribute Closure in DBMS
Functional dependency and Attribute Closure
If one attribute is determined by another attribute in a DBMS system then it is a functional dependency.
In this article, we will learn about Functional Dependencies in DBMS.
Functional dependency and Attribute Closure in DBMS
In this article, we will learn about Functional Dependency and Attribute Closure in DBMS.
- A Relation A->B is said to be a functional dependency whenever two tuples are having the same value for both attributes A and attribute B
- Simply
Functional dependencyis a relationship that exists when one attribute uniquely determines another attribute - Consider an example of table student
- Id->name, id->addr are functional dependencies, where as name->addr is not a functional dependency.
Finding functional dependencies in a relation (table)
Functional dependencies in a relation are dependent on the domain (set of possible values that a column can accept) in that table.
Consider the table student
| ID | Name | Age | Address | Country | State |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 | Priya | 20 | Chennai | India | Tamil Nadu |
| 66 | Rishi | 21 | Mumbai | India | Maharashtra |
| 67 | Keerthi | 19 | Delhi | India | Delhi |
| 68 | Amitha | 20 | Chennai | India | Tamilnadu |
- As we know, ID is capable of defining uniquely each record in the table hence ID-> Name, ID-> Address, ID->Age hold true
- In the same way State ->Country will also be true because there are chances for two rows to have the same state then they will have the same country as well.
Functional dependency set
- Functional dependency set is nothing but the set of all functional dependencies that are existed in a table or relation
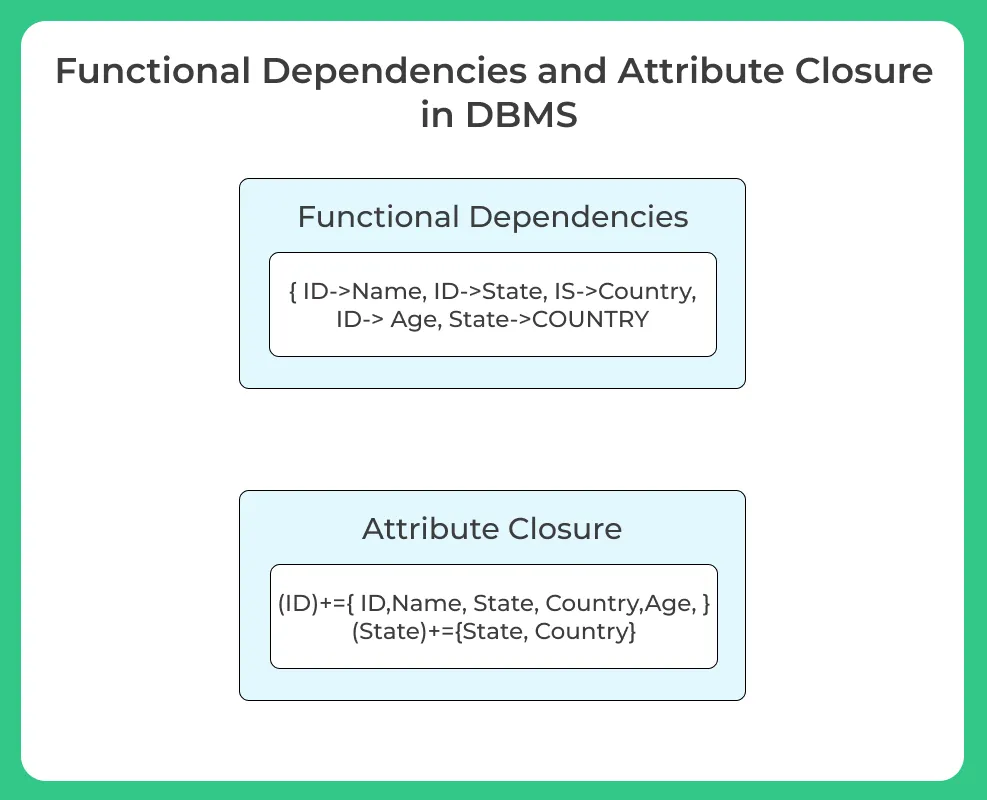
- For example, in the table student, we can observe the functional dependencies as
- {ID ->Name, ID ->State, ID-> Country, ID-> age, State-> Country}
Attribute closure
The set “A*” is said to be the closure set of “A” if the set of attributes are functionally dependent on the attributes of “A”
Finding attribute closure of an attribute set
- First, add elements of the attribute set to the result set
- Add elements to the result set which are functionally determined from the result set recursively
In the relation student an attribute closure is determined as
- (ID)+ = {ID, Name, State,Country,Age}
- (State)+ = {State, Country}
Finding candidate keys and super keys through attribute closure
- If all attributes of the relation are present in attribute closure of an attribute set then such an attribute set will have a super key for that relation
- If all attributes of the relation or determined by none of the attribute set then such a set will be a candidate key as well
- (ID, Name)+ = {ID, Name, State, Country, Age}
- (ID)+ = {ID, Name,State,Country, Age}
- (ID, Name) will be super key but not as a candidate key because its subset (ID) + is equal to all attributes present in the relation. Hence, ID will be a candidate key.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment