ER to Relational Model Conversion
ER to Relational Model Conversion

ER to Relational Model Conversion
- Conversion is nothing but converting ER diagram to tabular form.
- This is done because tables can be easily implemented by RDBMS like MySQL, Oracle etc.
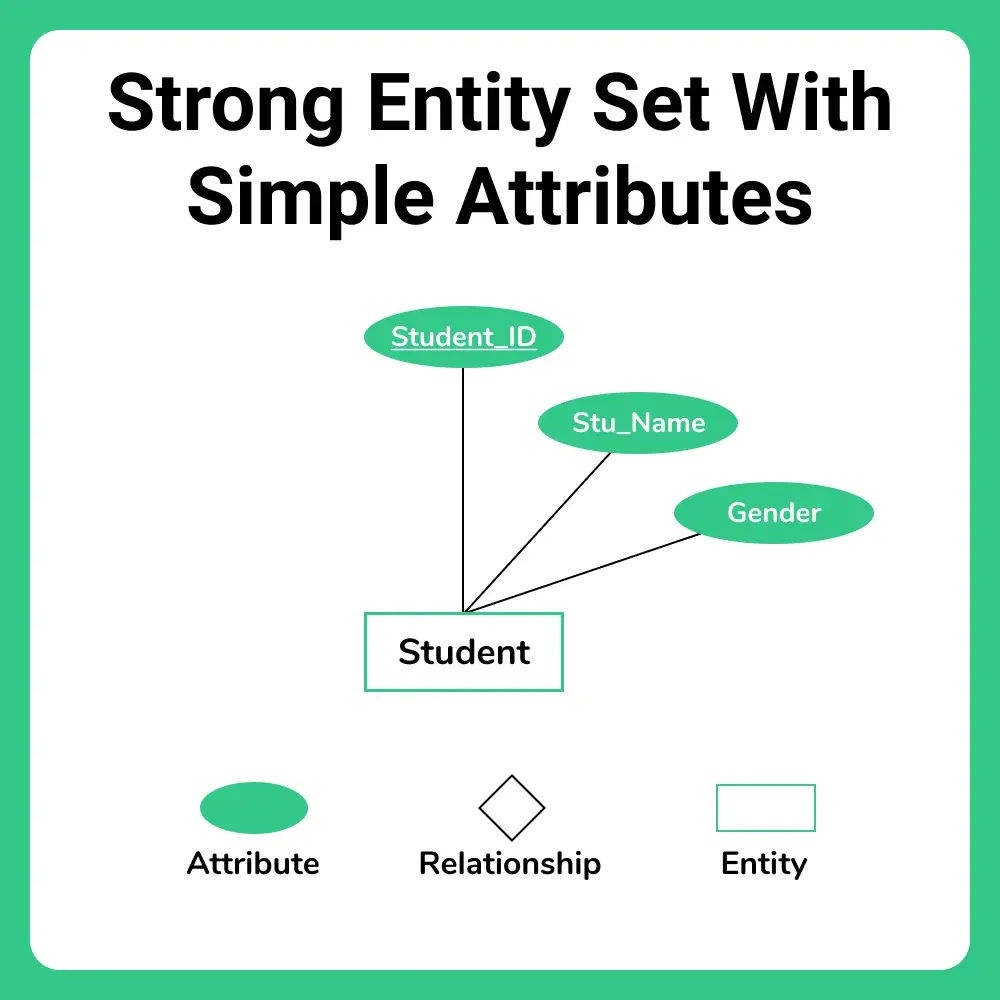
Rule-01: For Strong Entity Set With Only Simple Attributes
In relational model only one table is required to represent a strong entity set with simple attributes. In this
- Attributes are taken as columns of the table
- Key attribute is declared as primary key of the table
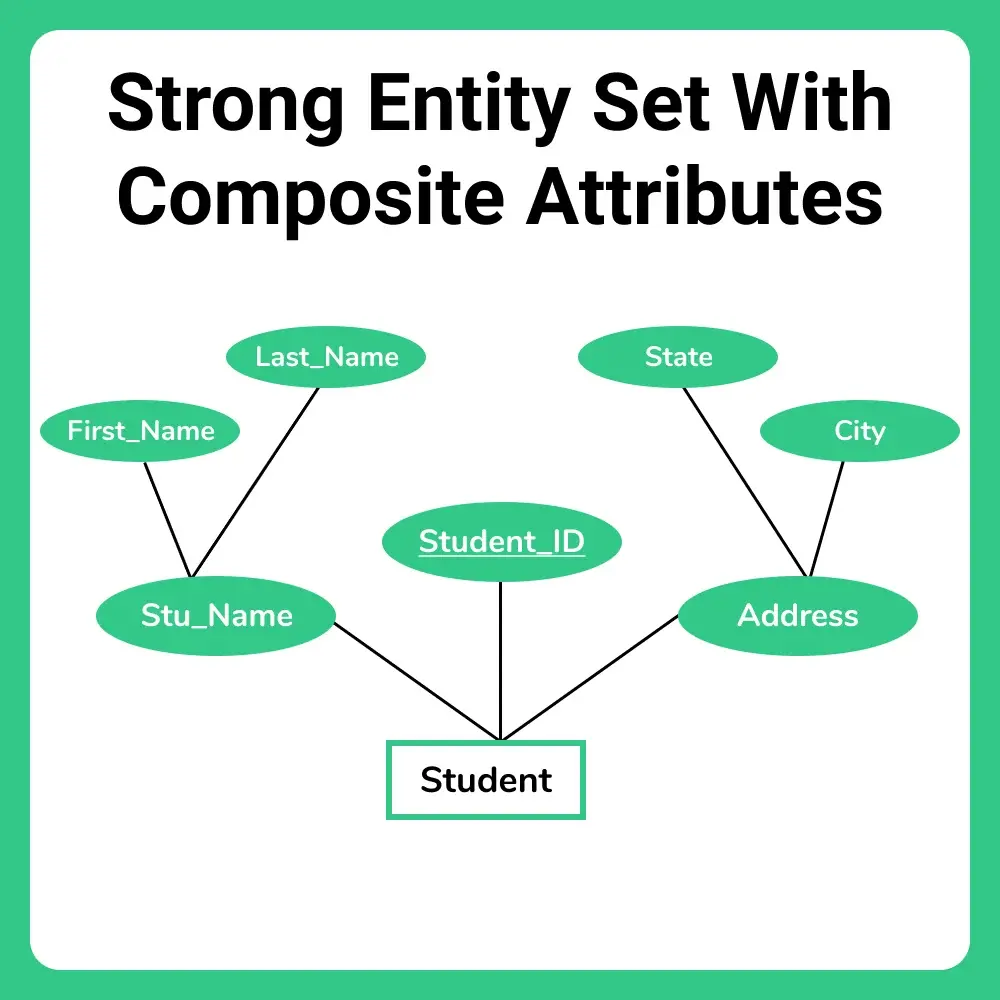
Rule-02: For Strong Entity Set With Composite Attributes
In relational model only one table is required to represent a strong entity set with composite attributes. In this
- Simple attributes are taken as columns of the table and
- Simple attributes of the composite attributes are considered as columns but not composite attributes themselves
- Key attribute is declared as primary key of the table
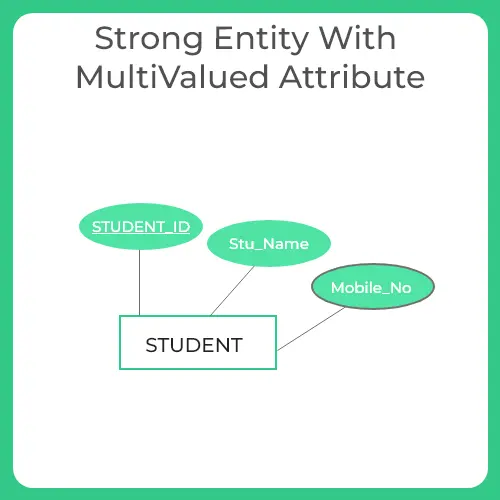
Rule-03: For Strong Entity Set With Multi Valued Attributes
In relational model two tables are required to represent a strong entity set with multi-valued attributes.
- One table with columns as primary key and multi-valued attributes and
- One table with columns as primary key and other simple attributes
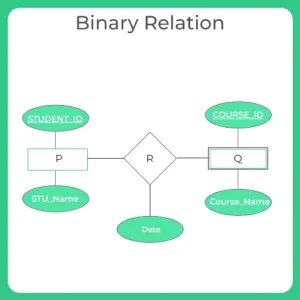
Rule-04: Translating Relationship Set into a Table
Only one table is required to represent a relationship set with columns as
- Key attributes of each participating entity set as primary keys
- Attributes of the relationship if any.
For suppose ,if we consider a relationship set with 2 entity sets , we require totally 3 tables to represent the whole ER diagram
- One table for first entity set with columns as its attributes
- Other table for second entity set with columns as its attributes
- Another table for relationship set with columns as primary keys of both entity sets and attributes of relationship set
Rule-05: For Binary Relationships With Cardinality Ratios
In this model four cases are possible. They are :
- Case-1: Binary relationship with cardinality ratio 1:1
- Case-2: Binary relationship with cardinality ratio m:1
- Case-3: Binary relationship with cardinality ratio 1:n
- Case-4: Binary relationship with cardinality ratio m:n
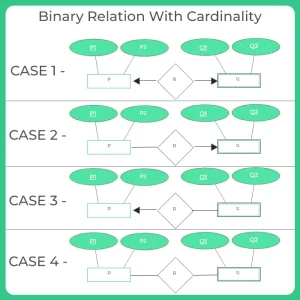
Case-1: For Binary Relationship With Cardinality Ratio 1:1
In this case two tables are required , we can combine the relationship set with either of the entity sets.
- First possible way
- PR ( p1 , p2 , q1 )
- Q ( q1 , q2 )
- Second possible way
- P( p1 , p2 )
- QR ( p1 , q1 , q2 )
Case-2: For Binary Relationship With Cardinality Ratio m:1
In this model two tables are required to represent the ER diagram. They are
- PR ( p1 , p2 , q1 )
- Q ( q1 , q2 )
Case-3: For Binary Relationship With Cardinality Ratio 1:n
In this model two tables are required to represent the ER diagram. They are
- P( p1 , p2)
- QR (p1, q1 , q2 )
Case-4: For Binary Relationship With Cardinality Ratio m:n
In this model three tables are required to represent the ER diagram. They are
- P ( p1 , p2 )
- R ( p1 , q1 )
- Q ( q1 , q2 )
Rule-06: For Binary Relationship With Both Cardinality Constraints and Participation Constraints
- In this model foreign key acquires NOT NULL costraint because of total participation constraint
- Rule 5 is followed to implement cardinality constraints.
- In this two cases are possible :
Case-01: For Binary Relationship With Cardinality Constraint and Total Participation Constraint From One Side
- Here we will combine the entity set Q and relationship set R as cardinality ratio is 1:n.
- Then, two tables will be required-
- P( p1 , p2 )
- QR ( p1 , q1 , q2 )
- Foreign key p1 has acquired NOT NULL constraint because of total participation constraint
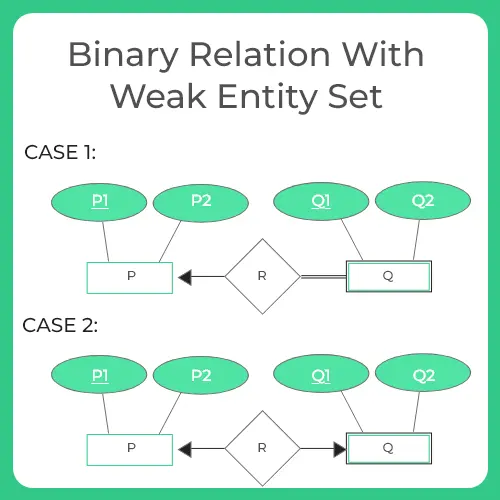
Case-02: For Binary Relationship With Cardinality Constraint and Total Participation Constraint From Both Sides
Only one table is required to represent a binary relationship when there is a key constraint from both the sides of entity set with total participation. It is
- PRQ( p1 , p2, q1 , q2 )
Rule-07: For Binary Relationship With Weak Entity Set
- Whenever a weak entity set appears, it will have identifying relationship set with total participation constraint.
- This model requires two tables to represent the ER diagram. They are
- P ( p1 , p2 )
- QR ( p1 , q1 , q2 )
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others





Login/Signup to comment