ACID Properties in DBMS

ACID Properties in DBMS
In this article, we will learn about ACID Properties in DBMS.- A transaction is a single logical action that accesses and modifies the contents of the database through reading and writing operations
- To maintain consistency of the database before and after a transaction, specific properties are followed called acid properties.
Atomicity (A)
- An atomic transaction simply means that the transaction happens only if it can be completed and achieve its purpose or if not it doesn’t happen at all.
- Atomicity defines that there are no transactions that occur partially hence the atomicity is also known as the “all or nothing rule”.
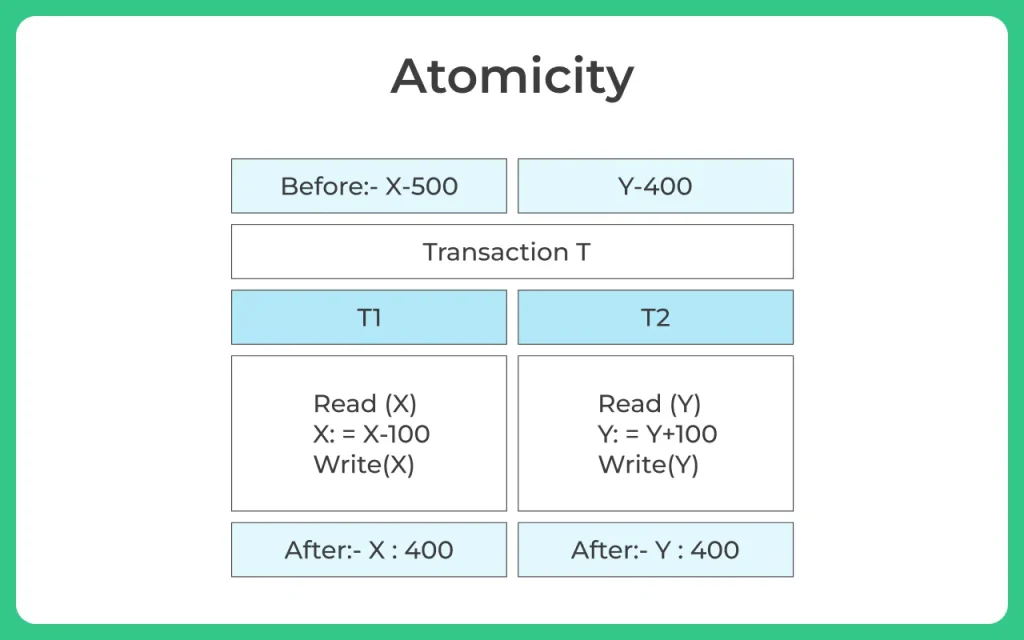
It is associated with two operations
- Abort: If a transaction is aborted i.e. it is incomplete, changes made to the database are not visible.
- Commit: If a transaction is committed i.e. it is complete changes made to the database or visible.
Example
Consider a transaction T which consists of T1 and T2: Task is to transfer 100 from account X to account Y
- T1: Deduct the amount from account X
- T2: Credit the amount to account Y
If the transaction fails after the completion of T1 and before completion of T2 then the amount will be deducted from account X but it will not be added to the account Y which ultimately results in an inconsistent database state.
Consistency(C)
- Integrity constraints (maintain certain rules to authenticate database) must be maintained to ensure your database is consistent before and after the transaction.
- Consistency refers to the correctness of the database.
Example
The total amount before and after the transaction must be maintained.
- Total amount before T occurs = 500 + 200 = 700.
- Total amount after T occurs = 400 + 300 = 700.
- The database is said to be inconsistent if T1 is completed but fails as a result total.
- Transaction P is incomplete.
Isolation (I)
- Isolation ensures that multiple transactions can occur at the same time provided each transaction is independent and shall not interfere in another transaction.
- Changes in one particular transaction are visible to any other transaction unless a particular change in the transaction is written to the memory.

Durability (D)
- Durability ensures that once after the completion of the transaction execution the updates and modifications to the database are stored and returned to a disc so that they can be used whenever a system failure occurs.
- So that all the changes become permanent and stored in non-volatile memory so that any action can be referred to and never lost.
What is the purpose of these ACID properties?
- Provides a mechanism for the correctness and consistency of a database system.
- As a result, each transaction is independent, consistent with each other and all actions are stored properly and permanently and support failure recovery.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others





Login/Signup to comment