Operations on a Stack
Operations on a Stack
There are many operations that can be used to manipulate a stack. A stack is a data structure in which the operations are executed in constant time.
There are a number of operations that can be performed on a stack, but there are two major operations that are used to manipulate a stack.
These operations are:
- Push()
- Pop()
Push()
- The push operation in a stack is synonymous to insertion in a data structure.
- In simpler words, inserting a new element in a stack is known as push.
- The time complexity of the Push() operation is O(1), i.e , it occurs in constant time.
Let us understand how a push() operation works. Let us consider we have to push a given number of elements in the stack.
The elements to be inserted are: 12 , 08 , 21 , 33 , 18 , 40.
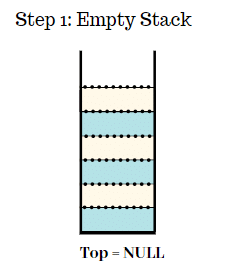
Step 1:
- Initially we have an empty stack.
- Top = NULL.
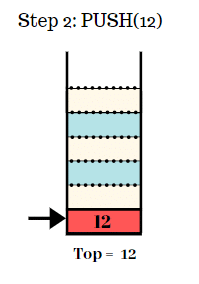
Step 2:
- Push the element 12 in the stack.
- Top = 12
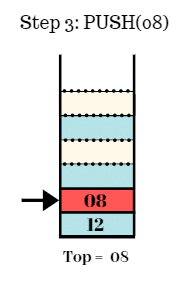
Step 3:
- Push the element 08 in the stack.
- Top = 08.
Step 4:
- Push the element 21 in the stack.
- Top = 21
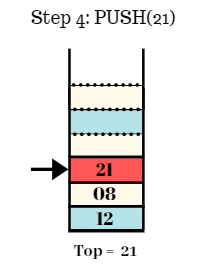
Step 5:
- Push the element 33 in the stack.
- Top = 33.
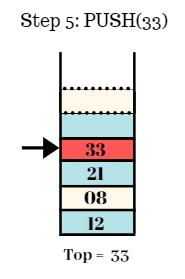
Step 6:
- Push the element 18 in the stack.
- Top = 18
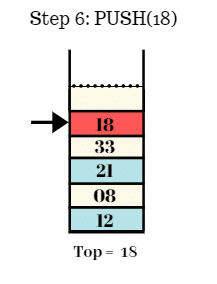
Step 7:
- Push the element 40 in the stack.
- Top = 40.
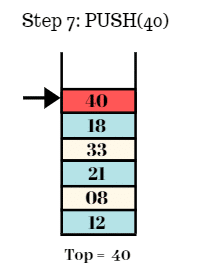
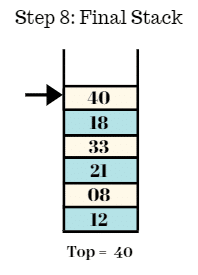
Step 8:
- Final stack is shown as follows.
- Top = 40
Pop()
- The Pop operation in a stack is synonymous to deletion in a data structure.
- In simpler words, deleting an existing element from a stack is known as pop.
- The time complexity of the Pop() operation is O(1), i.e , it occurs in constant time.
Let us understand how a pop() operation works. Let us consider we have to pop a given number of elements in the stack.
The elements to be deleted from the stack are : 40 , 18 , 33.
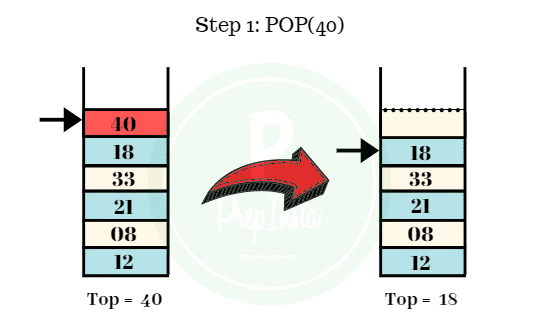
Step 1:
- The first element to be deleted from the stack is 40.
- We can see the value of top points to 40.
- We perform the pop operation and the element 40 is popped out off the stack.
- The remaining elements are shown in the image.
- Top = 18.
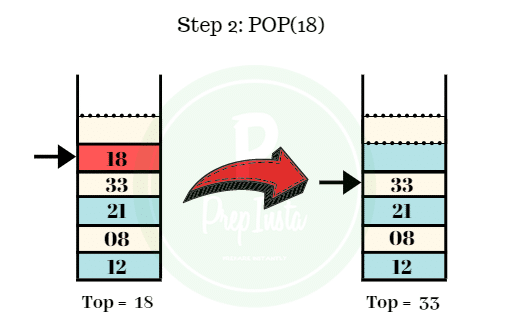
Step 2:
- The second element to be deleted from the stack is 18.
- We can see the value of top points to 18.
- We perform the pop operation and the element 18 is popped out off the stack.
- The remaining elements are shown in the image.
- Top = 33.
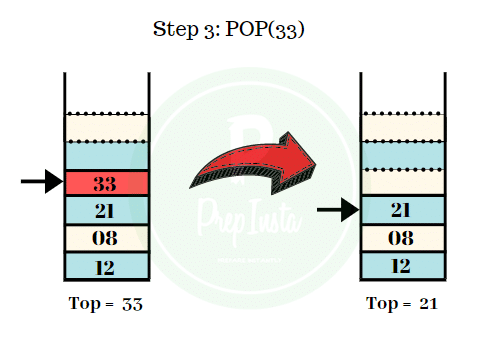
Step 3:
- The next element to be deleted from the stack is 33.
- We can see the value of top points to 33.
- We perform the pop operation and the element 33 is popped out off the stack.
- The remaining elements are shown in the image.
- Top = 21.
Code for Stack in C Program (using structure)
// C Program for Implmentation of stack (array) using structure
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<limits.h>
// A structure to represent a stack
struct Stack {
int top;
int maxSize;
int* array;
};
struct Stack* create(int max)
{
struct Stack* stack = (struct Stack*)malloc(sizeof(struct Stack));
stack->maxSize = max;
stack->top = -1;
stack->array = (int*)malloc(stack->maxSize * sizeof(int));
//here above memory for array is being created
// size would be 10*4 = 40
return stack;
}
// Checking with this function is stack is full or not
// Will return true is stack is full else false
//Stack is full when top is equal to the last index
int isFull(struct Stack* stack)
{
if(stack->top == stack->maxSize - 1){
printf("Will not be able to push maxSize reached\n");
}
// Since array starts from 0, and maxSize starts from 1
return stack->top == stack->maxSize - 1;
}
// By definition the Stack is empty when top is equal to -1
// Will return true if top is -1
int isEmpty(struct Stack* stack)
{
return stack->top == -1;
}
// Push function here, inserts value in stack and increments stack top by 1
void push(struct Stack* stack, int item)
{
if (isFull(stack))
return;
stack->array[++stack->top] = item;
printf("We have pushed %d to stack\n", item);
}
// Function to remove an item from stack. It decreases top by 1
int pop(struct Stack* stack)
{
if (isEmpty(stack))
return INT_MIN;
return stack->array[stack->top--];
}
// Function to return the top from stack without removing it
int peek(struct Stack* stack)
{
if (isEmpty(stack))
return INT_MIN;
return stack->array[stack->top];
}
int main()
{
struct Stack* stack = create(10);
push(stack, 5);
push(stack, 10);
push(stack, 15);
int flag=1;
while(flag)
{
if(!isEmpty(stack))
printf("We have popped %d from stack\n", pop(stack));
else
printf("Can't Pop stack must be empty\n");
flag=0;
}
return 0;
}
Output :
We have pushed 5 to stack We have pushed 10 to stack We have pushed 15 to stack We have popped 15 from the stack
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment