C++ program to find the frequency of elements in an array
Frequency of Elements in an array in C++
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to find the frequency of elements in an array in C++ Programming language. We will discuss various methods to count the frequency of each element.

Example
Input : arr[6] = [10, 20, 20, 30, 10, 20]Output : 10 occurs 2 times
20 occurs 3 times
30 occurs 1 times
Methods Discussed in this Page are :
- Method 1 : Naive Approach with extra space
- Method 2: Naive way without extra space.
- Method 3 : Using Sorting
- Method 4 : Using hash Map
Let’s discuss each method one by one,
Method 1 :
In this method we will count the frequency of each elements using two for loops.
- To check the status of visited elements create a array of size n.
- Run a loop from index 0 to n and check if (visited[i]==1) then skip that element.
- Otherwise create a variable count = 1 to keep the count of frequency.
- Run a loop from index i+1 to n
- Check if(arr[i]==arr[j]), then increment the count by 1 and set visited[j]=1.
- After complete iteration of for loop print element along with value of count.
Time and Space Complexity :
- Time Complexity : O(n2)
- Space Complexity : O(n)
Method 1 : Code in C++
Run
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Main function to run the program
int main()
{
int arr[] = {10, 30, 10, 20, 10, 20, 30, 10};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int visited[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
if(visited[i]!=1){
int count = 1;
for(int j=i+1; j<n; j++){
if(arr[i]==arr[j]){
count++;
visited[j]=1;
}
}
cout<<arr[i]<<" occurs at "<<count<<" times "<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}Output
30 occurs at 2 times 10 occurs at 3 times 20 occurs at 2 times
Method 2 :
In this method we will use the naive way to find the frequency of elements in the given integer array without using any extra space.
Time and Space Complexity :
- Time Complexity : O(n2)
- Space Complexity : O(1)
Method 2 : Code in C++
Run
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void countFrequency(int *arr, int size){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){
int flag = 0;
int count = 0;
// Counting of any element has to be delayed to its last occurrence
for (int j = i+1; j < size; j++){
if (arr[i] == arr[j]){
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
// The continue keyword is used to end the current iteration
// in a for loop (or a while loop), and continues to the next iteration
if (flag == 1)
continue;
for(int j = 0;j<=i;j++){
if(arr[i]==arr[j])
count +=1;
}
cout << arr[i] << ": " << count << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {5, 8, 5, 7, 8, 10};
int size = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
countFrequency(arr, size);
return 0;
}
Output
5 : 2
7 : 1
8 : 2
10 : 1
Method 3 :
In this method we will sort the array then, count the frequency of the elements.
Time and Space Complexity :
- Time Complexity : O(nlogn)
- Space Complexity : O(1)
Method 3 : Code in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void countDistinct(int arr[], int n)
{
sort(arr, arr + n);
// Traverse the sorted array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int count = 1;
// Move the index ahead whenever
// you encounter duplicates
while (i < n - 1 && arr[i] == arr[i + 1]){
i++;
count++;
}
cout << arr[i] << ": " << count << endl;
}
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
int arr[] = {5, 8, 5, 7, 8, 10};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
countDistinct(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Output
5 : 2
7 : 1
8 : 2
10 : 1
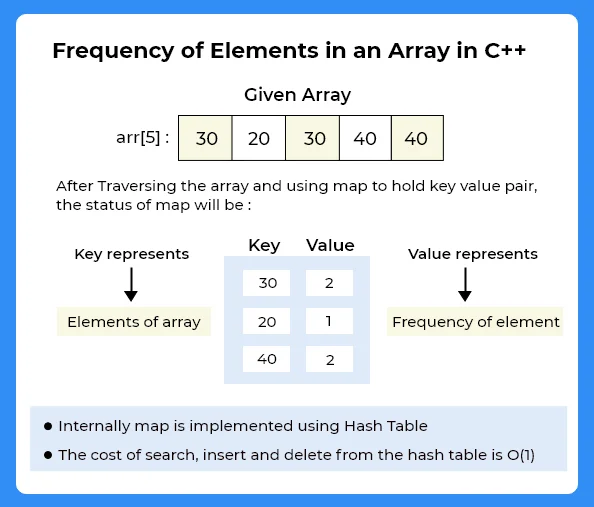
Method 4 :
In this method we will use hash-map to store the frequency of the elements.
- Create an unordered_map say mp.
- Run a loop to iterate over array
- Set mp[arr[i]]++
- After, complete iteration, run a loop over map
- And Print key value pair
About unordered_map
Internally unordered_map is implemented using Hash TableThe key provided to map are hashed into indices of a hash table that is why the performance of data structure depends on hash function a lot but on an average
The cost of search, insert and delete from the hash table is O(1).
Method 4 : Code in C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Main function to run the program
int main()
{
int arr[] = {10, 30, 10, 20, 10, 20, 30, 10};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
unordered_map <int, int>mp;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
mp[arr[i]]++;
for(auto it=mp.begin(); it!=mp.end(); it++)
cout<first<<" occurs "<second<<" times\n";
} Output
10 occurs 4 times
30 occurs 2 times
20 occurs 2 times
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription






Login/Signup to comment