Smallest Element in an array using C++
Smallest Element in an array using C++
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to find the smallest element in an array using C++ programming language. We are given with the elements of the array and need to print the smallest element among them. We discuss different methods to solve the given problem.
Here, in this page we will discuss different methods to find the smallest element in the array.
- Method 1: Simple iterative
- Method 2: Top Down recursive
- Method 3: Bottom Up Recursive
Method 1:-
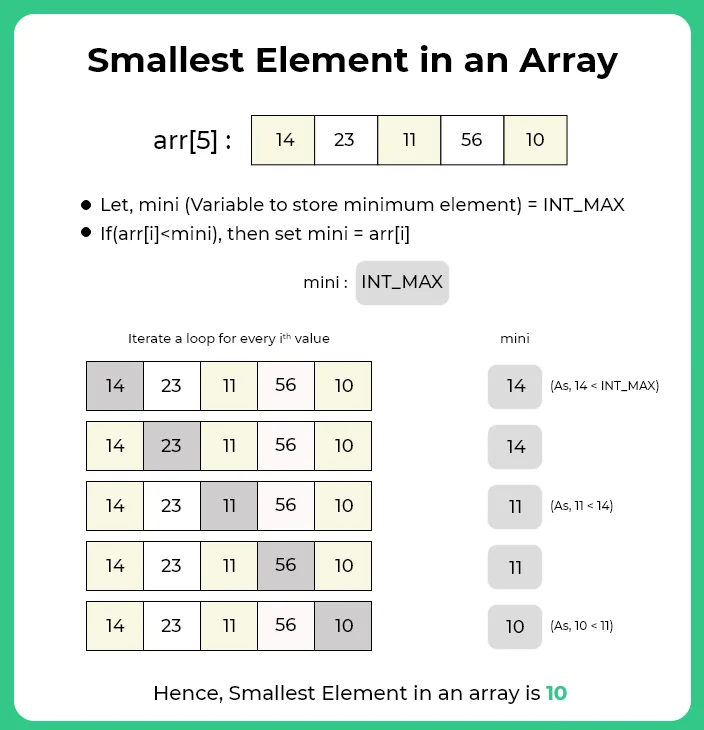
- Declare a variable say mini and initialize it with INT_MAX value.
- Run a loop from i=0 to i<n and check,
- If arr[i] < mini, then set mini = arr[i].
- After complete iteration print the value of mini.
Run
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int arr[] = { 34, 5, 89, 90, 56};
int n = sizeof(arr)/ sizeof(arr[0]);
int mini = INT_MAX;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
if(arr[i]<mini)
mini = arr[i];
}
cout<<mini;
}
Output
The smallest : 5
Code in C++
Method 2 (Using Recursion)
In this method we will discuss the recursive approach to find the smallest element in the given array.
- Create a recursive function say min_element(int arr[], int n)
- Base Condition : If(n==1) return arr[0]
- Otherwise, return min(arr[n-1], min(arr, n-1))
Method 2 C++ Program:-
Run
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//Recursive Function
int min_element(int arr[], int n)
{
// if size = 0 means whole array has been traversed
if (n == 1)
return arr[0];
return min(arr[n-1], min_element(arr, n-1));
}
// driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 34, 5, 89, 90, 56};
int n = sizeof(arr)/ sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << min_element(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// Time complexity: O(N)
// Space complexity: O(1)
// Auxilary space complexity : O(N) due to function call stack
Output
5
Method 3 (Using Bottom up recursion)
Call a function : minimum(int arr[], int i, int end)
- With initial call up values as minimum(arr, 0, end)
- Initially passing end as the index of last array element
- Initially passing ‘i’ as 0
- Recursively reach iteration where reading 2nd last element
- Find smaller between 2nd last and last array elements
- And return the result to min value of the previous recursive iteration
- In each of the remaining recursive callups find the smaller b/w current array index element and current min value
- Pass final min value from last recursive callup to main and print
Method 3 C++ Program:-
Run
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//Recursive Function
int minimum(int arr[], int i, int end)
{
int min;
if(i == end-1)
return (arr[i] < arr[i + 1]) ? arr[i] : arr[i + 1];
min = minimum(arr, i + 1, end);
return (arr[i] < min) ? arr[i] : min;
}
// driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 34, 5, 89, 90, 56};
int end = sizeof(arr)/ sizeof(arr[0]) - 1;
cout << minimum(arr, 0, end);
return 0;
}
Output
5
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription






#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int a[n];
for(int i=0;i>a[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
sort(a,a+n); //This is an inbuilt function which sorts an array in ascending order
}
cout<<a[0]; //So in ascending order obviously the 1st element must be the smaller one than all the remaining since ascending order starts from small to big
return 0;
}
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int a[n];
for(int i=0;i>a[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
sort(a,a+n);
}
cout<<a[0];
return 0;
}