Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder Traversals
Construct Tree From Given Inorder and Postorder Traversals in Java
There are three types of traversals in a tree: Inorder, Preorder and Postorder traversal. A tree can be formed with any two tree traversals in which one of them being the in order traversal.

Construct Tree From Given Inorder and Postorder Traversals
Example
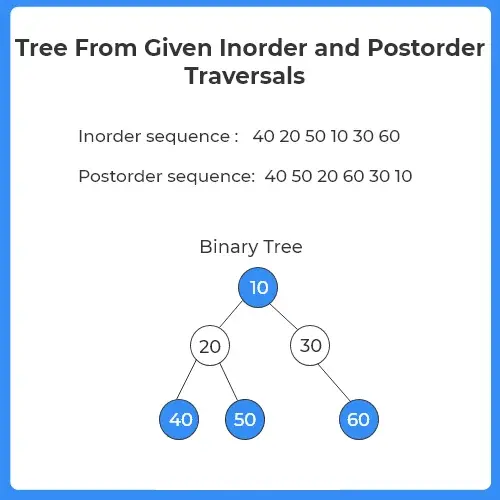
Given traversals:
Postorder: 12, 30, 40, 37, 25, 60, 70, 62, 87, 75, 50
Inorder:12, 25, 30, 37, 40, 50, 60, 62, 70, 75, 87
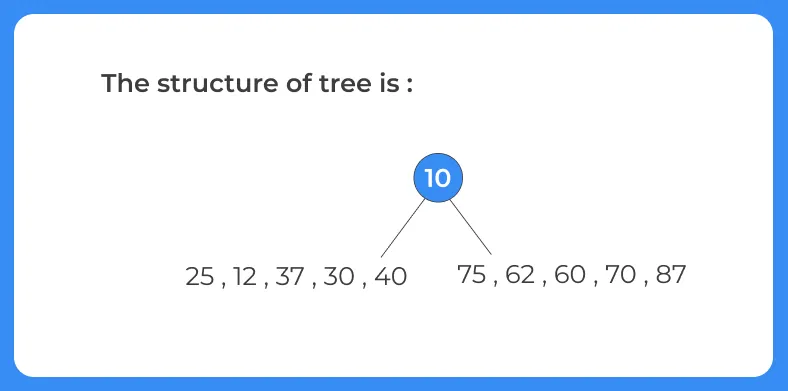
1. The last element in the postorder traversal is the root of the tree.
So, here 50 will be the root of the tree.
2. We will find the index of 50 in the inorder traversal.The index found is 5. Let this index is denoted by ‘pos’.
3. All the elements to the left of this index ( from 0 to 4 index) will be in the left subtree of 50.
4. And all the elements to the right of this index ( from 6 to 10) will be in the right subtree of 50.
Now, we will divide preorder and inorder array in two parts.
One is for the left subtree and other is for the right subtree.
Let
- psi: starting index for preorder array
- pei: ending index for preorder array
- isi: starting index of inorder array
- iei: ending index of preorder array
- clc: Number of elements in the left subtree
Clearly, clc= pos – isi;
For left subtree:
Postorder array: from index psi, psi + clc – 1
Inorder array: from index isi, isi + clc -1
For right subtree:
Postorder array: from index psi+clc, pei – 1
Inorder array: from index isi + clc + 1, iei
Using the above arrays, all the steps are recursively repeated.
The following binary tree is obtained:
Code For Binary Search Tree
public class Main
{
// Binary tree class
public static class BinaryTree
{
// Node class
public class Node
{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node (int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
private Node root;
private int size;
public BinaryTree (int[]post, int[]in)
{
this.root =
this.construct (post, 0, post.length -1, in, 0, in.length-1);
}
private Node construct (int[]post, int psi, int pei, int[]in, int isi,
int iei)
{
// Base case
if (psi > pei)
{
return null;
}
Node node = new Node (post[pei]);
node.left = null;
node.right = null;
this.size++;
// Searching post[pei] in inorder array
int pos = -1;
for (int i = isi; i <= iei; i++)
{
if (in[i] == node.data)
{
pos = i;
break;
}
}
// Number of elements in left subtree
int clc = pos-isi;
// Left subtree
node.left =
this.construct (post, psi, psi + clc-1, in, isi, isi + clc-1);
// Right subtree
node.right =
this.construct (post, psi + clc, pei-1, in, isi + clc + 1, iei);
return node;
}
// Postorder tree traversal
public void postOrder ()
{
postOrder (this.root);
}
private void postOrder (Node node)
{
if (node == null)
{
return;
}
postOrder (node.left);
postOrder (node.right);
System.out.print (node.data + " ");
}
}
public static void main (String[]args) throws Exception
{
// Construct binary tree
int[] in = { 12, 25, 30, 37, 40, 50, 60, 62, 70, 75, 87 };
int[] post = { 12, 30, 40, 37, 25, 60, 70, 62, 87, 75, 50 };
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree (post, in);
System.out.println("The new tree constructed is (Postorder) : ");
bt.postOrder ();
}
}
Output :
The new tree constructed is (Postorder) : 12 30 40 37 25 60 70 62 87 75 50
Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals in C
Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder Traversals
On this page we wiil discuss about how to construct tree from given postorder and inorder traversals in C .
There are three types of traversals in a tree: Inorder, Preorder and Postorder traversal. A tree can be formed with any two tree traversals in which one of them being the in order traversal.
Postorder Traversal: We first move to the left subtree and then to the right subtree and finally print the node.
Inorder Traversal: We move to the left subtree, then print the node and move to the right subtree.

Tree From Given Postorder and Inorder Traversal
Algorithm For InOrder Traversal
- Traverse The Left subtree.
- Print the node.
- Traverse the right subtree.
Algorithm For PostOrder Traversal
- Traverse the left subtree.
- Traverse the right subtree.
- Print the node.
Algorithm for tree construction:
- Start with root node, which will be the last element in the postorder sequence
- And find the boundary of its left and right subtree in the inorder sequence.
- To find the boundary, search for the index of the root node in the inorder sequence.
- All keys before the root node in the inorder sequence become part of the left subtree, and all the keys after the root node become part of the right subtree.
- Repeat the above step recursively for all the nodes in the tree and construct the tree.

Code in C to Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder Traversals
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Data structure to store a binary tree node
struct Node
{
int key;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Function to create a new binary tree node having a given key
struct Node* newNode(int key)
{
struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->key = key;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
// Recursive function to perform inorder traversal on a given binary tree
void inorderTraversal(struct Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
inorderTraversal(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->key);
inorderTraversal(root->right);
}
// Recursive function to perform postorder traversal on a given binary tree
void postorderTraversal(struct Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
postorderTraversal(root->left);
postorderTraversal(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->key);
}
// Recursive function to construct a binary tree from a given
// inorder and postorder traversals
struct Node* construct(int inorder[], int start, int end,
int postorder[], int *pIndex)
{
// base case
if (start > end) {
return NULL;
}
// Consider the next item from the end of a given postorder sequence.
// This value would be the root node of the subtree formed by the sequence
// inorder[start, end].
struct Node* node = newNode(postorder[(*pIndex)--]);
// search the current node index in inorder sequence to determine
// the boundary of the left and right subtree of the current node
int i;
for (i = start; i <= end; i++)
{
if (inorder[i] == node->key) {
break;
}
}
// recursively construct the right subtree
node->right= construct(inorder, i + 1, end, postorder, pIndex);
// recursively construct the left subtree
node->left = construct(inorder, start, i - 1, postorder, pIndex);
// return the current node
return node;
}
// Construct a binary tree from inorder and postorder traversals.
// This function assumes that the input is valid, i.e., given
// inorder and postorder sequences forming a binary tree.
struct Node* constructTree(int inorder[], int postorder[], int n)
{
// `pIndex` stores the index of the next unprocessed node from the end
// of the postorder sequence
int *pIndex = &n;
return construct(inorder, 0, n, postorder, pIndex);
}
int main(void)
{
/* Construct the following tree
1
/ \
/ \
2 3
/ / \
/ / \
4 5 6
/ \
/ \
7 8
*/
int inorder[] = { 4, 2, 1, 7, 5, 8, 3, 6 };
int postorder[] = { 4, 2, 7, 8, 5, 6, 3, 1 };
int n = sizeof(inorder)/sizeof(inorder[0]);
struct Node* root = constructTree(inorder, postorder, n - 1);
// traverse the constructed tree
printf("Inorder traversal is "); inorderTraversal(root);
printf("\nPostorder traversal is "); postorderTraversal(root);
return 0;
}
Output:
Inorder traversal is 4 2 1 7 5 8 3 6 Postorder traversal is 4 2 7 8 5 6 3 1



Login/Signup to comment