Spiral Order traversal of Tree in C
Spiral Order Traversal of Binary Tree in C
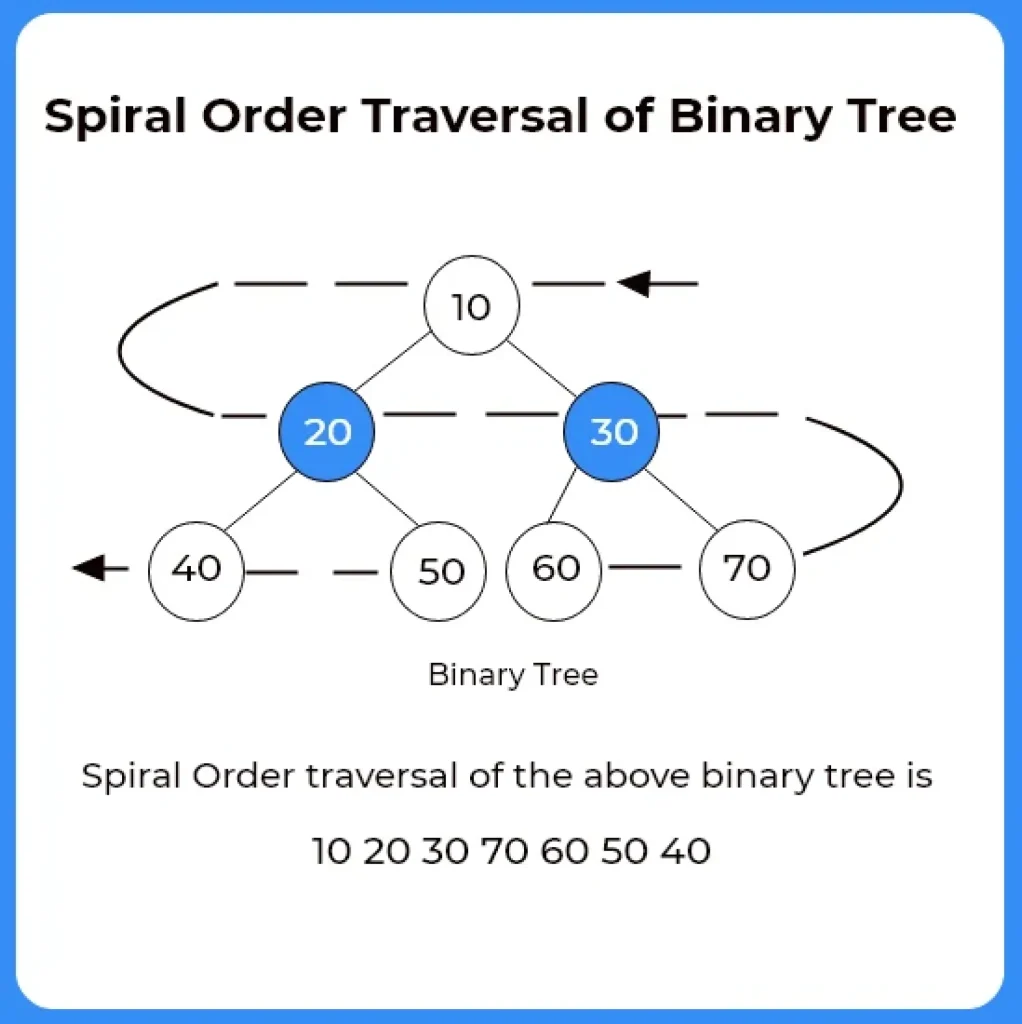
Given a Tree and we need to print the spiral order traversal of the given tree. By spiral Order Traversal We mean that alternate levels should be printed in alternate order .
Example – Level 0 to be printed left to right
Level 1 from right to left, and so on.

Spiral Order Traversal of Binary Tree In C
Algorithm :
- Create a Boolean variable ltr which is used to change printing order of levels.
- If ltr is 1 then printGivenLevel() prints nodes from left to right else from right to left. Value of ltr is flipped in each iteration to change the order.
- Function to print level order traversal :
- printSpiral(tree) set ltr to 0;
- Run a loop from 0 to height -1
- printGivenLevel(tree, d, ltr);
- ltr ~= ltr /*flip ltr*/
- To print the nodes is :if tree is NULL then return;
- if level is 1, then print(tree->data);
- else if level greater than 1, then
- if(ltr) printGivenLevel(tree->left, level-1, ltr) and printGivenLevel(tree->right, level-1, ltr);
- else printGivenLevel(tree->right, level-1, ltr) and printGivenLevel(tree->left, level-1, ltr);
Code in C for Spiral Order Traversal
Run
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
};
void printGivenLevel (struct node *root, int level, int ltr);
int height (struct node *node);
struct node *newNode (int data);
void printSpiral (struct node *root)
{
int h = height (root);
int i;
bool ltr = false;
for (i = 1; i <= h; i++)
{
printGivenLevel (root, i, ltr);
ltr = !ltr;
}
}
void printGivenLevel (struct node *root, int level, int ltr)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (level == 1)
printf ("%d ", root->data);
else if (level > 1)
{
if (ltr)
{
printGivenLevel (root->left, level - 1, ltr);
printGivenLevel (root->right, level - 1, ltr);
}
else
{
printGivenLevel (root->right, level - 1, ltr);
printGivenLevel (root->left, level - 1, ltr);
}
}
}
int height (struct node *node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
else
{
int lheight = height (node->left);
int rheight = height (node->right);
if (lheight > rheight)
return (lheight + 1);
else
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
struct node *newNode (int data)
{
struct node *node = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
int main ()
{
struct node *root = newNode (10);
root->left = newNode (20);
root->right = newNode (30);
root->left->left = newNode (40);
root->left->right = newNode (50);
root->right->left = newNode (60);
root->right->right = newNode (70);
printf ("Spiral Order traversal of binary tree is \n");
printSpiral (root);
return 0;
}
Output
Spiral Order traversal of binary tree is 10 20 30 70 60 50 40



Login/Signup to comment