C Program for Reversing a Linked List without changing the links between the nodes(Data Reverse Only)
Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only)
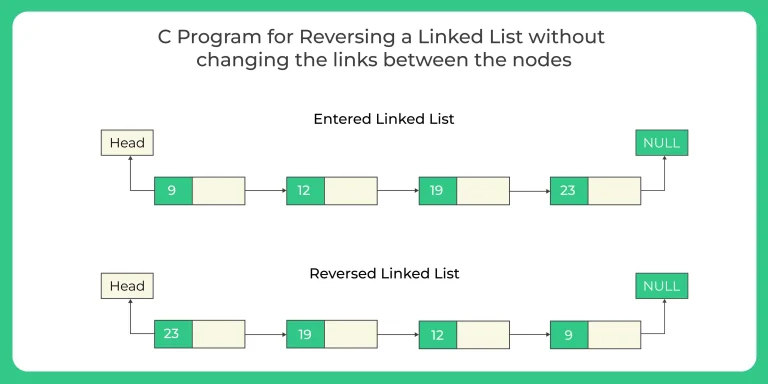
Here, in this page we will discuss Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes in C. We create a vector and store the elements of the linked list and them change the linked list node data by iterating the vector in reverse manner.
Algorithm :
- Create a node say current and set it to head.
- Now, Create a variable to store size of linked list. We will iterate over all nodes of linked list and increment the size variable by 1 and set current to next node. Repeat this till the current node does not become NULL.
- Create an array of size (size) to store the node value in it.And create a variable say x points to last index of the array. We will iterate over all nodes of linked list and insert the current node data in that array position and decrement the x by 1 and set current to next node. Repeat this till the current node does not become NULL.
- Now, again set current to head and take a variable say x and set it to 0.
- Now, change the current node data with array[x] and increment the x by 1 and set current to next node. Repeat this till current node does not become NULL.
- In this way we can Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes in C.
Code in C based on above Algorithm
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
/* Link list node */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
/* Function to reverse the linked list */
static void reverse (struct Node **head_ref)
{
struct Node *current = *head_ref;
int size = 0;
while (current != NULL)
{
size++;
current = current->next;
}
int a[size];
int x = size - 1;
current = *head_ref;
while (current != NULL)
{
a[x--] = current->data;
current = current->next;
}
current = *head_ref;
x = 0;
while (current != NULL)
{
current->data = a[x++];
current = current->next;
}
}
/* Function to push a node by user
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
*/
/* Function to print linked list */
void Display (struct Node *head)
{
struct Node *temp = head;
while (temp != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
/* Driver code*/
int main ()
{
//creating 4 pointers of type struct Node
//So these can point to address of struct type variable
struct Node *head = NULL;
struct Node *node2 = NULL;
struct Node *node3 = NULL;
struct Node *node4 = NULL;
// allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node2 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node3 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node4 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
head->data = 5; // data set for head node
head->next = node2; // next pointer assigned to address of node2
node2->data = 10;
node2->next = node3;
node3->data = 15;
node3->next = node4;
node4->data = 20;
node4->next = NULL;
printf ("Given Linked list: ");
Display (head);
reverse (&head);
printf ("\n\nReversed Linked list: ");
Display (head);
return 0;
}
Output:
Given Linked list: 5 10 15 20
Reversed Linked list: 20 15 10 5



Login/Signup to comment