C Program for Deletion from end in Circular Linked List

Deleting node from LAST in circular linked list
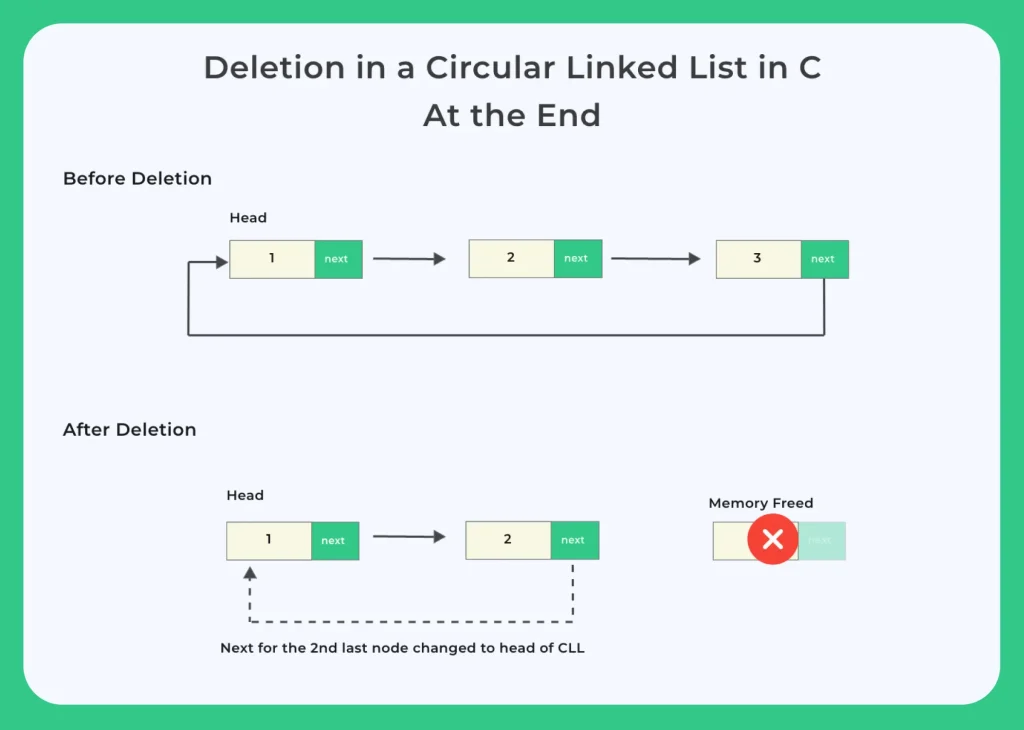
In this section we will learn C Program for Deletion from end in Circular Linked List. Removing end node from the linked list means replacing the pointer of the second last node with the pointer of first node in circular sequenced list.
For Example :- Input : 19 5 2 110
Output : 19 5 2 (delete node from the last)
Deletion From End in Circular Linked List in C
Algorithm
- Step 1: IF HEAD = NULL ( GO TO STEP 8 )
- Step 2: NOW SET POINTER = HEAD
- Step 3: REPEAT STEP 4 AND 5 UNTIL POINTER → NEXT != HEAD
- Step 4: ASSIGN PRE_POINTER = POINTER
- Step 5: ASSIGN POINTER = POINTER → NEXT
- Step 6: ASSIGN PRE_POINTER → NEXT = HEAD
- Step 7: REMOVE OR FREE POINTER
- Step 8: EXIT
Construction of node in circular linked list :-
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* next;
}; 
Working
- CASE 1 :- If the linked list is empty then head == NULL and exit.
- CASE 2 :- If the linked list have only single node then, head → next == head. In this scenario, we need to delete the list and make the head pointer free.
- CASE 3 :- If the linked list contains more than one node then, we need to move whole linked list by using the pointer to reach the last node of the list.
- We need to keep the second last node of the list.
- Then we need to make the two pointers pointer and prepointer.
- After that we need to make one more next pointer of prepointer point to the next of pointer(head node)
- Last make pointer free.
C Program For Deletion From End
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// structure for Circular Linked List
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void deleteEnd (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *tempNode = *head;
struct Node *previous;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (tempNode->next == *head)
{
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// else traverse to the last node
while (tempNode->next != *head)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode->next;
}
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to head
previous->next = *head;
// delete the last node
free (tempNode);
// 2nd last now becomes the last node
}
void insert (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
(*head)->next = *head;
return;
}
struct Node *curr = *head;
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = newNode;
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
void display (struct Node *head)
{
// if there are no node in CLL
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node *temp = head;
//need to take care of circular structure of CLL
do
{
printf ("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
// first node will be null at creation
struct Node *head = NULL;
insert (&head, 10);
insert (&head, 11);
insert (&head, 12);
insert (&head, 13);
insert (&head, 14);
insert (&head, 15);
insert (&head, 16);
display (head);
deleteEnd (&head);
display (head);
return 0;
}
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 16 15 14 13 12 11
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription






Login/Signup to comment