C Program for deletion at the nth node of the Singly Linked List
Delete a Linked List Node at a given position in C
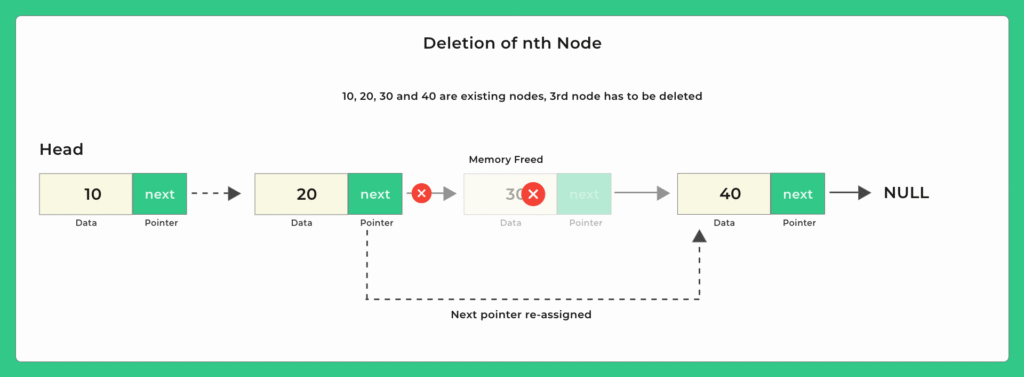
Deleting any node from the middle is easy, in this blog we will look at ways to delete the nth node of singly linked list, Lets see deletion at the nth node of the Singly Linked List in C .

Deletion at Specific Position
Method for Linked List Delete from Specific node in C
- Accept the position from the user to delete
- If it is the first node to delete, change the head to the next node and free the first node memory.
- While traversing to the nth node, always store the previous (n-1)th node
- Assign next of (n-1)th node to nth node’s next i.e. (n+1)th node
- Free the memory for nth node.
C Program for deletion at the nth node of the Singly Linked List
Program to delete the nth node of a Linked list is given below –
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
// required for deletePosition
int getCurrSize (struct Node *node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
// to delete nth node
void deletePosition (struct Node **head, int n)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
struct Node *previous;
//if the head node itself needs to be deleted
int size = getCurrSize (*head);
// not valid
if (n < 1 || n > size)
{
printf ("Enter valid position\n");
return;
}
// delete the first node
if (n == 1)
{
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
printf ("Deleted: %d\n", temp->data);
free (temp);
return;
}
// traverse to the nth node
while (--n)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// change previous node's next node to nth node's next node
previous->next = temp->next;
printf ("Deleted: %d\n", temp->data);
// delete this nth node
free (temp);
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
printf ("LinkedList : ");
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n\n");
}
int main ()
{
//creating 4 pointers of type struct Node
//So these can point to address of struct type variable
struct Node *head = NULL;
struct Node *node2 = NULL;
struct Node *node3 = NULL;
struct Node *node4 = NULL;
struct Node *node5 = NULL;
// allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node2 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node3 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node4 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node5 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
head->data = 25; // data set for head node
head->next = node2; // next pointer assigned to address of node2
node2->data = 20;
node2->next = node3;
node3->data = 15;
node3->next = node4;
node4->data = 10;
node4->next = node5;
node5->data = 5;
node5->next = NULL;
display (head);
// delete 2nd node
deletePosition (&head, 2);
display (head);
// delete 1st node
deletePosition (&head, 1);
display (head);
deletePosition (&head, 3);
deletePosition (&head, 1);
deletePosition (&head, 1);
display (head); // Linked List becomes empty now
// invalid, position to delete > size
// empty linked list size : 0
deletePosition (&head, 1);
return 0;
}
Output
LinkedList : 25 20 15 10 5
Deleted: 20
LinkedList : 25 15 10 5
Deleted: 25
LinkedList : 15 10 5
Deleted: 5
Deleted: 15
Deleted: 10
LinkedList :
Enter valid position



Login/Signup to comment