Doubly Linked List Insertion and Deletion in C (All Programs)
Doubly Linked List Insertion and Deletion Program in C
Doubly Linked List insertion and deletion may be confusing. We will look at all possible ways of insertion and deletion and at all possible places do it in a double Linked List.

Why Doubly Linked List?
Singly Linked List allows traversal only in one direction, since they have information about the next node, using next pointers.
While with doubly Linked List we can travel in both directions as they have both next and previous node pointers.
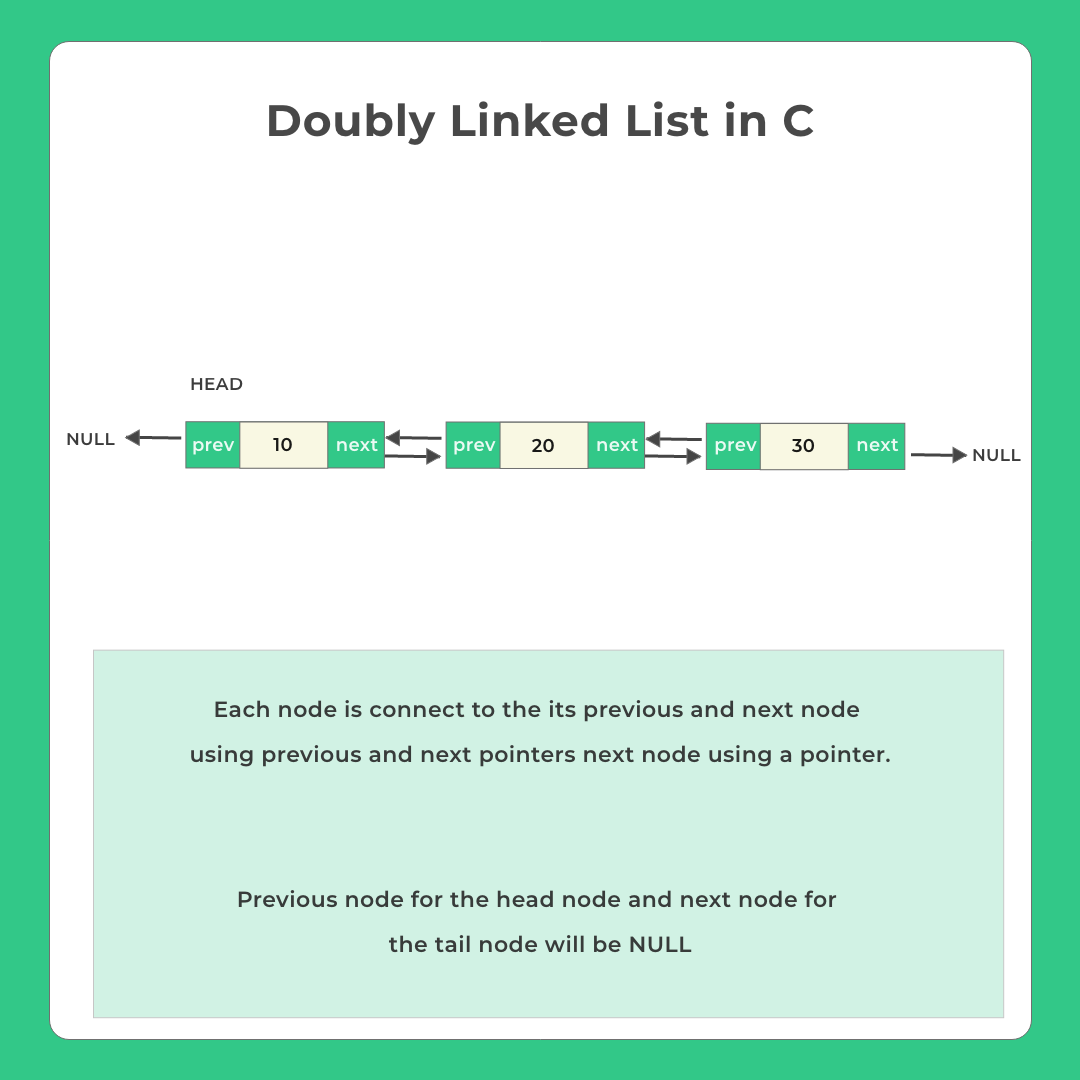
Doubly Linked List Components
Doubly Linked List has the following components generally –
- Node – Individual collection of data, next and previous pointers are called as a node
- Data – The value or data held inside the doubly linked lists data structure
- Head – This denotes the starting node of the doubly linked list
- Previous Pointer – For any given node it contains the address to the previous node in a doubly-linked list chain
- Next Pointer – Contains the next node in doubly linked list chain
Head node previous will be NULL and the Last node’s next will be null as well.
Some implementations can also have a tail node while it’s not necessary
Tail – Some doubly linked list implementations can have a tail node in data structure to denote the last node in the doubly Linked list
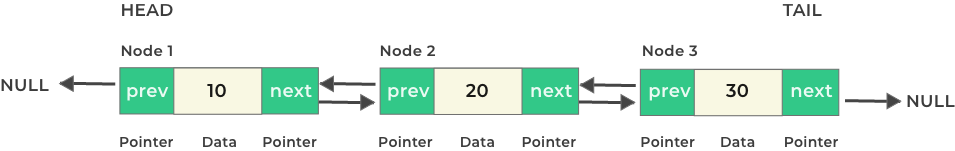
Basic Structure of a Doubly Linked List in C
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
}; Possible Positions to do Insertion And Deletion
We will write the program to take care of all possible positions in a Doubly Linked List, which can be –
- At start(default nature)
- At Last
- In the middle (After a position)
Lets have a look at the Code
Code for Insertion in Doubly Linked List
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
int getLength (struct Node *node);
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
newNode->prev = NULL;
//If the linked list already had atleast 1 node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// *head->prev = newNode; would not work it has (*head) must be used
//changing the new head to this freshly entered node
*head = newNode;
}
void insertLast (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
//need this if there is no node present in linked list at all
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
newNode->prev = NULL;
return;
}
struct Node *temp = *head;
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = temp;
}
void insertPosition (struct Node **head, int n, int data)
{
int len = getLength (*head);
// if insertion has to happen at start
if (n == 0)
{
insertStart (head, data);
return;
}
// if insertion has to happen at end
if (n == len)
{
insertLast (head, data);
return;
}
// other wise if insertion needs to happen in the middle
// if position to enter after is greater than size of List
// if position to enter is negative, we can't insert
if (n < 0 || n > len)
printf ("Invalid position to insert\n");
else
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
newNode->prev = NULL;
// temp used to traverse the Linked List
struct Node *temp = *head;
// traverse till the nth node
while (--n)
temp = temp->next;
// assigning (n+1)th node's previous to this new node
(temp->next)->prev = newNode;
// newNode's next assigned to (n+1)th node
// newNode's previous assigned to nth node
newNode->next = temp->next;
newNode->prev = temp;
// assign nth node's next to newNode
temp->next = newNode;
}
}
//function to print the doubly linked list
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end = NULL;
printf ("List in Forward direction: ");
while (node != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\nList in backward direction: ");
while (end != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", end->data);
end = end->prev;
}
}
// required for insertAfter
int getLength (struct Node *node)
{
int len = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
insertStart (&head, 20);
insertStart (&head, 0);
insertLast (&head, 40);
insertLast (&head, 60);
insertLast (&head, 80);
// 500 to be entered after 3rd node
insertPosition (&head, 3, 500);
// & not required to be passed as head will not change
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
List in Forward direction: 0 20 40 500 60 80 List in backward direction: 80 60 500 40 20 0
Code For Deletion in Doubly Linked List
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
int getLength (struct Node *node);
void insert (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
newNode->prev = NULL;
// If the linked list already had atleast 1 node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// newNode will become head
*head = newNode;
}
void deleteStart (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
// if DLL is empty
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete\n\n");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (temp->next == NULL)
{
printf ("%d deleted\n\n", temp->data);
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
// assign head node's previous to NULL
(*head)->prev = NULL;
printf ("%d deleted\n\n", temp->data);
free (temp);
}
void deleteLast (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
// if DLL is empty
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete\n\n");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (temp->next == NULL)
{
printf ("%d deleted\n\n", temp->data);
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// else traverse to the last node
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
struct Node *secondLast = temp->prev;
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to Null
secondLast->next = NULL;
printf ("%d deleted\n\n", temp->data);
free (temp);
}
void deleteNthNode (struct Node **head, int n)
{
//if the head node itself needs to be deleted
int len = getLength (*head);
// not valid
if (n < 1 || n > len)
{
printf ("Enter valid position\n\n");
return;
}
// delete the first node
if (n == 1)
{
deleteStart (head);
return;
}
if (n == len)
{
deleteLast (head);
return;
}
struct Node *temp = *head;
// traverse to the nth node
while (--n)
{
temp = temp->next;
}
struct Node *previousNode = temp->prev; // (n-1)th node
struct Node *nextNode = temp->next; // (n+1)th node
// assigning (n-1)th node's next pointer to (n+1)th node
previousNode->next = temp->next;
// assigning (n+1)th node's previous pointer to (n-1)th node
nextNode->prev = temp->prev;
// deleting nth node
printf ("%d deleted \n\n", temp->data);
free (temp);
}
// required for deleteNthNode
int getLength (struct Node *node)
{
int len = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
//function to print the doubly linked list
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end = NULL;
printf("Linked List:");
while (node != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n\n");
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
insert (&head, 1);
insert (&head, 5);
insert (&head, 10);
insert (&head, 15);
insert (&head, 20);
insert (&head, 25);
printf ("Linked List Before Deletion");
display (head);
printf ("Linked List After Deletion From Beginning\n\n");
deleteStart (&head);
display (head);
printf ("Linked List After Deletion From Last\n\n");
deleteLast (&head);
display (head);
// delete 3rd node
printf ("Linked List After Deletion From 3rd Position\n\n");
deleteNthNode (&head, 3);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List Before DeletionLinked List: 25 20 15 10 5 1 Linked List After Deletion From Beginning 25 deleted Linked List: 20 15 10 5 1 Linked List After Deletion From Last 1 deleted Linked List: 20 15 10 5 Linked List After Deletion From 3rd Position 10 deleted Linked List: 20 15 5



Login/Signup to comment