Construct Tree From Given Inorder and Preorder traversals in C
Construct Tree From Given Inorder and Preorder Traversals
There are three types of traversals in a tree: Inorder, Preorder and Postorder traversal. A tree can be formed with any two tree traversals in which one of them being the in order traversal.
Preorder Traversal: We first print the node, then move to the left subtree and the right subtree.
Inorder Traversal: We first move to the left subtree, then print the node and move to the right subtree.

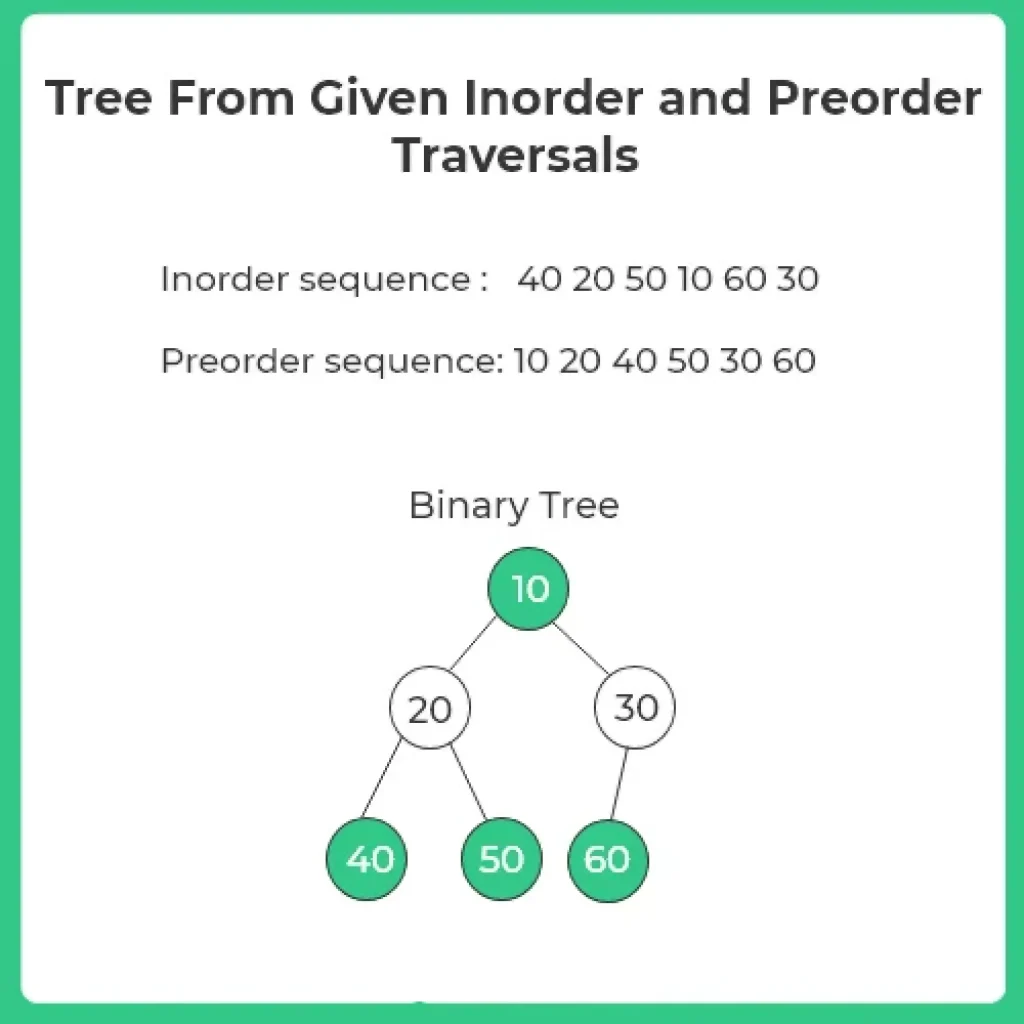
Tree From Given Inorder and Preorder Traversel
Algorithm :
- Pick an element from Preorder. Increment a Preorder Index Variable (preIndex in below code) to pick the next element in the next recursive call.
- Create a new tree node tNode with the data as the picked element.
- Find the picked element’s index in Inorder. Let the index be inIndex.
- Call buildTree for elements before inIndex and make the built tree as a left subtree of tNode.
- Call buildTree for elements after inIndex and make the built tree as a right subtree of tNode.
- return tNode.
C Program based on above Algorithm
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node
{
char data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
};
int search (char arr[], int strt, int end, char value);
struct node *newNode (char data);
struct node *buildTree (char in[], char pre[], int inStrt, int inEnd)
{
static int preIndex = 0;
if (inStrt > inEnd)
return NULL;
struct node *tNode = newNode (pre[preIndex++]);
if (inStrt == inEnd)
return tNode;
int inIndex = search (in, inStrt, inEnd, tNode->data);
tNode->left = buildTree (in, pre, inStrt, inIndex - 1);
tNode->right = buildTree (in, pre, inIndex + 1, inEnd);
return tNode;
}
int search (char arr[], int strt, int end, char value)
{
int i;
for (i = strt; i <= end; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
}
}
struct node *newNode (char data)
{
struct node *node = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
void printInorder (struct node *node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
printInorder (node->left);
printf ("%c ", node->data);
printInorder (node->right);
}
int main ()
{
char in[] = { 'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C' };
char pre[] = { 'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F' };
int len = sizeof (in) / sizeof (in[0]);
struct node *root = buildTree (in, pre, 0, len - 1);
printf ("Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is \n");
printInorder (root);
getchar ();
}
Output:
Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is D B E A F C



Login/Signup to comment