Loop control in C
Introduction to loops
While writing a program in C when we need to perform a single task a number of times, then instead of typing the same exact line/s over and over again we can type them inside a loop and they would get executed as many times as we want them to .
You have provided loops in C language. With the help of loops, you can execute the same statement repeatedly. Each type of loop provides a block in which statements are written which you want to execute more than once.

Types of loops:
There are 3 types of loops in C :
- While loop
- Do while loop
- For loop
While loop
In a while we have a condition and as long that condition is being satisfied the loop will keep running.
- while loop is a simple loop, it executes, as long as the condition remains true.
- when the condition is false, this loop gets terminated.
- This loop is used when the number of iteration is not known.
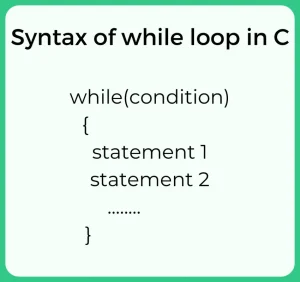
Syntax of while loop
Below is the syntax of while loop in C.
C program using while loop
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a = 1;
while(a<=5) //loop will run as long as a is less than or equal to 5
{
printf("loop ran\n"); //the \n will make the next output to be print in next line
a++; //value of a increases by one
}
}
Output :
loop ran loop ran loop ran loop ran loop ran
Do-While loop
- Do while loop is exactly like while loop the only difference being in do while loop the loop will run the once even if the condition is not satisfied and it checks the condition from the 2nd time and onwards.
- Do while is also known as exit control loop.
Syntax of do while loop
Below is the syntax of do-while loop in C.
C program using do-while loop
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a = 10;
do
{
printf("loop ran\n");//the \n will make the next output to be print in next line
a++; //value of a increases by one
}while(a<=5); //loop will run once an then as long as a is less or equal to 5
}
Output :
loop ran
For loop
- In C loops, for loop is mostly used.
- This loop is very easy and gets define in a single statement.
For loop is like a while loop but in a for loop we tell the loop the new initialization (if any) ,the condition/s and the increment/decrements (after the loop runs) each separated by a semicolon .
Syntax of for loop
Below is the syntax of for loop in C.
C program using for loop
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
for(int a = 1; a <= 5;a++) //loop will run as long as a is less or equal to 5
{
printf("loop ran\n"); // \n will make the next output to be printed in next line
}
}
Output :
loop ran loop ran loop ran loop ran loop ran
Loop control
Sometimes for special reasons we need more control on our loop and these are provided by loop control statements.
Loop control statements are statements that change the execution of the loop according to any condition. These statements are very useful for changing the loop accordingly.
The three types of loop control statements are
break
continue
goto
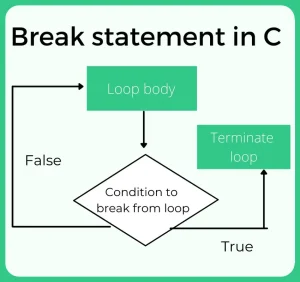
Break
The break statement is used to terminate the loop. When a break statement is executed inside a loop, the loop get terminated at the same time and the execution of next statement begins after that loop.
Syntax
break;
C Program using break statement
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
for(int j=1;i<=5;j++)
{
printf("%d %d \n",i,j); //prints value of i and j in that iteration of the loop
if(j==3 || i==3)
{
break;
}
}
}
}
Output :
1 1 1 2 1 3 2 1 2 2 2 3 3 1 4 1 4 2 4 3 5 1 5 2 5 3
Continue Statement:
It is used to skip remainder part of the loop. Statement written after continue is ignored. For example, if you want the third iteration of the loop to not execute, then you can skip it by writing continue.Syntax
continue;
C Program using continue statement
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
if(i==3)
{
printf("Third iteration skipped\n"); // skipping third iteration using continue statement
continue;
}
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}
Output :
1 2 Third iteration skipped 4 5
Continue Statement:
It is used to skip remainder part of the loop. Statement written after continue is ignored. For example, if you want the third iteration of the loop to not execute, then you can skip it by writing continue.Syntax
continue;
C Program using continue statement
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
if(i==3)
{
printf("Third iteration skipped\n"); // skipping third iteration using continue statement
continue;
}
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}
Output :
1 2 Third iteration skipped 4 5
Goto Statement:
With the goto statement we can go back to a previous step or jump some steps coming up by putting a label followed by a colon and then compiler will start executing the program from there again.
Syntax:
... ... goto label-name ... label-name ... ...
C program using goto
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int age;
lab1:
printf("You are not eligible to vote\n");
printf("Enter your age\n");
scanf("%d",&age);
if(age<18)
goto lab1;
else
printf("You are eligible to vote\n");
}
Input :
16 14 21
Output :
You are not eligible to vote You are not eligible to vote You are not eligible to vote You are eligible to vote
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






In break statement program , a small correction is there
#include
remaining program all are correct except that standard input and output command
sir this code not showing correct output in my compiler
#include
void main()
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
if(i==3)
{
printf(" third iteration skipped"); // skipping third iteration using continue statement
continue;
}
printf("%d",i);
}
}
The actual code is :
#include
void main()
{
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){
for(int j=1;i<=5;j++){
printf("%d %d \n",i,j); //prints value of i and j in that iteration of the
loop
if(j==3 || i==3)
{
break;
}
}
}
}
And then the output is
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 2
2 3
3 1
4 1
4 2
4 3
5 1
5 2
5 3
Whenever the break keyword encounter by compiler and it is inside loop it exits from whole that's y it just stop of 13,23….
#include
void main()
{
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
for(int j=1;i<=5;j++)
printf("%d %d \n",i,j); //prints value of i and j in that iteration of the loop
if(j==3 || i==3)
{
break;
}
}
Plz explain this??
There is a small problem with this code Angel, some brackets are missing
This is the code used to print a matrix!
The actual code is :
#include
void main()
{
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){
for(int j=1;i<=5;j++){
printf("%d %d \n",i,j); //prints value of i and j in that iteration of the
loop
if(j==3 || i==3)
{
break;
}
}
}
}
And then the output is
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 2
2 3
3 1
4 1
4 2
4 3
5 1
5 2
5 3
Whenever the break keyword encounter by compiler and it is inside loop it exits from whole that's y it just stop of 13,23….