Variables in C++
Variables
Here, in this page we will discuss about the variables in C++. A variable is a memory unit that is capable of storing data which can be modified (rewritten) at any point of time in a program. Simply a variable is a name given to a memory location.
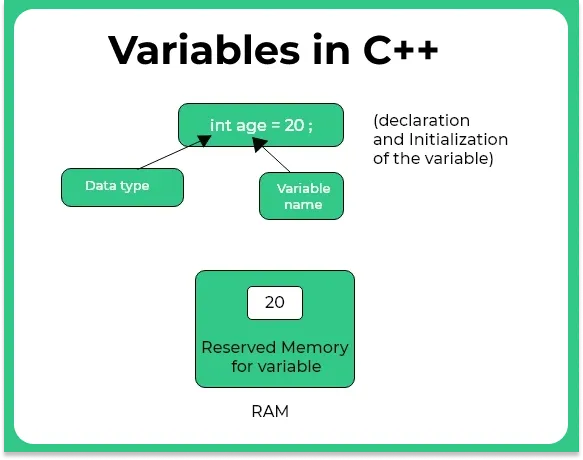
Variable Declaration & Definition
Note
Note - The definition of declaration/definition is given wrong on g4g.
Declaration
Variable declaration is the notification to the program/programmer that a particular type of memory may be required and we plan to call that memory with some name.
- Memory creation (as per specified datatypes) happens at the time of declaration itself.
- But the variables may have garbage values.
- Variables can not be used before declaration
Example
int a,b,c;
Example program to demonstrate variable declaration
Run
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int var; // variable declaration
cout << "Value:" << var << endl; // garbage value
cout << "Address of var: " << &var << endl; // a's assigned address
cout << "Size of var: " << sizeof(var) << " bytes"; // allocated memory in bytes
return 0;
}
Output
Value var: 10 Value: var2: 10.25
Variable Definiton/Initialization
In this stage, the user assigns value as per the requirement within the memory bounds i.e garbage value is overriddenExample
//declaration int a; float b; // definition/initialization later a = 10; b = 78.9;
Example program to demonstrate variable initialization
Run
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int var; //variable declaration
cout << "Value: " << var << endl; // garbage
var = 3; // variable initialization/definition
cout << "var value: " << var << endl;
var = 5 + var; //data overriding
cout << "New var value: " << var << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
Value: 0 var value: 3 New var value: 8
Declaration cum initialization
Variable can be initialized at the time of declaration itselfExample
Run
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// declaration & initialization at same time
int var = 10;
float var2 = 10.25;
cout << "Value var: " << var << endl;
cout << "Value: var2: " << var2 << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
Value var: 10 Value: var2: 10.25
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment