Implementation of Priority Queue using Linked List in C
Implementation of Priority Queue using Linked List
In this post, we will learn to implement Priority Queue using Linked List It has the following methods –- Push()
- Pop()
- Peek()

Priority Queue using Linked List in C
Operations
- Push: Pushing/inserting a new item in the priority queue at a position in accordance with its priority
- Pop: Popping/removing a new item in the priority queue in accordance with its priority
- Peek: Displaying the topmost priority item of the queue
Note
A lower priority number for an item means higher priority.
Example: (item1, 2) and (item2, 5). Here is item one is higher priority as it has lower priority number,
Example: (item1, 2) and (item2, 5). Here is item one is higher priority as it has lower priority number,
Syntax for Priority Queue as Linked List
struct Node
{
int data;
int priority; // lower value means higher priority
struct Node* next;
};Advantage of implementing Priority Queue as Linked List over Array
- Implementation of priority Queue data by using a linked list is more efficient as compared to arrays.
- The linked list provides you with the facility of Dynamic memory allocation.
- The memory is not wasted as memory, not in use can be freed, using free(); method
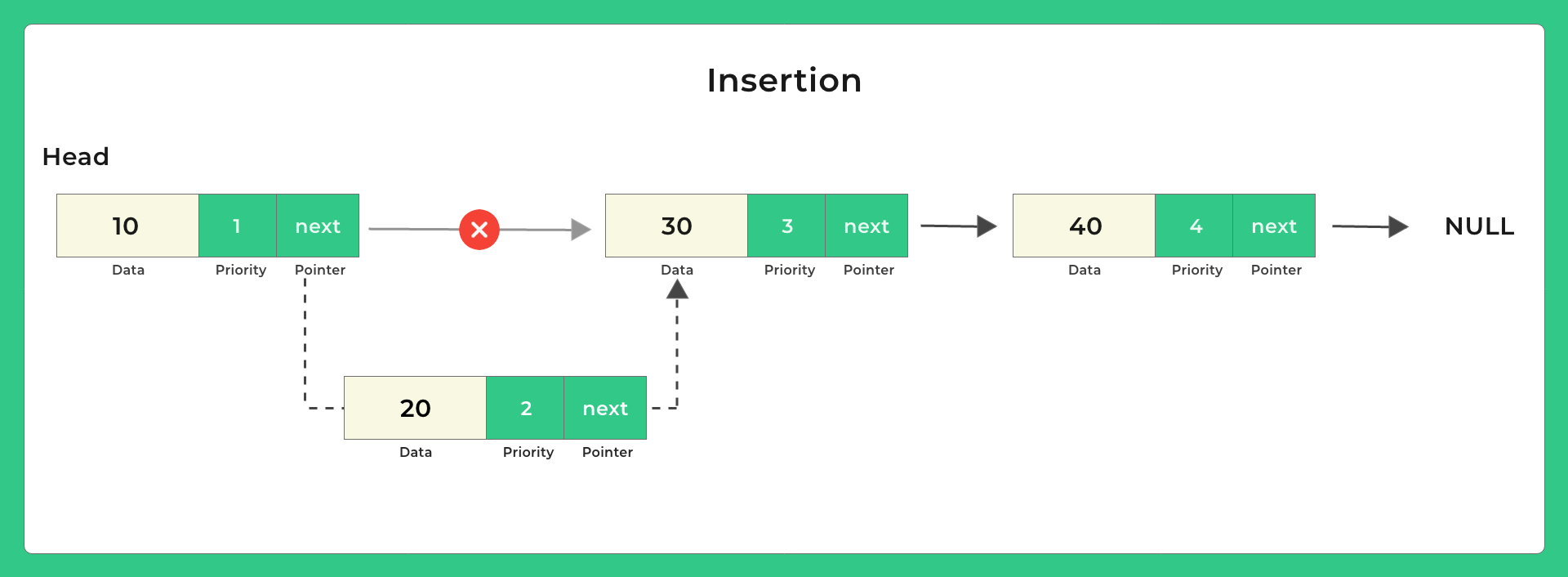
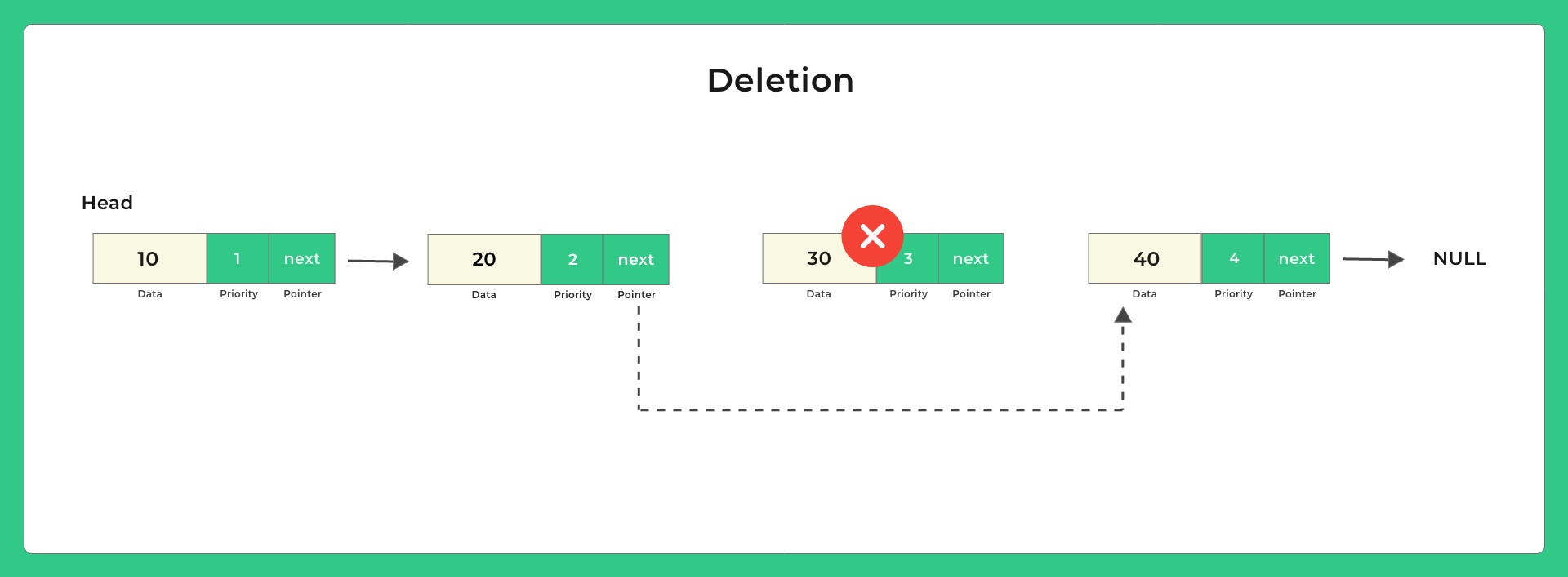
C Program to Implement Priority Queue using Linked list
Code in C
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
int priority; // lower value means higher priority
struct Node* next;
};
// Function to Create A New Node
struct Node* create(int data, int priorityVal)
{
struct Node* temp = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = data;
temp->priority = priorityVal;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Return the value at head
int peek(struct Node** head)
{
return (*head)->data;
}
// Function to push in accodance with priority
void push(struct Node** head, int data, int priorityVal)
{
struct Node* curr = (*head);
// Create new Node
struct Node* temp = create(data, priorityVal);
// If incoming node has lower priority value
// than the current head. This incoming node
// is inserted before head
// Note: Lower priority value means higher priority
if ((*head)->priority > priorityVal) {
// new node inserted before head
temp->next = *head;
(*head) = temp;
}
else {
// else we traverse the list to find
// correct position to insert the incoming node
while (curr->next != NULL &&
curr->next->priority < priorityVal) { curr = curr->next;
}
// incoming node inserted here
// either at req. position or end of the list
temp->next = curr->next;
curr->next = temp;
}
}
// Here we remove the element with highest priotity
// highest priority will be at the head itself
void pop(struct Node** head)
{
struct Node* temp = *head;
(*head) = (*head)->next;
printf("(%d, priority: %d) popped\n",temp->data,temp->priority);
free(temp);
}
// Function to check is list is empty
int isEmpty(struct Node** node)
{
return (*node) == NULL;
}
void display(struct Node* node){
printf("Priority Queue: ");
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ",node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
struct Node* pq = create(10, 1);
push(&pq, 30, 3);
push(&pq, 20, 2);
push(&pq, 40, 4);
display(pq);
pop(&pq);
pop(&pq);
display(pq);
push(&pq, 15, 2);
// if two items have same priority then
// they are served in their order of entry
push(&pq, 20, 2);
push(&pq, 50, 5);
push(&pq, 5, 1);
display(pq);
return 0;
}
Output
Priority Queue: 10 20 30 40 (10, priority: 1) popped (20, priority: 2) popped Priority Queue: 30 40 Priority Queue: 5 15 20 30 40 50



Login/Signup to comment