C Program for Deletion from end in doubly linked list
Deletion from end in doubly linked list
Today we will study in C Program for Deletion from end in doubly linked list . In doubly linked we have three field which contain previous pointer ,node having data and next pointer which have the address of next node.The advantage of doubly linked list is that the traversal of nodes is easy because having two pointer in the one node.

Working require for deletion in doubly linked list at the last node :-
- First to delete the last node from the list we have to start moving on the list from the first node until the address part of the node is null.
- After that we will keep going of the second last node in some extra node that is previous node.
- As the address part of the node is null then set the address part of the previous node as null.
- At last free the last node.
The Structure of the Node in the Doubly Linked List :-
struct node
{
struct node *prev;
int data;
struct node *next;
}
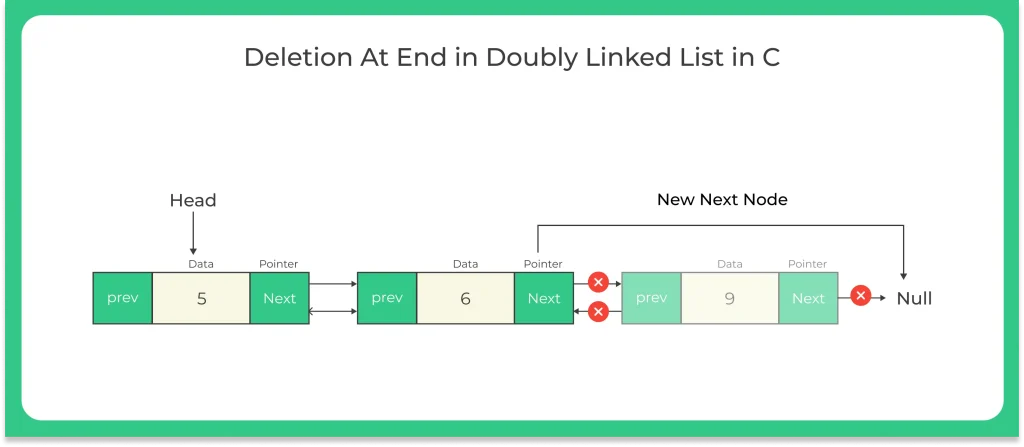
Algorithm for doubly linked list to delete an element from the end :-
- STEP 1 : NOW IF HEAD = NULL (GO TO STEP 6)
- STEP 2 : ASSIGN EXTRA = HEAD
- STEP 3 : MAKE A LOOP WHILE EXTRA = NEXT != NULL
- STEP 4 : ASSIGN EXTRA = EXTRA -> NEXT (END THE WHILE LOOP)
- STEP 5 : THAN ASSIGN EXTRA -> PREVIOUS -> NEXT = NULL
- STEP 6 : THAN FREE EXTRA
- STEP 7 : EXIT
Code for Deletion From End in a Doubly Linked List
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
void insert (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *freshNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
freshNode->data = data;
freshNode->next = *head;
freshNode->prev = NULL;
// If the linked list already had atleast 1 node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = freshNode;
// freshNode will become head
*head = freshNode;
}
void deleteEnd (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *tempNode = *head;
// if DLL is empty
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete\n\n");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (tempNode->next == NULL)
{
printf ("%d deleted\n\n", tempNode->data);
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// else traverse to the last node
while (tempNode->next != NULL)
tempNode = tempNode->next;
struct Node *secondLast = tempNode->prev;
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to Null
secondLast->next = NULL;
printf ("%d deleted\n\n", tempNode->data);
free (tempNode);
}
//function to print the doubly linked list
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end = NULL;
while (node != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n\n");
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
insert (&head, 7);
insert (&head, 8);
insert (&head, 9);
insert (&head, 10);
insert (&head, 11);
insert (&head, 12);
printf("Linked List Before Deletion");
display (head);
deleteEnd (&head);
printf("Linked List After Deletion");
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List Before Deletion 12 11 10 9 8 7 7 deleted Linked List After Deletion 12 11 10 9 8



Login/Signup to comment