C++ Program for Consecutive Prime Sum (TCS Codevita) | PrepInsta
Consecutive Prime Sum Problem
TCS CodeVita is one of the most prestigious coding competition that is held on a global platform by TCS in the search of world’s best coder. It is being conducted from last 8 years now. Consecutive prime sum is one of the sample problem for TCS CodeVita season 9 edition. Here we have provided a C++ solution for Consecutive Prime Sum problem
Problem Description
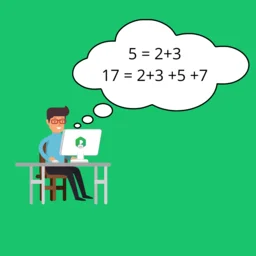
Question – : Some prime numbers can be expressed as a sum of other consecutive prime numbers.
- For example
- 5 = 2 + 3,
- 17 = 2 + 3 + 5 + 7,
- 41 = 2 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 11 + 13.
Your task is to find out how many prime numbers which satisfy this property are present in the range 3 to N subject to a constraint that summation should always start with number 2.
Write code to find out the number of prime numbers that satisfy the above-mentioned property in a given range.
Input Format: First line contains a number N
Output Format: Print the total number of all such prime numbers which are less than or equal to N.
Constraints: 2<N<=12,000,000,000
| S.no | Input | Output | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 2 | (Below 20 there are two such members; 5 and 17) 5=2+3 17=2+3+65+7 |
| 2 | 15 | 1 |
Cpp Code for Consecutive Prime Sum Problem
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int prime(int b) { int j,cnt; cnt=1; for(j=2;j<=b/2;j++) { if(b%j==0) cnt=0; } if(cnt==0) return 1; else return 0; } int main() { int i,j,n,cnt,a[25],c,sum=0,count=0,k=0; cout<<"Enter a number : "; cin>>n; for(i=2;i<=n;i++) { cnt=1; for(j=2;j<=n/2;j++) { if(i%j==0) cnt=0; } if(cnt==1) { a[k]=i; k++; } } for(i=0;i<k;i++) { sum=sum+a[i]; c= prime(sum); if(c==1) count++; } cout<<count; return 0; }
Output Enter a number : 5 1
Consecutive Prime Sum Problem in Other Coding Languages
C
To find the solution of Consecutive Prime sum problem in C Programming language click on the button below:
Java
To find the solution of Consecutive Prime sum problem in Java Programming language click on the button below:
Python
To find the solution of Consecutive Prime sum problem in Python Programming language click on the button below:
Login/Signup to comment



#include
#include
using namespace std;
bool isPrime(int n)
{
for (int j = 2; j <= (n / 2); j++)
if ((n % j) == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
void solution(int N)
{
int prmTotal = 2;
int j = 3;
vector arr;
while (prmTotal <= N)
{
if (isPrime(j))
{
prmTotal += j;
arr.push_back((prmTotal + j));
}
j++;
}
j = 0;
while (j N)
break;
j++;
}
cout << j <> N;
solution(N);
return 0;
}
This will be the simplest and easier solution for this problem © Avishkar
#include
#include
using namespace std;
bool isprime(int num)
{
for (int i = 2; i > n;
for (int i = 2; i 3 && sum < n))
count++;
}
}
cout << count;
}
solved with help of set and vector
first find prime numbers upto n and store it in vector
second – make a loop for elements of vector which contains prime numbers
third – make a variable sum and store it in set
and check with the help of if statement
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
set s;
int sum = 0;
int ans = 0;
vector vec;
vec.emplace_back(2);
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){
int count=0;
for(int j=2;j<i;j++){
if(i%j==0){
count++;
break;
}
}
if(count==0){
vec.emplace_back(i);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<vec.size();i++){
sum += vec[i];
if(s.find(vec[i])!=s.end()){
ans++;
}
s.emplace(sum);
}
cout<<ans;
}
We can solve this problem using Sieve of Eratosthenes… here is my solution in c++
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int N;
cin>>N;
bool primeArray[N] = {0};
for(int i=2;i<N;i++){
if(primeArray[i]==0){
for(int j=i*i;j<N;j+=i){
primeArray[j] = 1;
}
}
}
primeArray[0] = 1;
primeArray[1] = 1;
int sum = 0;
vector vi;
/*for(int i=2;i<N;i++){
if(primeArray[i]==0 && sum<=N){
sum += i;
if(primeArray[sum]==0 && sum <= N){
vi.push_back(sum);
}
}
}*/ // same loop using while loop
int i=2;
while(i<N){
if(primeArray[i]==0){
sum += i;
if(primeArray[sum]==0 && sum<=N && sum!=2){
vi.push_back(sum);
}
}
i++;
}
cout<<"Size is : ";
cout<<vi.size()<<"\n"; // this is the answer
for(int j=0;j<vi.size();j++){ // this will print all that number
cout<<vi[j]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
Time Complexity = O(N Log N)
Space Complexity = O(N)
#include
using namespace std;
int prime(int p)
{
int count=0;
for(int j=2;j>n;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
s=prime(i);
if(s==0)
{
//cout<<i<<" ";
sum=sum+i;
//cout<<sum<2 && sum<n)
{
//cout<<sum<<" ";
k++;
}
}
}
cout<<k;
return 0;
}
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector p;
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
bool prime=true;
for(int j=2;j<i;j++)
{
if(i%j==0)
{
prime=false;
break;
}
else
prime=true;
}
if(prime==true)
p.push_back(i);
}
int count=0;
for(int i=2;i<p.size();i++)
{
int sum=0;
for(int j=0;jp.at(i))
break;
}
}
cout<<count;
}
Hey Omkar, thank you for contributing this code, but it has some error in it
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int num,count=0;
cin>>num;
for(int i=2;i<=num/2;i++){
int sec=num-i,flag=1,flag1=1;
for(int k=2;k<=i/2;k++){
if(i%k==0){
flag=0;
}
}
if(flag==1){
for(int j=2;j<=sec/2;j++){
if(sec%j==0){
flag=0;
}
}
}
if(flag==1 && flag1==1){
++count;
}
}
cout<<count;
}
wrong solution
Yes Manish, we are fixing it, if you have the correct answer for this problem, you can submit your answer in the comment section only, and we’ll post it on our page