Java Primitive Data Type

What is Java Primitive Data Type?
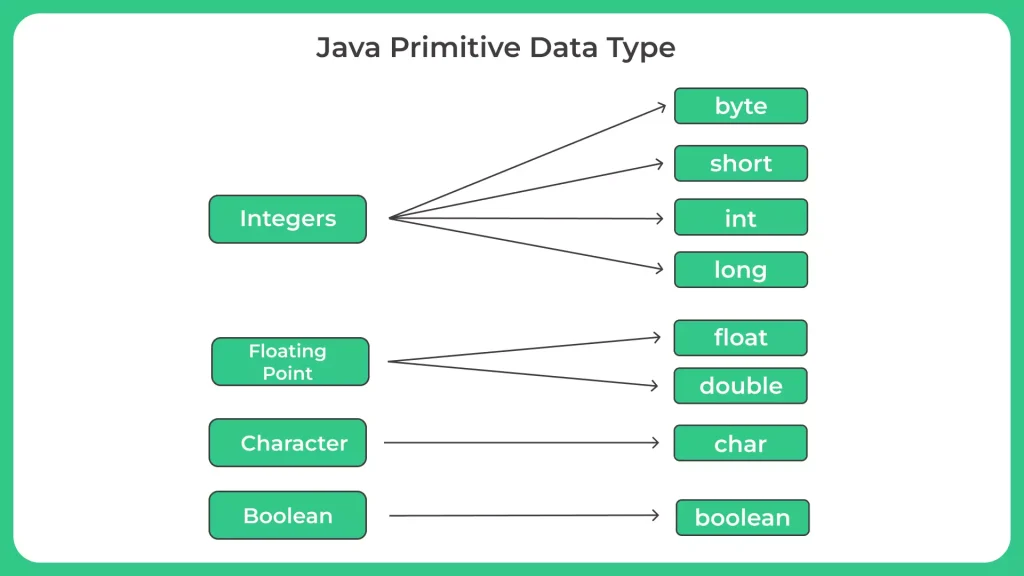
Java primitive data type are the basic data types that are built-in to the Java programming language. There are eight primitive data types in Java, including byte, short, int, long, float, double, char, and boolean.
These data types are used to store simple values, such as numbers and characters, and are not objects.
To understand the more about Java Primitive Data Type, Read the Complete Article.
How many Primitive Data Type In Java ?
- There are eight primitive data types in Java:
- byte: The byte data type is an 8-bit signed two’s complement integer, with a minimum value of -128 and a maximum value of 127. It is used when you need to store small integers.
- short: The short data type is a 16-bit signed two’s complement integer, with a minimum value of -32,768 and a maximum value of 32,767. It is used when you need to store integers that are larger than bytes but smaller than integers.
- int: The int data type is a 32-bit signed two’s complement integer, with a minimum value of -2^31 and a maximum value of 2^31-1. It is used when you need to store integers that are larger than shorts.
- long: The long data type is a 64-bit signed two’s complement integer, with a minimum value of -2^63 and a maximum value of 2^63-1. It is used when you need to store integers that are larger than ints.
- float: The float data type is a single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating-point, which is used when you need to store decimal values with a relatively low precision.
- double: The double data type is a double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating-point, which is used when you need to store decimal values with high precision.
- boolean: The boolean data type represents a single bit of information and can only have two possible values: true or false. It is used when you need to store a binary value.
- char: The char data type is a 16-bit Unicode character, which can represent any character from the Unicode character set. It is used when you need to store characters such as letters, digits, and symbols.
Points To Remember for Primitive Data Type:
byte - 8-bit signed two's complement integer (-128 to 127)
short - 16-bit signed two's complement integer (-32,768 to 32,767)
int - 32-bit signed two's complement integer (-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647)
Long- 64-bit signed two's complement integer (-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807)
float - 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point number
double - 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point number
char - 16-bit Unicode character (0 to 65,535)
boolean - true or false
Some important notes about each of the Java primitive data types:
byte and short
The byte data type is mainly used to save memory in large arrays.
It can also be used in place of int data type for improving code performance in some cases.
The short data type is mainly used to save memory in large arrays.
It can also be used in place of int data type for improving code performance in some cases.
int and long
The int data type is the most commonly used data type for representing integers.
It is generally used for loop counters, array indexes, and other integer-based calculations.
The long data type is used to represent larger integer values than what int can represent.
To indicate that a literal value is a long, append an "L" to the end of the value.
float & double
The float data type is used to represent decimal values with a low level of precision.
To indicate that a literal value is a float, append an "f" to the end of the value.
The double data type is used to represent decimal values with a high level of precision.
It is the default choice for representing decimal values.
boolean and char
The boolean data type is used to represent logical values.
It can only take on the values true or false.
The char data type is used to represent a single character.
It can represent any Unicode character, including letters, digits, and symbols.
To represent a char value, use single quotes ('') around the character.
Difference between primitive and non primitive data types in Java?
- The main differences between primitive and non-primitive data types in Java are as follows:
- Memory allocation: Primitive data types are stored in the stack memory, while non-primitive data types are stored in the heap memory.
- Initialization: Primitive data types are automatically initialized with default values when they are declared, while non-primitive data types must be initialized explicitly.
- Default values: Primitive data types have default values, which are zero or false for numeric and boolean types, respectively, while non-primitive data types have a default value of null.
- Size: Primitive data types have a fixed size, which depends on the type, while non-primitive data types can have varying sizes, depending on the data they are storing.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment