Java LinkedHashSet

What is Java LinkedHashSet?
- Java LinkedHashSet is a class in the Java Collection Framework that extends the HashSet class and implements the Set interface.
- It is an ordered version of HashSet, which means it maintains the insertion order of elements. It also allows null elements. The LinkedHashSet internally uses a Hash table and a linked list to maintain the order of elements.
- To Understand Java LinkedHashSet, Read the Complete Article.
Create a LinkedHashSet:
- Import the java.util.LinkedHashSet package:
- Before creating a LinkedHashSet, you need to import the java.util.LinkedHashSet package using the import statement.
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
- Create a LinkedHashSet object:
- To create a new LinkedHashSet, you need to create an instance of the LinkedHashSet class using the new keyword.
- You can specify the type of elements that the set will hold in angle brackets (<>). For example, the following code creates a new LinkedHashSet to hold String objects:
LinkedHashSet set = new LinkedHashSet<>();
- Add elements to the LinkedHashSet:
- Once you have created a LinkedHashSet, you can add elements to it using the add() method.
- For example, the following code adds three String objects to the set:
set.add("apple");
set.add("banana");
set.add("orange");
- Access elements in the LinkedHashSet:
- You can access the elements of a LinkedHashSet using an enhanced for loop or the iterator() method.
- For example, the following code prints out the contents of the set:
for (String element : set) {
System.out.println(element);
} - Remove elements from the LinkedHashSet:
- To remove an element from a LinkedHashSet, you can use the remove() method.
- For example, the following code removes the orange from the set:
set.remove("orange");
- Check the size of the LinkedHashSet:
- To check the number of elements in a LinkedHashSet, you can use the size() method.
- For example, the following code prints the size of the set:
System.out.println("Set size: " + set.size());
Some important features of LinkedHashSet are:
It does not allow duplicate elements.
It allows null elements.
It maintains the order of insertion.
It implements the Set interface, so it has all the methods of the Set interface.
It is not synchronized, so it is not thread-safe.
It has a constructor that takes an initial capacity and load factor as parameters.
Methods of LinkedHashSet
Here is a table of some other commonly used methods of LinkedHashSet in Java:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| clear() | Removes all of the elements from the set. |
| contains(Object o) | Returns true if the set contains the specified element. |
| isEmpty() | Returns true if the set contains no elements. |
| iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in the set in the order they were inserted. |
| remove(Object o) | Removes the specified element from the set. Returns true if the set contained the specified element. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of the set. |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in the set in the order they were inserted. |
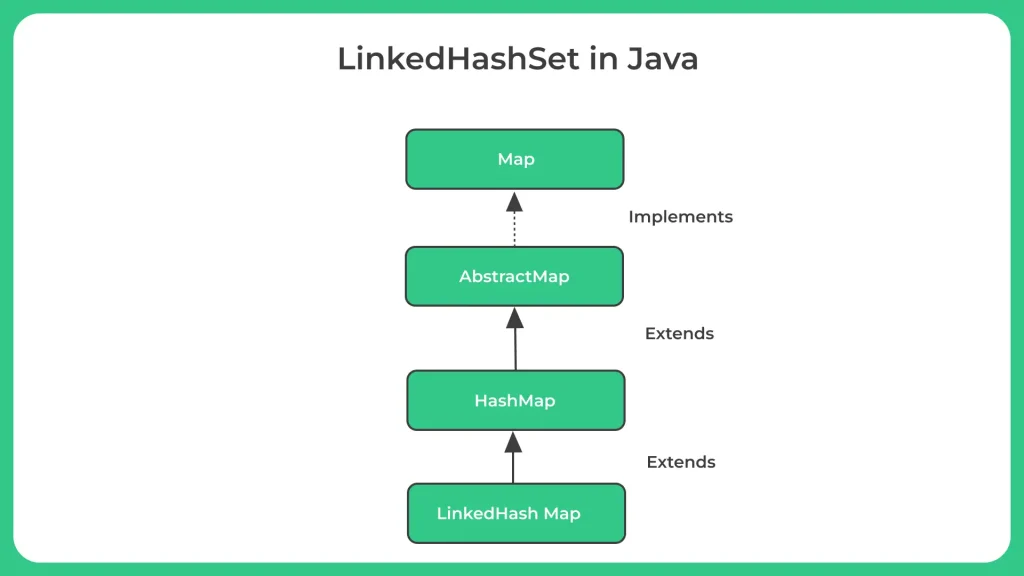
Let’s look at the Java LinkedHashSet to perform certain operations.
Example 1:Java program to Insert Elements to LinkedHashSet.
Run
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
// Create a LinkedHashSet of Strings
LinkedHashSet < String > linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet < String > ();
// Add individual elements to the LinkedHashSet using add() method
linkedHashSet.add ("apple");
linkedHashSet.add ("banana");
linkedHashSet.add ("orange");
// Display the elements of the LinkedHashSet
System.out.println ("LinkedHashSet elements after adding individually: " +
linkedHashSet);
// Create an array of Strings
String[] fruits =
{
"pear", "grape", "kiwi"};
// Add all elements of the array to the LinkedHashSet using addAll() method
linkedHashSet.addAll (Arrays.asList (fruits));
// Display the elements of the LinkedHashSet
System.out.println
("LinkedHashSet elements after adding all elements of an array: " +
linkedHashSet);
}
}
Output
LinkedHashSet elements after adding individually: [apple, banana, orange] LinkedHashSet elements after adding all elements of an array: [apple, banana, orange, pear, grape, kiwi]
Explanation:
In this program, we first create an empty LinkedHashSet of Strings called linkedHashSet.
Then,
we use the add() method to add individual elements "apple", "banana", and "orange" to the linkedHashSet. We print the elements of the linkedHashSet using System.out.println().
Next,
we create an array of Strings called fruits containing the elements "pear", "grape", and "kiwi". We add all the elements of the fruits array to the linkedHashSet using the addAll() method along with Arrays.asList(fruits) method to convert array to List.
We print the updated elements of the linkedHashSet again using System.out.println().
Example 2 : Java program to Access LinkedHashSet Elements
Run
//AccessLinkedHashSetElementsExample
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
public class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
// Create a LinkedHashSet of Strings
LinkedHashSet < String > linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet < String > ();
// Add some elements to the LinkedHashSet
linkedHashSet.add ("apple");
linkedHashSet.add ("banana");
linkedHashSet.add ("orange");
// Display the elements of the LinkedHashSet using for-each loop
System.out.println ("Elements of LinkedHashSet:");
for (String fruit:linkedHashSet)
{
System.out.println (fruit);
}
// Check if an element exists in the LinkedHashSet
boolean containsOrange = linkedHashSet.contains ("orange");
System.out.println ("LinkedHashSet contains 'orange': " + containsOrange);
// Get the size of the LinkedHashSet
int size = linkedHashSet.size ();
System.out.println ("Size of LinkedHashSet: " + size);
}
}
Output
Elements of LinkedHashSet: apple banana orange LinkedHashSet contains 'orange': true Size of LinkedHashSet: 3
Explanation:
In this program, we first create an empty LinkedHashSet of Strings called linkedHashSet.
Then, we use the add() method to add three elements "apple", "banana", and "orange" to the linkedHashSet.
Next, we display the elements of the linkedHashSet using a for-each loop.
We iterate over each element of the linkedHashSet and print it using System.out.println().
After that, we check if the linkedHashSet contains the element "orange" using the contains() method. .
Example 3 : Java program to Remove Elements from HashSet
Run
//RemoveElementsFromHashSet
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a HashSet of Strings
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
// Add some elements to the HashSet
hashSet.add("apple");
hashSet.add("banana");
hashSet.add("orange");
// Display the elements of the HashSet before removing any element
System.out.println("HashSet elements before removing any element: " + hashSet);
// Remove an element from the HashSet using remove() method
hashSet.remove("banana");
// Display the elements of the HashSet after removing an element
System.out.println("HashSet elements after removing an element: " + hashSet);
// Remove all elements from the HashSet using clear() method
hashSet.clear();
// Display the elements of the HashSet after removing all elements
System.out.println("HashSet elements after removing all elements: " + hashSet);
}
}
Output
HashSet elements before removing any element: [banana, orange, apple] HashSet elements after removing an element: [orange, apple] HashSet elements after removing all elements: []
Explanation:
In this program, we first create an empty HashSet of Strings called hashSet. Then, we use the add() method to add three elements "apple", "banana", and "orange" to the hashSet.
Next, we display the elements of the hashSet using System.out.println().
After that, we remove an element "banana" from the hashSet using the remove() method. We print the updated elements of the hashSet using System.out.println().
Finally, we remove all the elements from the hashSet using the clear() method. We print the updated elements of the hashSet again using System.out.println().
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment