Java Map Interface

What is Java Map Interface?
- The Java Map interface is a part of the Java Collections Framework, which provides a way to store and manipulate groups of objects.
- A Map is an object that maps keys to values, where each key is unique.
- The Map interface provides methods for adding, removing, and accessing elements by their key.
- To understand the Java Map Interface, Read the Complete Article.
How to use Map?:
To use a Map in Java, you need to follow these basic steps:
- Import the Map class and the specific Map implementation that you want to use, such as HashMap or TreeMap.
- Create a new instance of the Map implementation using the constructor.
- Use the put() method to add key-value pairs to the map. The key is used to retrieve the associated value later.
- Use the get() method to retrieve values from the map using the key.
- Use the remove() method to remove key-value pairs from the map.
- Use the keySet(), values(), or entrySet() methods to get a Set, Collection, or Set of Map.Entry objects, respectively, that you can then iterate over to access all key-value pairs in the map.
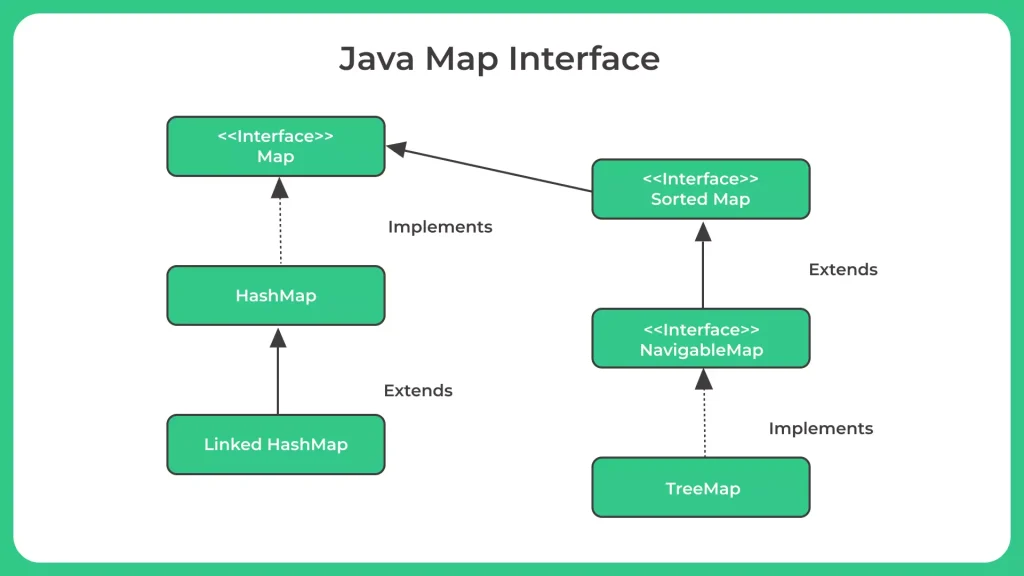
Classes that implement Map :
- There are several classes in Java that implement the Map interface. Some of the most commonly used ones are:
- HashMap - This class provides a fast, constant-time performance for basic operations (put, get, remove) on average. It uses a hash table to store key-value pairs, and provides no ordering guarantees for the keys.
- TreeMap - This class provides a sorted map implementation based on a red-black tree data structure. It provides ordered traversal of the keys, but with a slower performance than HashMap.
- LinkedHashMap - This class provides a combination of the features of both HashMap and TreeMap. It maintains a linked list of the entries in the order they were inserted, providing insertion-ordered iteration.
- WeakHashMap - This class provides a variant of HashMap that uses weak references for the keys. This means that if a key has no other references in the program, it can be garbage-collected, and the associated value will be removed from the map automatically.
- EnumMap - This class provides an implementation of Map specifically designed for use with enum types. It is highly efficient and provides constant-time performance for basic operations.
- IdentityHashMap- This class provides an implementation of Map that compares keys by reference equality instead of object equality. This means that two keys with the same object content but different object references will be treated as distinct.
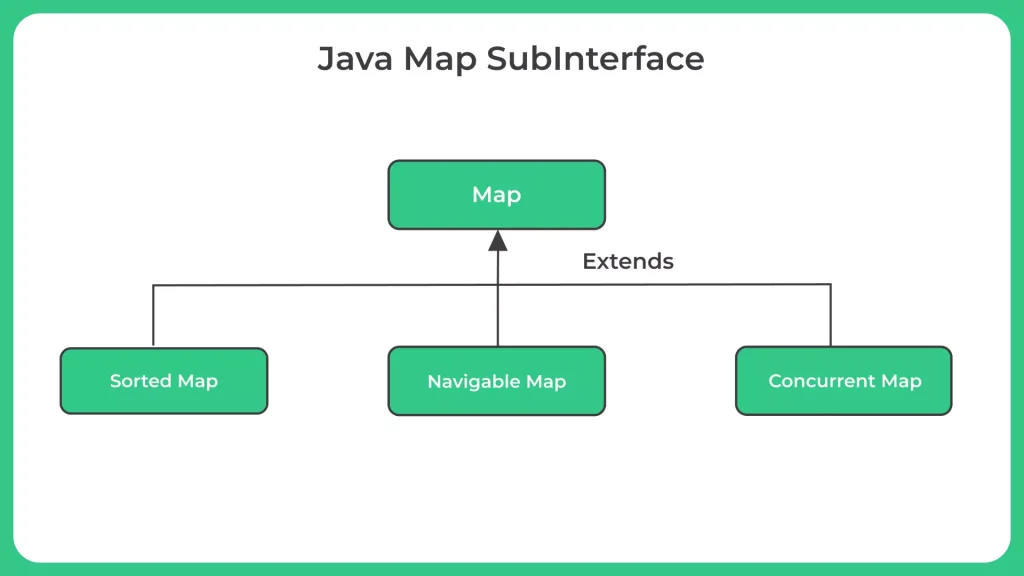
Interfaces that extend Map:
- There are two interfaces in Java that extend the Map interface:
- SortedMap - This interface extends the Map interface and provides a sorted map of key-value pairs. It adds methods for retrieving the first and last keys in the map, and for getting a submap of keys that fall within a specified range. The TreeMap class implements this interface.
- NavigableMap- This interface extends the SortedMap interface and provides additional navigation methods for finding keys that are greater than or less than a specified key. It also provides methods for finding the closest matching key, and for iterating over the keys in reverse order. The TreeMap class also implements this interface.
- Both SortedMap and NavigableMap provide sorted and navigable key-value pairs, with the latter providing additional functionality for navigating the map in various ways. These interfaces can be useful for applications that require the use of ordered data or need to search for keys based on specific criteria.
Methods in the Map interface:
- Some of the most commonly used methods in the Map interface are:
- put(key, value) – Adds a key-value pair to the map.
- get(key) – Returns the value associated with the given key, or null if the key is not found.
- remove(key) – Removes the key-value pair associated with the given key.
- containsKey(key) – Returns true if the map contains the given key, otherwise false.
- containsValue(value) – Returns true if the map contains the given value, otherwise false.
- size() – Returns the number of key-value pairs in the map.
Let’s look at the Implementation of the Map Interface to perform certain operations.
Example 1: Implementation of the Map Interface using HashMap Class
Run
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
// create a new HashMap instance
Map < String, Integer > myMap = new HashMap <> ();
// add key-value pairs to the map
myMap.put ("Ashish", 25);
myMap.put ("Ayush", 30);
myMap.put ("Rishi", 42);
// get the value associated with a key
int johnAge = myMap.get ("Ashish");
System.out.println ("Ashish's age is " + johnAge);
// remove a key-value pair from the map
myMap.remove ("Ayush");
// print the size of the map
System.out.println ("Size of the map: " + myMap.size ());
// iterate over the key-value pairs in the map
for (Map.Entry < String, Integer > entry:myMap.entrySet ())
{
String name = entry.getKey ();
int age = entry.getValue ();
System.out.println (name + " is " + age + " years old.");
}
}
}
Output
Ashish's age is 25 Size of the map: 2 Ashish is 25 years old. Rishi is 42 years old.
Explanation:
In this program, we create a new HashMap instance with key type String and value type Integer. We add three key-value pairs to the map using the put() method.
We then retrieve the value associated with the key Ashish" using the get() method and print it to the console. We remove the key-value pair with the key "Ayush" using the remove() method.
We then print the size of the map using the size() method. Finally, we iterate over all the key-value pairs in the map using a for-each loop and print them to the console.
Example 2 : Implementation of the Map Interface using Tree Map Class
Run
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
// create a new TreeMap instance
Map < String, Integer > myMap = new TreeMap <> ();
// add key-value pairs to the map
myMap.put ("Ayush", 25);
myMap.put ("Ashley", 30);
myMap.put ("Bob", 42);
// get the value associated with a key
int AyushAge = myMap.get ("Ayush");
System.out.println ("Ayush's age is " + AyushAge);
// remove a key-value pair from the map
myMap.remove ("Ashley");
// print the size of the map
System.out.println ("Size of the map: " + myMap.size ());
// iterate over the key-value pairs in the map
for (Map.Entry < String, Integer > entry:myMap.entrySet ())
{
String name = entry.getKey ();
int age = entry.getValue ();
System.out.println (name + " is " + age + " years old.");
}
}
}
Output
Ayush's age is 25 Size of the map: 2 Ayush is 25 years old. Bob is 42 years old.
Explanation:
In this program, we create a new TreeMap instance with key type String and value type Integer. We add three key-value pairs to the map using the put() method.
We then retrieve the value associated with the key "Ayush" using the get() method and print it to the console. We remove the key-value pair with the key "Ashish" using the remove() method. We then print the size of the map using the size() method.
Finally, we iterate over all the key-value pairs in the map using a for-each loop and print them to the console.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment