Java LinkedHashMap

What is Java LinkedHashMap?
- Java LinkedHashMap is a class in the Java Collection Framework that extends the functionality of HashMap. It is an implementation of the Map interface that maintains the insertion order of the elements.
- Like HashMap, LinkedHashMap uses key-value pairs to store data and provides constant-time performance for the basic operations like adding, removing, and accessing elements. It also allows null keys and values.
- LinkedHashMap maintains a doubly-linked list of the entries in the map, which ensures that the iteration order is predictable and consistent.
- To understand the Java LinkedHashMap, Read the Complete Article.
Steps to Create Java LinkedHashMap
- Here are the steps to check Java Linked HashMap in Java:
- Import the LinkedHashMap class from the java.util package.
- Create a new instance of the LinkedHashMap class using the default constructor or specifying an initial capacity and load factor.
- Add elements to the LinkedHashMap using the put() method.
- Access elements in the LinkedHashMap using the get() method or by iterating over its key-value pairs.
Commonly used methods of the LinkedHashMap class in Java::
- put(key, value) - Inserts the specified key-value pair into the map.
- get(key) - Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or null if the key is not present in the map.
- containsKey(key) - Returns true if the map contains the specified key, otherwise false.
- containsValue(value) - Returns true if the map contains the specified value, otherwise false.
- remove(key) - Removes the key-value pair with the specified key from the map, if present.
- size() - Returns the number of key-value pairs in the map.
- clear() - Removes all key-value pairs from the map.
- keySet() - Returns a set view of the keys in the map.
- values() - Returns a collection view of the values in the map, in the same order as the corresponding keys.
- entrySet() - Returns a set view of the key-value pairs in the map.
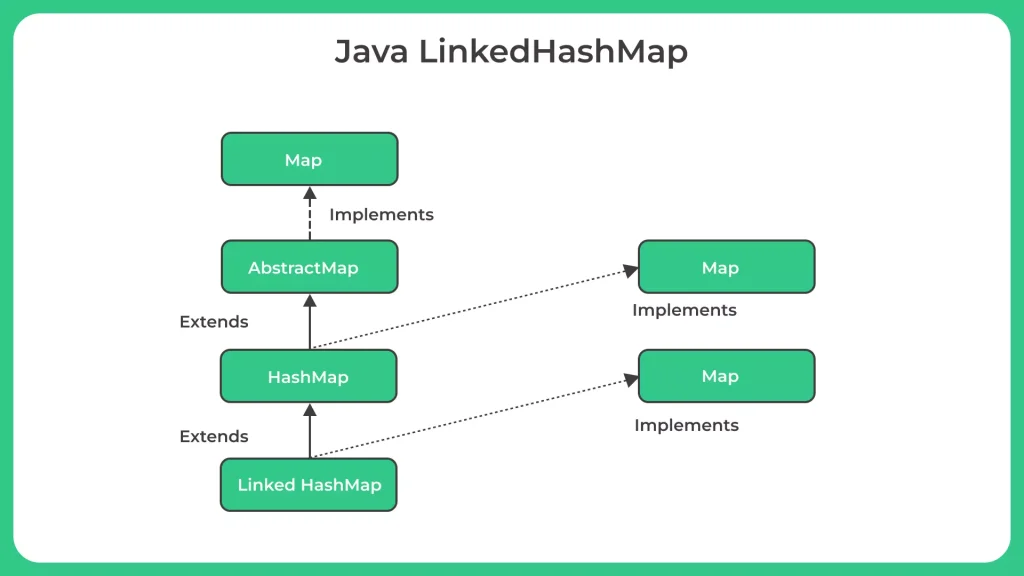
Let’s look at the Java LinkedHashMap to perform certain operations.
Example 1: Java Program to Insert Elements to LinkedHashMap
Run
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// Insert elements into the map using the put() method
map.put("apple", 1);
map.put("banana", 2);
map.put("orange", 3);
// Print the contents of the map using a for-each loop
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " = " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
Output
apple = 1 banana = 2 orange = 3
Explanation:
In this program, we create a new LinkedHashMap and then insert three elements into the map using the put() method. The keys are "apple", "banana", and "orange", and their corresponding values are 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
To print the contents of the map, we use a for-each loop to iterate over the key-value pairs in the map. We obtain each key-value pair using the entrySet() method of the LinkedHashMap, and then print the key and value using the getKey() and getValue() methods of the Map.Entry interface, respectively.
Example 2 : Java Program Access LinkedHashMap Elements Using entrySet(), keySet() and values()
Run
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// Insert elements into the map using the put() method
map.put("apple", 1);
map.put("banana", 2);
map.put("orange", 3);
// Access elements using the entrySet() method
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey() + ", Value = " + entry.getValue());
}
// Access elements using the keySet() method
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println("Key = " + key + ", Value = " + map.get(key));
}
// Access elements using the values() method
for (int value : map.values()) {
System.out.println("Value = " + value);
}
}
}
Output
Key = apple, Value = 1 Key = banana, Value = 2 Key = orange, Value = 3 Key = apple, Value = 1 Key = banana, Value = 2 Key = orange, Value = 3 Value = 1 Value = 2 Value = 3
Explanation:
In this program, we create a new LinkedHashMap and insert three elements into the map using the put() method. The keys are "apple", "banana", and "orange", and their corresponding values are 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
To access the elements in the map using the entrySet() method, we use a for-each loop to iterate over the key-value pairs in the map. We obtain each key-value pair using the entrySet() method of the LinkedHashMap, and then print the key and value using the getKey() and getValue() methods of the Map.Entry interface, respectively.
To access the elements in the map using the keySet() method, we use a for-each loop to iterate over the keys in the map. We obtain each key using the keySet() method of the LinkedHashMap, and then print the key and corresponding value using the get() method of the map.
To access the elements in the map using the values() method, we use a for-each loop to iterate over the values in the map. We obtain each value using the values() method of the LinkedHashMap, and then print the value.
Example 3: Java Program Access LinkedHashMap Elements Using Using get() and getOrDefault()
Run
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// Insert elements into the map using the put() method
map.put("apple", 1);
map.put("banana", 2);
map.put("orange", 3);
// Retrieve a value using the get() method
int value1 = map.get("apple");
System.out.println("Value for key 'apple' is " + value1);
// Retrieve a value using the getOrDefault() method
int value2 = map.getOrDefault("grape", 4);
System.out.println("Value for key 'grape' is " + value2);
}
}
Output
Value for key 'apple' is 1 Value for key 'grape' is 4
Explanation:
In this program, we create a new LinkedHashMap and insert three elements into the map using the put() method. The keys are "apple", "banana", and "orange", and their corresponding values are 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
To retrieve a value associated with a key, we use the get() method of the map. For example, we retrieve the value associated with the key "apple" using map.get("apple"). The value 1 is returned, since the key "apple" is present in the map.
To retrieve a value associated with a key, or a default value if the key is not present in the map, we use the getOrDefault() method of the map. For example, we retrieve the value associated with the key "grape" using map.getOrDefault("grape", 4). The value 4 is returned, since the key "grape" is not present in the map, and the default value is set to 4.
Example 4: Java Program to Remove LinkedHashMap Elements
Run
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// Insert elements into the map using the put() method
map.put("Samsung", 1);
map.put("Apple", 2);
map.put("Nokia", 3);
// Print the contents of the map
System.out.println("Initial map: " + map);
// Remove an element from the map using the remove() method
int removedValue = map.remove("Apple");
// Print the contents of the map after removing an element
System.out.println("Map after removing 'Apple': " + map);
// Attempt to remove a key that is not present in the map
int notPresentValue = map.remove("Nokia");
// Print the contents of the map after attempting to remove a key that is present
System.out.println("Map after attempting to remove 'Nokia': " + map);
}
}
Output
Initial map: {Samsung=1, Apple=2, Nokia=3}
Map after removing 'Apple': {Samsung=1, Nokia=3}
Map after attempting to remove 'Nokia': {Samsung=1}
Explanation:
In this program, we create a new LinkedHashMap and insert three elements into the map using the put() method. The keys are "samsung", "apple", and "Nokia", and their corresponding values are 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
To remove an element from the map, we use the remove() method of the map. For example, we remove the element associated with the key "Apple" using map.remove("apple"). The variable removedValue will contain the value 2, which was associated with the key "apple".
LinkedHashMap Vs. HashMap
In Java, LinkedHashMap and HashMap are both implementations of the Map interface. They are similar in many ways, but there are some differences between them.Here are some of the main differences between LinkedHashMap and HashMap:
- Ordering: LinkedHashMap maintains the order of elements as they were inserted into the map. HashMap does not guarantee any specific order of elements.
- Performance: LinkedHashMap is slightly slower than HashMap because it needs to maintain the order of elements. However, the performance difference is usually negligible for small maps.
- Iteration: When iterating over a LinkedHashMap, the elements are returned in the order in which they were inserted. When iterating over a HashMap, the order of elements is undefined.
- Memory usage: LinkedHashMap uses slightly more memory than HashMap because it needs to maintain the order of elements.
- Thread-safety: Both LinkedHashMap and HashMap are not thread-safe by default. If you need thread-safety, you can use ConcurrentHashMap.
Example 5: Java Program to Remove LinkedHashMap Elements
Run
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new LinkedHashMap and a new HashMap
Map<String, Integer> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
Map<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
// Insert elements into both maps in a specific order
linkedHashMap.put("Apple", 1);
linkedHashMap.put("Samsung", 2);
linkedHashMap.put("Nokia", 3);
hashMap.put("Apple", 1);
hashMap.put("Samsung", 2);
hashMap.put("Nokia", 3);
// Print the elements of the LinkedHashMap
System.out.println("LinkedHashMap:");
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : linkedHashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
// Print the elements of the HashMap
System.out.println("\nHashMap:");
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : hashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
Output
LinkedHashMap: Apple: 1 Samsung: 2 Nokia: 3 HashMap: Apple: 1 Samsung: 2 Nokia: 3
Explanation:
In this program, we create a LinkedHashMap and a HashMap and insert three elements into both maps in the same order. We then iterate over the elements of both maps and print them to the console.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment