C Preprocessor
Introduction to C Preprocessor
The Preprocessor used in C is one of the important step which is used in the compilation process but it is not a part of the compiler. In simple terms, a preprocessor is system software or a program which process the source code before the compilation step.

C Program Compilation:
A C Preprocessor performs processing of source code or high level language(HLL).The first step in the language processing system is preprocessing. This language processing system converts the high level language into a language that is easily understood by the machine i.e. machine level language.
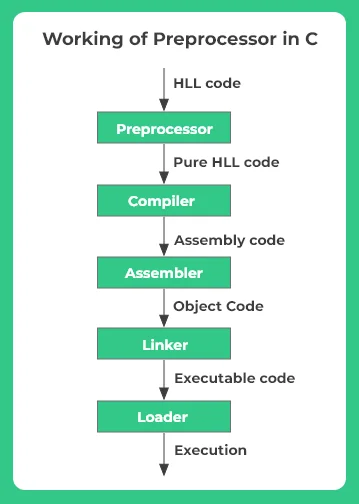
The intermediate steps involved between writing a C program and it’s execution are shown in the figure above.
A preprocessor is primarily used for performing three tasks on high level language(HLL) code given below:
- Expanding macros: The preprocessor replaces occurrences of macro names with their corresponding definitions.
- Including files: The preprocessor inserts the contents of specified files into the source code at the point where the #include directive appears.
- Conditional compilation: The preprocessor can include or exclude parts of the source code based on specified conditions, using the #if, #ifdef, and #ifndef directives.
- Replacing constants: The preprocessor replaces occurrences of constants with their corresponding values, using the #define directive.
C Preprocessor Directives
All preprocessing directives begin with a hash symbol(#).
Some of the commonly used preprocessor directives are listed below:
| Directive | Description |
|---|---|
| #define | This directive substitutes a preprocessor macro. |
| #include | This directive inserts a particular header from another file. |
| #undef | This directive undefines a preprocessor macro. |
| #ifdef | This directive returns true if this macro is defined. |
| #ifndef | This directive returns true if this macro is not defined. |
Example
#include <stdio.h>
#define PI 3.1415
int main ()
{
float r, a;
printf ("Enter the radius: ");
scanf ("%f", &r);
// Notice, the use of PI
a = PI * r * r;
printf ("Area=%.2f", a);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the radius: 6 Area = 113.09
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment