Spiral Matrix
Traversing a Matrix in Spiral Order
Traversing a matrix in spiral order is a common problem in programming, where the goal is to extract all elements of a matrix following a specific pattern.
The traversal begins at the top-left corner and proceeds in a clockwise spiral until all elements are covered.

Problem Statement
You are given a rectangular matrix of integers with dimensions m×nm \times nm×n. The task is to return a list containing all the elements of the matrix arranged in spiral order.
This means traversing the matrix in a clockwise spiral pattern, starting from the top-left corner.
Constraints:
- 1 <= matrix.length, matrix[i].length <= 10
- -100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
Example 1
Input: matrix = [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: [1,2,4,3]
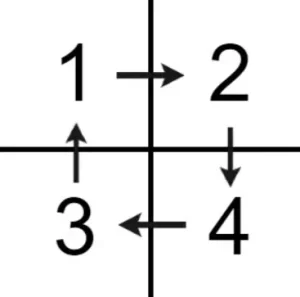
Example 2
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
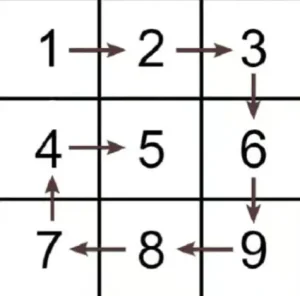
Example 3
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]
Output: [1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
There are mainly 3 approach to solve this problem –
- Recursion
- Iteration
- Iteration (Optimal)
1. Recursion
- Time complexity: O(m∗n)O(m∗n)
- Space complexity: O(min(m,n))
Where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns.
Python
C++
Java
JavaScript
Python
class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
res = []
# append all the elements in the given direction
def dfs(row, col, r, c, dr, dc):
if row == 0 or col == 0:
return
for i in range(col):
r += dr
c += dc
res.append(matrix[r][c])
# sub-problem
dfs(col, row - 1, r, c, dc, -dr)
# start by going to the right
dfs(m, n, 0, -1, 0, 1)
return res
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector spiralOrder(vector>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
vector res;
// append all the elements in the given direction
dfs(m, n, 0, -1, 0, 1, matrix, res);
return res;
}
void dfs(int row, int col, int r, int c, int dr, int dc,
vector>& matrix, vector& res) {
if (row == 0 || col == 0) return;
for (int i = 0; i < col; i++) {
r += dr;
c += dc;
res.push_back(matrix[r][c]);
}
// sub-problem
dfs(col, row - 1, r, c, dc, -dr, matrix, res);
}
};
Java
public class Solution {
public List spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
List res = new ArrayList<>();
// append all the elements in the given direction
dfs(m, n, 0, -1, 0, 1, matrix, res);
return res;
}
private void dfs(int row, int col, int r, int c,
int dr, int dc, int[][] matrix, List res) {
if (row == 0 || col == 0) return;
for (int i = 0; i < col; i++) {
r += dr;
c += dc;
res.add(matrix[r][c]);
}
// sub-problem
dfs(col, row - 1, r, c, dc, -dr, matrix, res);
}
}
JavaScript
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @return {number[]}
*/
spiralOrder(matrix) {
const m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
const res = [];
// append all the elements in the given direction
const dfs = (row, col, r, c, dr, dc) => {
if (row === 0 || col === 0) return;
for (let i = 0; i < col; i++) {
r += dr;
c += dc;
res.push(matrix[r][c]);
}
// sub-problem
dfs(col, row - 1, r, c, dc, -dr);
};
// start by going to the right
dfs(m, n, 0, -1, 0, 1);
return res;
}
}2. Iteration
Time & Space Complexity
- Time complexity: O(m∗n)O(m∗n)
- Space complexity: O(1)O(1)
Where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns.
Code
C++
Java
Python
JavaScript
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector spiralOrder(vector>& matrix) {
vector res;
int left = 0, right = matrix[0].size();
int top = 0, bottom = matrix.size();
while (left < right && top < bottom) {
for (int i = left; i < right; i++) {
res.push_back(matrix[top][i]);
}
top++;
for (int i = top; i < bottom; i++) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][right - 1]);
}
right--;
if (!(left < right && top < bottom)) {
break;
}
for (int i = right - 1; i >= left; i--) {
res.push_back(matrix[bottom - 1][i]);
}
bottom--;
for (int i = bottom - 1; i >= top; i--) {
res.push_back(matrix[i][left]);
}
left++;
}
return res;
}
};
Java
public class Solution {
public List spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
int left = 0, right = matrix[0].length;
int top = 0, bottom = matrix.length;
while (left < right && top < bottom) {
for (int i = left; i < right; i++) {
res.add(matrix[top][i]);
}
top++;
for (int i = top; i < bottom; i++) {
res.add(matrix[i][right - 1]);
}
right--;
if (!(left < right && top < bottom)) {
break;
}
for (int i = right - 1; i >= left; i--) {
res.add(matrix[bottom - 1][i]);
}
bottom--;
for (int i = bottom - 1; i >= top; i--) {
res.add(matrix[i][left]);
}
left++;
}
return res;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
res = []
left, right = 0, len(matrix[0])
top, bottom = 0, len(matrix)
while left < right and top < bottom:
for i in range(left, right):
res.append(matrix[top][i])
top += 1
for i in range(top, bottom):
res.append(matrix[i][right - 1])
right -= 1
if not (left < right and top < bottom):
break
for i in range(right - 1, left - 1, -1):
res.append(matrix[bottom - 1][i])
bottom -= 1
for i in range(bottom - 1, top - 1, -1):
res.append(matrix[i][left])
left += 1
return resJavaScript
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @return {number[]}
*/
spiralOrder(matrix) {
const res = [];
let left = 0;
let right = matrix[0].length;
let top = 0;
let bottom = matrix.length;
while (left < right && top < bottom) {
for (let i = left; i < right; i++) {
res.push(matrix[top][i]);
}
top++;
for (let i = top; i < bottom; i++) {
res.push(matrix[i][right - 1]);
}
right--;
if (!(left < right && top < bottom)) {
break;
}
for (let i = right - 1; i >= left; i--) {
res.push(matrix[bottom - 1][i]);
}
bottom--;
for (let i = bottom - 1; i >= top; i--) {
res.push(matrix[i][left]);
}
left++;
}
return res;
}
}3. Iteration (Optimal)
- Time complexity: O(m∗n)O(m∗n)
- Space complexity: O(1)O(1)
Where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns.
Code
C++
Java
Python
JavaScript
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector spiralOrder(vector>& matrix) {
vector res;
vector> directions = {{0, 1}, {1, 0},
{0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
vector steps = {matrix[0].size(), matrix.size() - 1};
int r = 0, c = -1, d = 0;
while (steps[d % 2]) {
for (int i = 0; i < steps[d % 2]; i++) {
r += directions[d].first;
c += directions[d].second;
res.push_back(matrix[r][c]);
}
steps[d % 2]--;
d = (d + 1) % 4;
}
return res;
}
};
Java
public class Solution {
public List spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
int[][] directions = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
int[] steps = {matrix[0].length, matrix.length - 1};
int r = 0, c = -1, d = 0;
while (steps[d % 2] > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < steps[d % 2]; i++) {
r += directions[d][0];
c += directions[d][1];
res.add(matrix[r][c]);
}
steps[d % 2]--;
d = (d + 1) % 4;
}
return res;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
res = []
directions = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)]
steps = [len(matrix[0]), len(matrix) - 1]
r, c, d = 0, -1, 0
while steps[d & 1]:
for i in range(steps[d & 1]):
r += directions[d][0]
c += directions[d][1]
res.append(matrix[r][c])
steps[d & 1] -= 1
d += 1
d %= 4
return resJavaScript
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @return {number[]}
*/
spiralOrder(matrix) {
const res = [];
const directions = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]];
const steps = [matrix[0].length, matrix.length - 1];
let r = 0, c = -1, d = 0;
while (steps[d % 2]) {
for (let i = 0; i < steps[d % 2]; i++) {
r += directions[d][0];
c += directions[d][1];
res.push(matrix[r][c]);
}
steps[d % 2]--;
d = (d + 1) % 4;
}
return res;
}
}


