K Closest Points to Origin Problem
K Closest Points to Origin: An In-Depth Explanation
Finding the closest points to a specific location, such as the origin (0, 0), is a common problem in computational geometry and has a variety of applications in fields like computer vision, geospatial analysis, and clustering.
In this article, we will explore the problem, break it down step-by-step, and discuss an efficient solution.

Problem:
You are given an 2-D array points where points[i] = [xi, yi] represents the coordinates of a point on an X-Y axis plane. You are also given an integer k.
Return the k closest points to the origin
The distance between two points is defined as the Euclidean distance (sqrt((x1 – x2)^2 + (y1 – y2)^2)).
You may return the answer in any order.
Problem Breakdown
You are given:
- A list of 2D points, where each point is represented as [xi, yi].
- An integer k, which represents the number of closest points to the origin (0, 0) that you need to return.
You need to find the k points that have the smallest distances to the origin. If there are multiple solutions (points with the same distance), any valid output order is acceptable.
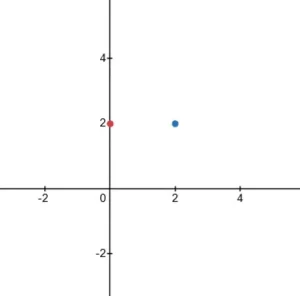
Example 1:
Explanation:
The distance between (0, 2) and the origin (0, 0) is 2. The distance between (2, 2) and the origin is sqrt(2^2 + 2^2) = 2.82842. So the closest point to the origin is (0, 2).
Explanation: The output [2,0],[0,2] would also be accepted.
Constraints:
- 1 <= k <= points.length <= 1000
- -100 <= points[i][0], points[i][1] <= 100
Approach
Key Idea: Max-Heap Simulation
To efficiently retrieve the two heaviest stones, we use a max-heap. However, Python’s heapq library provides a min-heap implementation by default, so we simulate a max-heap by storing negative values.
Algorithm
Steps
- Initialize the Heap: Convert all stone weights to negative and push them into a heap.
- Simulation Loop:
- Pop the two largest elements (smallest in the min-heap due to negative values).
- If the stones are not equal, compute the new weight and push it back into the heap.
- Result:
- If the heap is empty, return
0. - Otherwise, return the absolute value of the remaining stone.
- If the heap is empty, return
There are mainly Four approach to solve this problem –
- Sorting
- Binary Search
- Heap
- Bucket Sort
1. Sorting
- Time complexity: O(n^2logn)
- Space complexity: O(1) or O(n)depending on the sorting algorithm.
class Solution:
def kClosest(self, points: List[List[int]], k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
points.sort(key=lambda p: p[0]**2 + p[1]**2)
return points[:k]class Solution {
public:
vector> kClosest(vector>& points, int k) {
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), [](const auto& a, const auto& b) {
return (a[0] * a[0] + a[1] * a[1]) < (b[0] * b[0] + b[1] * b[1]);
});
return vector>(points.begin(), points.begin() + k);
}
}; public class Solution {
public int[][] kClosest(int[][] points, int k) {
Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> (a[0] * a[0] + a[1] * a[1]) -
(b[0] * b[0] + b[1] * b[1]));
return Arrays.copyOfRange(points, 0, k);
}
}class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[][]} points
* @param {number} k
* @return {number[][]}
*/
kClosest(points, k) {
points.sort((a, b) => (a[0] ** 2 + a[1] ** 2) -
(b[0] ** 2 + b[1] ** 2));
return points.slice(0, k);
}
}2. Binary Search
Time & Space Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n^2)
- Space complexity: O(1) or O(n)O(n) depending on the sorting algorithm.
class Solution:
def lastStoneWeight(self, stones: List[int]) -> int:
stones.sort()
n = len(stones)
while n > 1:
cur = stones.pop() - stones.pop()
n -= 2
if cur > 0:
l, r = 0, n
while l < r:
mid = (l + r) // 2
if stones[mid] < cur:
l = mid + 1
else:
r = mid
pos = l
n += 1
stones.append(0)
for i in range(n - 1, pos, -1):
stones[i] = stones[i - 1]
stones[pos] = cur
return stones[0] if n > 0 else 0public class Solution {
public int lastStoneWeight(int[] stones) {
Arrays.sort(stones);
int n = stones.length;
while (n > 1) {
int cur = stones[n - 1] - stones[n - 2];
n -= 2;
if (cur > 0) {
int l = 0, r = n;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (stones[mid] < cur) {
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid;
}
}
int pos = l;
n++;
stones = Arrays.copyOf(stones, n);
for (int i = n - 1; i > pos; i--) {
stones[i] = stones[i - 1];
}
stones[pos] = cur;
}
}
return n > 0 ? stones[0] : 0;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int lastStoneWeight(vector& stones) {
sort(stones.begin(), stones.end());
int n = stones.size();
while (n > 1) {
int cur = stones[n - 1] - stones[n - 2];
n -= 2;
if (cur > 0) {
int l = 0, r = n;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (stones[mid] < cur) {
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid;
}
}
int pos = l;
stones.push_back(0);
for (int i = n + 1; i > pos; i--) {
stones[i] = stones[i - 1];
}
stones[pos] = cur;
n++;
}
}
return n > 0 ? stones[0] : 0;
}
}; /**
* const { MinPriorityQueue } = require('@datastructures-js/priority-queue');
*/
class KthLargest {
/**
* @param {number} k
* @param {number[]} nums
*/
constructor(k, nums) {
this.minHeap = new MinPriorityQueue();
this.k = k;
for (const num of nums) {
this.minHeap.enqueue(num);
}
while (this.minHeap.size() > k) {
this.minHeap.dequeue();
}
}
/**
* @param {number} val
* @return {number}
*/
add(val) {
this.minHeap.enqueue(val);
if (this.minHeap.size() > this.k) {
this.minHeap.dequeue();
}
return this.minHeap.front();
}
}Where mm is the number of calls made to add().
2. Binary Search
Time & Space Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n^2)
- Space complexity: O(1) or O(n) depending on the sorting algorithm.
class Solution:
def lastStoneWeight(self, stones: List[int]) -> int:
stones.sort()
n = len(stones)
while n > 1:
cur = stones.pop() - stones.pop()
n -= 2
if cur > 0:
l, r = 0, n
while l < r:
mid = (l + r) // 2
if stones[mid] < cur:
l = mid + 1
else:
r = mid
pos = l
n += 1
stones.append(0)
for i in range(n - 1, pos, -1):
stones[i] = stones[i - 1]
stones[pos] = cur
return stones[0] if n > 0 else 0public class Solution {
public int lastStoneWeight(int[] stones) {
Arrays.sort(stones);
int n = stones.length;
while (n > 1) {
int cur = stones[n - 1] - stones[n - 2];
n -= 2;
if (cur > 0) {
int l = 0, r = n;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (stones[mid] < cur) {
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid;
}
}
int pos = l;
n++;
stones = Arrays.copyOf(stones, n);
for (int i = n - 1; i > pos; i--) {
stones[i] = stones[i - 1];
}
stones[pos] = cur;
}
}
return n > 0 ? stones[0] : 0;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int lastStoneWeight(vector& stones) {
sort(stones.begin(), stones.end());
int n = stones.size();
while (n > 1) {
int cur = stones[n - 1] - stones[n - 2];
n -= 2;
if (cur > 0) {
int l = 0, r = n;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (stones[mid] < cur) {
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid;
}
}
int pos = l;
stones.push_back(0);
for (int i = n + 1; i > pos; i--) {
stones[i] = stones[i - 1];
}
stones[pos] = cur;
n++;
}
}
return n > 0 ? stones[0] : 0;
}
}; /**
* const { MinPriorityQueue } = require('@datastructures-js/priority-queue');
*/
class KthLargest {
/**
* @param {number} k
* @param {number[]} nums
*/
constructor(k, nums) {
this.minHeap = new MinPriorityQueue();
this.k = k;
for (const num of nums) {
this.minHeap.enqueue(num);
}
while (this.minHeap.size() > k) {
this.minHeap.dequeue();
}
}
/**
* @param {number} val
* @return {number}
*/
add(val) {
this.minHeap.enqueue(val);
if (this.minHeap.size() > this.k) {
this.minHeap.dequeue();
}
return this.minHeap.front();
}
}3. Heap
Time & Space Complexity
- Time complexity: O(nlogn)
- Space complexity: O(1) or O(n) depending on the sorting algorithm.
class Solution:
def lastStoneWeight(self, stones: List[int]) -> int:
stones = [-s for s in stones]
heapq.heapify(stones)
while len(stones) > 1:
first = heapq.heappop(stones)
second = heapq.heappop(stones)
if second > first:
heapq.heappush(stones, first - second)
stones.append(0)
return abs(stones[0])class Solution {
public int lastStoneWeight(int[] stones) {
PriorityQueue minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int s : stones) {
minHeap.offer(-s);
}
while (minHeap.size() > 1) {
int first = minHeap.poll();
int second = minHeap.poll();
if (second > first) {
minHeap.offer(first - second);
}
}
minHeap.offer(0);
return Math.abs(minHeap.peek());
}
} class Solution {
public:
int lastStoneWeight(vector& stones) {
priority_queue maxHeap;
for (int s : stones) {
maxHeap.push(s);
}
while (maxHeap.size() > 1) {
int first = maxHeap.top();
maxHeap.pop();
int second = maxHeap.top();
maxHeap.pop();
if (second < first) {
maxHeap.push(first - second);
}
}
maxHeap.push(0);
return maxHeap.top();
}
}; /**
* const { MaxPriorityQueue } = require('@datastructures-js/priority-queue');
*/
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[]} stones
* @return {number}
*/
lastStoneWeight(stones) {
const maxPQ = new MaxPriorityQueue();
for (const stone of stones) {
maxPQ.enqueue(stone);
}
while (maxPQ.size() > 1) {
const stone1 = maxPQ.dequeue();
const stone2 = maxPQ.dequeue();
if (stone1 !== stone2) {
maxPQ.enqueue(stone1 - stone2);
}
}
return maxPQ.size() === 1 ? maxPQ.dequeue() : 0;
}
}4. Bucket Sort
Time & Space Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n+w)
- Space complexity: O(w)
class Solution:
def lastStoneWeight(self, stones: List[int]) -> int:
maxStone = max(stones)
bucket = [0] * (maxStone + 1)
for stone in stones:
bucket[stone] += 1
first = second = maxStone
while first > 0:
if bucket[first] % 2 == 0:
first -= 1
continue
j = min(first - 1, second)
while j > 0 and bucket[j] == 0:
j -= 1
if j == 0:
return first
second = j
bucket[first] -= 1
bucket[second] -= 1
bucket[first - second] += 1
first = max(first - second, second)
return firstpublic class Solution {
public int lastStoneWeight(int[] stones) {
int maxStone = 0;
for (int stone : stones) {
maxStone = Math.max(maxStone, stone);
}
int[] bucket = new int[maxStone + 1];
for (int stone : stones) {
bucket[stone]++;
}
int first = maxStone, second = maxStone;
while (first > 0) {
if (bucket[first] % 2 == 0) {
first--;
continue;
}
int j = Math.min(first - 1, second);
while (j > 0 && bucket[j] == 0) {
j--;
}
if (j == 0) {
return first;
}
second = j;
bucket[first]--;
bucket[second]--;
bucket[first - second]++;
first = Math.max(first - second, second);
}
return first;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int lastStoneWeight(vector& stones) {
int maxStone = 0;
for (int stone : stones) {
maxStone = max(maxStone, stone);
}
vector bucket(maxStone + 1, 0);
for (int stone : stones) {
bucket[stone]++;
}
int first = maxStone, second = maxStone;
while (first > 0) {
if (bucket[first] % 2 == 0) {
first--;
continue;
}
int j = min(first - 1, second);
while (j > 0 && bucket[j] == 0) {
j--;
}
if (j == 0) {
return first;
}
second = j;
bucket[first]--;
bucket[second]--;
bucket[first - second]++;
first = max(first - second, second);
}
return first;
}
}; class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[]} stones
* @return {number}
*/
lastStoneWeight(stones) {
let maxStone = 0;
for (let stone of stones) {
maxStone = Math.max(maxStone, stone);
}
let bucket = Array(maxStone + 1).fill(0);
for (let stone of stones) {
bucket[stone]++;
}
let first = maxStone, second = maxStone;
while (first > 0) {
if (bucket[first] % 2 === 0) {
first--;
continue;
}
let j = Math.min(first - 1, second);
while (j > 0 && bucket[j] === 0) {
j--;
}
if (j === 0) {
return first;
}
second = j;
bucket[first]--;
bucket[second]--;
bucket[first - second]++;
first = Math.max(first - second, second);
}
return first;
}
}

