Cheapest Flights Within K Stops
Cheapest Flights Within K Stops
You are given n airports, labeled from 0 to n-1, connected by flights.
Array “flights” contains details of one-way flights in the form [from_i, to_i, price_i], where “from_i” is the starting airport, “to_i” is the destination airport, and “price_i” is the cost of the flight.
There are no duplicate flights, and no flights go from an airport to itself.

src: The starting airport.
dst: The destination airport.
k: The maximum number of stops allowed (excluding the source and destination).
The task is to find the cheapest price to travel from src to dst with at most k stops.
If no such route exists, return -1.
Examples related to Cheapest Flights Within K Stops Problem
Example 1:
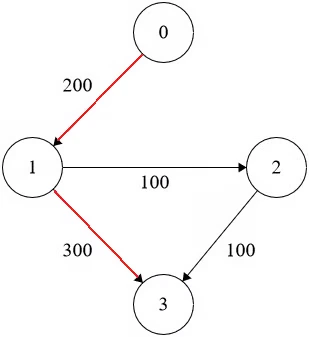
Output: 500
Explanation:
Optimal path with at most 1 stop from airport 0 to 3 is shown in red, with total cost 200 + 300 = 500.
Note that the path [0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3] costs only 400, and thus is cheaper, but it requires 2 stops, which is more than k.
Example 2:
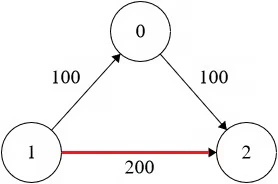
Output: 200
Explanation:
Optimal path with at most 1 stop from airport 1 to 2 is shown in red and has cost 200.
Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 100
- fromi != toi
- 1 <= pricei <= 1000
- 0 <= src, dst, k < n
Hints to solve Cheapest Flights Within K Stops Problem
Recommended Time & Space Complexity
Aim for a solution with O(n + (m * k)) time and O(n) space, where n is the number of cities, m is the number of flights, and k is the maximum number of stops.
Hint 1:
- Treat this as a graph problem, where cities are nodes and flights are directed edges with ticket costs as weights.
- Can you think of a shortest path algorithm that accommodates the k stops condition? More suitable algorithm than Dijkstra’s may help.
Hint 2:
Consider using the Bellman-Ford algorithm. Initialize a price array of size n with infinity, setting prices[source] = 0.
This array tracks the minimum cost to reach each city. Iterate (k+1) times, updating the cost of each city by extending paths from cities with valid costs.
How would you implement this?
Hint 3:
At each iteration, update the price array with minimum costs by processing each flight.
Use a temporary array to store the updated values.
After completing all iterations, return prices[dst]. If it’s still infinity, return -1.
Methods to Solve Cheapest Flights Within K Stops Problem
There are mainly 3 approaches to solve Cheapest Flights Within K Stops problem:
- Dijkstra’s Algorithm
- Bellman Ford Algorithm
- Shortest Path Faster Algorithm
1. Dijkstra’s Algorithm Method
This is a greedy algorithm used to find the shortest path between a source node and all other nodes in a weighted graph.
It works by selecting the node with the smallest tentative distance, then updating the distances of its neighboring nodes, and repeats this until all nodes are visited.
- Time complexity: O((n+m)∗k)
- Space complexity: O(n∗k)
Where n is the number of cities, m is the number of flights and k is the number of stops.
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
int INF = 1e9;
vector>> adj(n);
vector> dist(n, vector(k + 5, INF));
for (auto& flight : flights) {
adj[flight[0]].emplace_back(flight[1], flight[2]);
}
dist[src][0] = 0;
priority_queue,
vector>, greater<>> minHeap;
minHeap.emplace(0, src, -1);
while (!minHeap.empty()) {
auto [cst, node, stops] = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
if (node == dst) return cst;
if (stops == k || dist[node][stops + 1] < cst) continue;
for (auto& [nei, w] : adj[node]) {
int nextCst = cst + w;
int nextStops = stops + 1;
if (dist[nei][nextStops + 1] > nextCst) {
dist[nei][nextStops + 1] = nextCst;
minHeap.emplace(nextCst, nei, nextStops);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
public class Solution {
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
List[] adj = new ArrayList[n];
int[][] dist = new int[n][k + 5];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) Arrays.fill(dist[i], INF);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] flight : flights) {
adj[flight[0]].add(new int[]{flight[1], flight[2]});
}
dist[src][0] = 0;
PriorityQueue minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(
Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0])
);
minHeap.offer(new int[]{0, src, -1});
while (!minHeap.isEmpty()) {
int[] top = minHeap.poll();
int cst = top[0], node = top[1], stops = top[2];
if (node == dst) return cst;
if (stops == k || dist[node][stops + 1] < cst) continue;
for (int[] neighbor : adj[node]) {
int nei = neighbor[0], w = neighbor[1];
int nextCst = cst + w;
int nextStops = stops + 1;
if (dist[nei][nextStops + 1] > nextCst) {
dist[nei][nextStops + 1] = nextCst;
minHeap.offer(new int[]{nextCst, nei, nextStops});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
class Solution:
def findCheapestPrice(self, n: int, flights: List[List[int]], src: int, dst: int, k: int) -> int:
INF = float("inf")
adj = [[] for _ in range(n)]
dist = [[INF] * (k + 5) for _ in range(n)]
for u, v, cst in flights:
adj[u].append([v, cst])
dist[src][0] = 0
minHeap = [(0, src, -1)] # cost, node, stops
while len(minHeap):
cst, node, stops = heapq.heappop(minHeap)
if dst == node: return cst
if stops == k or dist[node][stops + 1] < cst:
continue
for nei, w in adj[node]:
nextCst = cst + w
nextStops = 1 + stops
if dist[nei][nextStops + 1] > nextCst:
dist[nei][nextStops + 1] = nextCst
heapq.heappush(minHeap, (nextCst, nei, nextStops))
return -1class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} flights
* @param {number} src
* @param {number} dst
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
findCheapestPrice(n, flights, src, dst, k) {
const INF = Infinity;
const adj = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
const dist = Array.from({ length: n }, () =>
Array(k + 5).fill(INF));
for (let [u, v, cst] of flights) {
adj[u].push([v, cst]);
}
dist[src][0] = 0;
const minHeap = new MinPriorityQueue(entry => entry[0]);
minHeap.push([0, src, -1]); // cost, node, stops
while (!minHeap.isEmpty()) {
const [cst, node, stops] = minHeap.pop();
if (node === dst) return cst;
if (stops === k || dist[node][stops + 1] < cst) continue;
for (let [nei, w] of adj[node]) {
const nextCst = cst + w;
const nextStops = stops + 1;
if (dist[nei][nextStops + 1] > nextCst) {
dist[nei][nextStops + 1] = nextCst;
minHeap.push([nextCst, nei, nextStops]);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
2. Bellman Ford Algorithm
Dynamic programming approach that calculates the shortest path in a weighted graph, even when negative edge weights exist. It works by iteratively relaxing all edges, updating the shortest distance for each node, and can detect negative weight cycles.
- Time complexity: O(n+(m∗k))
- Space complexity: O(n)
Where n is the number of cities, m is the number of flights and k is the number of stops.
Code:
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
vector prices(n, INT_MAX);
prices[src] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++) {
vector tmpPrices = prices;
for (const auto& flight : flights) {
int s = flight[0];
int d = flight[1];
int p = flight[2];
if (prices[s] == INT_MAX)
continue;
if (prices[s] + p < tmpPrices[d])
tmpPrices[d] = prices[s] + p;
}
prices = tmpPrices;
}
return prices[dst] == INT_MAX ? -1 : prices[dst];
}
};
public class Solution {
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
int[] prices = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(prices, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
prices[src] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++) {
int[] tmpPrices = Arrays.copyOf(prices, n);
for (int[] flight : flights) {
int s = flight[0];
int d = flight[1];
int p = flight[2];
if (prices[s] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
continue;
}
if (prices[s] + p < tmpPrices[d]) {
tmpPrices[d] = prices[s] + p;
}
}
prices = tmpPrices;
}
return prices[dst] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : prices[dst];
}
}
class Solution:
def findCheapestPrice(self, n: int, flights: List[List[int]], src: int, dst: int, k: int) -> int:
prices = [float("inf")] * n
prices[src] = 0
for i in range(k + 1):
tmpPrices = prices.copy()
for s, d, p in flights: # s=source, d=dest, p=price
if prices[s] == float("inf"):
continue
if prices[s] + p < tmpPrices[d]:
tmpPrices[d] = prices[s] + p
prices = tmpPrices
return -1 if prices[dst] == float("inf") else prices[dst]
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} flights
* @param {number} src
* @param {number} dst
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
findCheapestPrice(n, flights, src, dst, k) {
let prices = new Array(n).fill(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER);
prices[src] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= k; i++) {
const tmpPrices = [...prices];
for (const flight of flights) {
const s = flight[0];
const d = flight[1];
const p = flight[2];
if (prices[s] === Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER) continue;
if (prices[s] + p < tmpPrices[d]) tmpPrices[d] = prices[s] + p;
}
prices = tmpPrices;
}
return prices[dst] === Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ? -1 : prices[dst];
}
}
3. Shortest Path Faster Algorithm
This is an optimized version of the Bellman-Ford algorithm, where nodes are processed in order of the shortest known distance. It uses a priority queue to speed up the relaxation process, offering better performance for many graphs.
- Time complexity: O(n∗k)
- Space complexity: O(n+m)
Where n is the number of cities, m is the number of flights and k is the number of stops.
Code:
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
vector prices(n, INT_MAX);
prices[src] = 0;
vector>> adj(n);
for (const auto& flight : flights) {
adj[flight[0]].emplace_back(flight[1], flight[2]);
}
queue> q;
q.push({0, src, 0});
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [cst, node, stops] = q.front();
q.pop();
if (stops > k) continue;
for (const auto& neighbor : adj[node]) {
int nei = neighbor.first, w = neighbor.second;
int nextCost = cst + w;
if (nextCost < prices[nei]) {
prices[nei] = nextCost;
q.push({nextCost, nei, stops + 1});
}
}
}
return prices[dst] == INT_MAX ? -1 : prices[dst];
}
};
public class Solution {
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
int[] prices = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(prices, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
prices[src] = 0;
List[] adj = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (var flight : flights) {
adj[flight[0]].add(new int[] { flight[1], flight[2] });
}
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[] { 0, src, 0 });
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
var curr = q.poll();
int cst = curr[0], node = curr[1], stops = curr[2];
if (stops > k) continue;
for (var neighbor : adj[node]) {
int nei = neighbor[0], w = neighbor[1];
int nextCost = cst + w;
if (nextCost < prices[nei]) {
prices[nei] = nextCost;
q.offer(new int[] { nextCost, nei, stops + 1 });
}
}
}
return prices[dst] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : prices[dst];
}
}
class Solution:
def findCheapestPrice(self, n: int, flights: List[List[int]], src: int, dst: int, k: int) -> int:
prices = [float("inf")] * n
prices[src] = 0
adj = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v, cst in flights:
adj[u].append([v, cst])
q = deque([(0, src, 0)])
while q:
cst, node, stops = q.popleft()
if stops > k:
continue
for nei, w in adj[node]:
nextCost = cst + w
if nextCost < prices[nei]:
prices[nei] = nextCost
q.append((nextCost, nei, stops + 1))
return prices[dst] if prices[dst] != float("inf") else -1
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} flights
* @param {number} src
* @param {number} dst
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
findCheapestPrice(n, flights, src, dst, k) {
const prices = Array(n).fill(Infinity);
prices[src] = 0;
const adj = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [u, v, cst] of flights) {
adj[u].push([v, cst]);
}
const q = new Queue([[0, src, 0]]); // [cost, node, stops]
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
const [cst, node, stops] = q.pop();
if (stops > k) continue;
for (const [nei, w] of adj[node]) {
const nextCost = cst + w;
if (nextCost < prices[nei]) {
prices[nei] = nextCost;
q.push([nextCost, nei, stops + 1]);
}
}
}
return prices[dst] === Infinity ? -1 : prices[dst];
}
}


