__init__ in Python
__init__ in Python
Whenever we listen class, object or Opps one thing comes to our mind is Constructor if we know basic of c++. In this article, we will discuss __init__ in Python, its usages and many more things. If you are familiar with c++, you might have the idea of constructor, __init__ method is the constructor in python.
Let’s understand the function of __init__ in Python.

Function of __init__
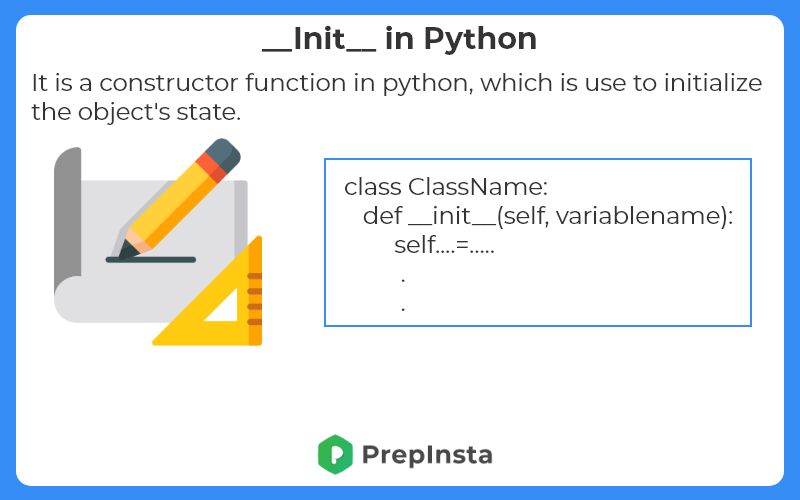
- The __init__ method is similar to constructors in c++ and Java.
- Constructors are used to initialize the object’s state.
- The task of constructors is to initialize(assign values) to the data members of the class when an object of class is created.
Synatx:
class ClassName:
def __init__( self , variables...):
##body
Code #1:
#python Program
#Rishikesh
class Prepster:
def __init__(self, name , userid,password): ##constructor
self.name=name ## assigning values to variables
self.userid=userid
self.password=password
ob1=Prepster(‘rishikesh’,‘Abc’,‘abc@123’) ##object
print(ob1.name)
Output:
rishikesh
Let’s understand this code:
- a prepster name “rishikesh” is created. While creating a prepster, “rishikesh”, “Userid”, “password” is passed as an argument, this argument will be passed to the __init__ method to initialize the object.
- The keyword self represents the instance of a class and binds the attributes with the given arguments.
Code #2 (init with inheritance):
#python Program
#Rishikesh
class PrepInsta:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name=name
print(‘You are in Parent class’)
class Prepster(PrepInsta):
def __init__(self, name): ##constructor
PrepInsta.__init__(self,name)
print(‘You are in Child Class’)
self.name=name ## assigning values to variables
ob1=Prepster(‘rishikesh’) ##object
Output:
You are in Parent class
You are in Child Class
- Here the parent class constructor is called first, but in Python, it is not compulsory that parent class constructor will always be called first. The order in which the __init__ method is called for a parent or a child class can be modified. This can simply be done by calling the parent class constructor after the body of child class constructor.
#python Program
#Rishikesh
class PrepInsta:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name=name
print(‘You are in Parent class’)
class Prepster(PrepInsta):
def __init__(self, name): ##constructor
print(‘You are in Child Class’)
self.name=name ## assigning values to variables
PrepInsta.__init__(self,name)
ob1=Prepster(‘rishikesh’) ##object
Output:
You are in Child Class
You are in Parent class



Login/Signup to comment