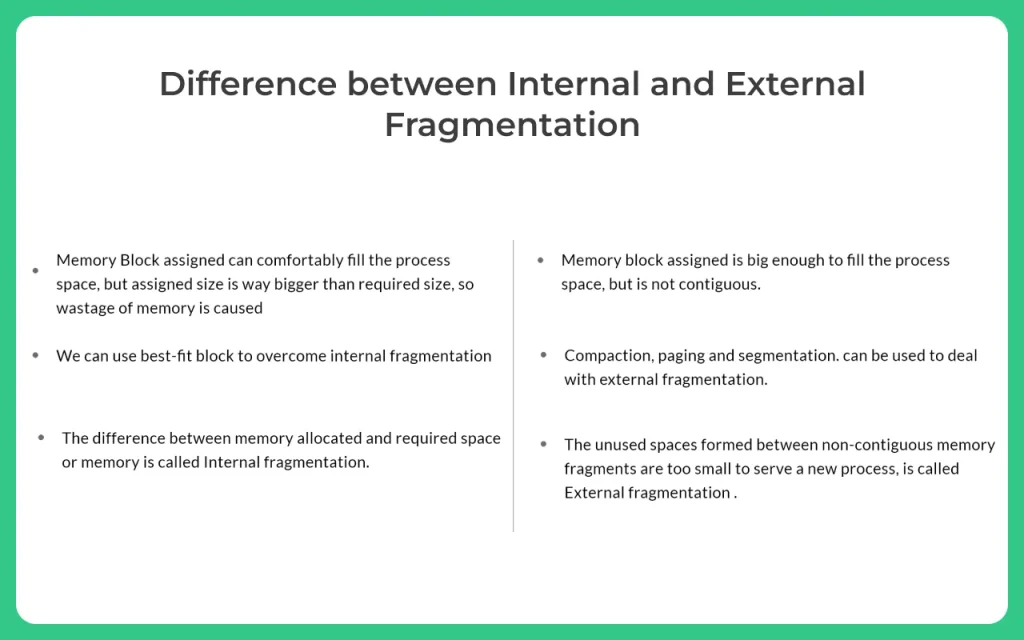
Internal Fragmentation vs External Fragmentation
Internal vs External
Fragmentation
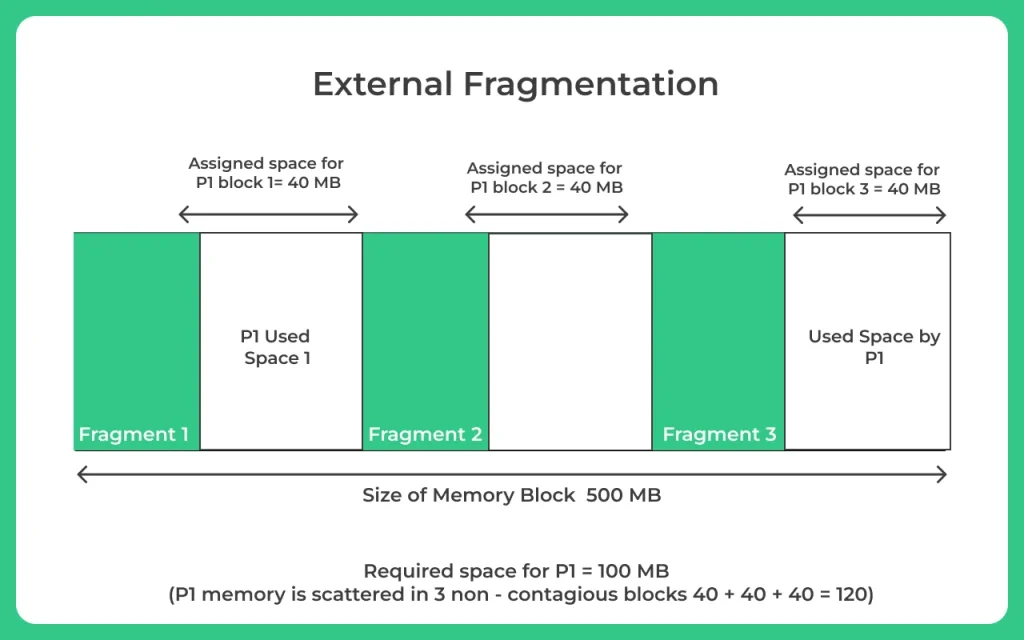
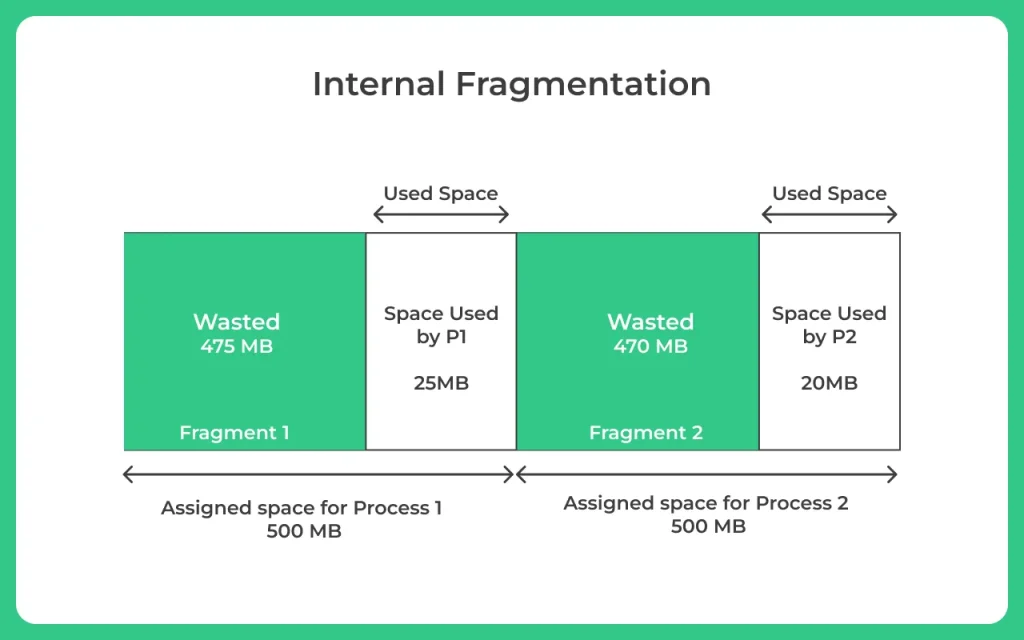
Users keep loading and unloading processes from main memory. Processes are typically stored in blocks in memory. The available memory blocks may not be large enough to accommodate processes that require contiguous memory space. This condition is called fragmentation. In other words, fragmentation occurs when a user dynamically allocates memory for a process and the process fails to load even though sufficient memory is available because continuous memory allocation is not possible .
External Fragmentation
When the process is loaded or removed from the memory, a free space is created. This free space creates an empty space in the memory which is called external fragmentation.
Note
In a nutshell, both internal and external fragmentation are natural process related to empty memory space or memory being wasted. However, the problem with both cases cannot be resolved entirely but can be mitigated to some extent with solutions given above.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others





Login/Signup to comment