Inheritance in Java
Inheritance in Java
Inheritance is a mechanism that allows us to extend the definition of a class without making any physical changes to the existing class.
Inheritance creates a new class from an existing class. Any new class that we create from an existing class is called a derived class, and an existing class is called a base class.
Concept and Types of inheritance
The inheritance relationship enables a derived class to inherit features from its base class. A derived class can add new features of its own. Therefore rather than creating completely new classes from scratch, we can take advantage of inheritance and reduce software complexity.
- Class: A class is a group of objects which have common properties. It is a template or blueprint from which objects are created.
- Sub Class/Child Class: Subclass is a class that inherits the other class. It is also called a derived class, extended class, or child class.
- Super Class/Parent Class: Superclass is the class from where a subclass inherits the features. It is also called a base class or a parent class.
- Reusability: As the name specifies, reusability is a mechanism that facilitates you to reuse the fields and methods of the existing class when you create a new class. You can use the same fields and methods already defined in the previous class.
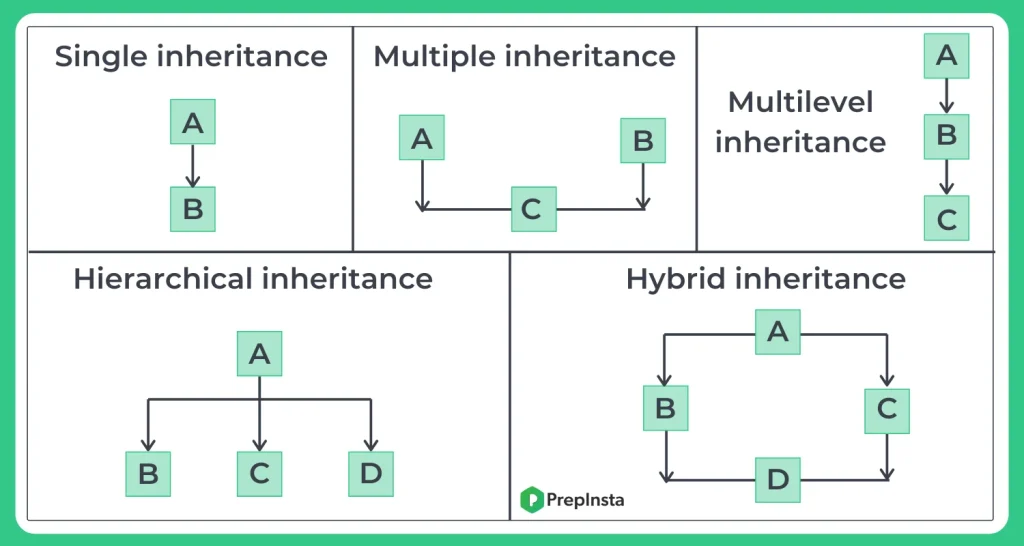
Types of inheritance :
- Single Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
1. Single Inheritance
It is the inheritance hierarchy wherein one derived class inherits from one base class.
2. Multiple Inheritance
It is the inheritance hierarchy wherein one derived class inherits from multiple base classes.
3. Hierarchical Inheritance
It is the inheritance hierarchy wherein multiple derived classes inherit from one base class.
4. Multilevel Inheritance
It is the inheritance hierarchy wherein subclass acts as a base class for other classes.
5. Hybrid Inheritance
It is the inheritance hierarchy that reflects any legal combination of the other four types of inheritance
Syntax
class XYZ extends ABC
{
// block of code
}
Example
class Bicycle
{
// the Bicycle class has two fields
public int gear;
public int speed;
// the Bicycle class has one constructor
public Bicycle(int gear, int speed)
{
this.gear = gear;
this.speed = speed;
}
// the Bicycle class has three methods
public void applyBrake(int decrement)
{
speed -= decrement;
}
public void speedUp(int increment)
{
speed += increment;
}
// toString() method to print info of Bicycle
public String toString()
{
return("No of gears are "+gear
+"\n"
+ "speed of bicycle is "+speed);
}
}
// derived class
class MountainBike extends Bicycle
{
// the MountainBike subclass adds one more field
public int seatHeight;
// the MountainBike subclass has one constructor
public MountainBike(int gear,int speed,
int startHeight)
{
// invoking base-class(Bicycle) constructor
super(gear, speed);
seatHeight = startHeight;
}
// the MountainBike subclass adds one more method
public void setHeight(int newValue)
{
seatHeight = newValue;
}
// overriding toString() method
// of Bicycle to print more info
@Override
public String toString()
{
return (super.toString()+
"\nseat height is "+seatHeight);
}
}
// driver class
public class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
MountainBike mb = new MountainBike(3, 100, 25);
System.out.println(mb.toString());
}
}
Output
No. of gears are 3
The speed of bicycle is 100
Seat height is 25
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others



Login/Signup to comment