Run
public
class Main {
private
static int minJumps(int[] arr, int n) {
// jumps[n-1] will hold the
int jumps[] = new int[n];
int i, j;
// if first element is 0,
if (n == 0 || arr[0] == 0) return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// end cannot be reached
jumps[0] = 0;
// Find the minimum number of jumps to reach arr[i]
// from arr[0], and assign this value to jumps[i]
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
jumps[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (i <= j + arr[j] && jumps[j] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
jumps[i] = Math.min(jumps[i], jumps[j] + 1);
break;
}
}
}
return jumps[n - 1];
}
// driver program to test above function
public
static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {2, 1, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 8};
System.out.println("Minimum number of jumps to reach end is : " +
minJumps(arr, arr.length));
}
} 


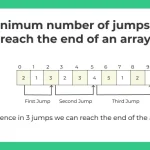


int arr[] = { 2, 1, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 8 };
int ptr = 0;
int destination = 0;
int jump = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
destination = Math.max(destination, arr[i] + i);
if (ptr == i && destination < arr.length) {
ptr = destination;
jump++;
}
}
System.out.println(jump);