Three way Partitioning of an Array around a Given Range in Java
Three way Partitioning of an Array around a Given Range in Java
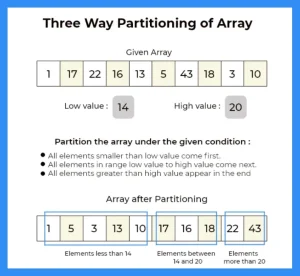
Here, in this page we will discuss the program for Three way partitioning of an array around a given range in Java programming language. We are given with an array and a range say [low, high], we need to partition the array in such a way,
- All the elements less than low value, should come first.
- Elements between the low and high value come in middle.
- All elements greater than high should come at the last.

Method Discussed :
- Method 1 : Using Brute Approach
- Method 2 : Using Dutch Algorithm
Let’s discuss them one by one in brief,
Method 1:
In this method we use recursion. At each point in the recursion, we append 0 and 1 to the partially formed number and recur with one less digit.
Method 1 : Code in Java
Run
import java.util.Arrays;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
int arr[] = { 23, 5, 18, 10, 20, 89 };
int n = arr.length, low = 1, high=4;
Arrays.sort(arr);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
Output :
5 10 18 20 23 89
Method 2:
- We traverse given array elements from left.
- We keep track of two pointers, first (called start in below code) to store next position of smaller element (smaller than range) from beginning;
- And second (called end in below code) to store next position of greater element from end.
Method 2 : Code in Java
Run
import java.io.*;
class Main
{
public static void threeWayPartition(int[] arr, int lowVal, int highVal)
{
int n = arr.length;
int start = 0, end = n-1;
for(int i = 0; i <= end;)
{
if(arr[i] < lowVal)
{
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
start++;
i++;
}
else if(arr[i] > highVal)
{
int temp = arr[end];
arr[end] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
end--;
}
else
i++;
}
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {1, 14, 5, 20, 4, 2, 54, 20, 87, 98, 3, 1, 32};
threeWayPartition(arr, 10, 20);
for (int i=0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
Output :
1 5 4 2 1 3 14 20 20 98 87 32 54
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription



Login/Signup to comment