Median of Two Sorted Arrays of Different Size in Java
Median of Two Sorted Arrays of Different Size in Java
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to find the Median of two sorted arrays of different size in Java programming language. We are given with two sorted arrays say a[] and b[] of size n and m respectively. We need to find the median of these two sorted arrays.
Case 1 : If (n +m) is odd then the median will be (n+m)/2-th element .
Case 2 : If (n+m) is even, then median will be the average of the ((n+m/2)-1)-th and (n+m)/2-th element.

Method Discussed :
- Method 1 : Linear Approach
- Method 2 : By comparing the medians of two arrays
Let’s discuss them one by one in brief,
Method 1:
- Create a variable count to have a count of elements in the output array.
- If the value of (m+n) is odd then there is only one median else the median is the average of elements at index (m+n)/2 and ((m+n)/2 – 1).
- To merge the both arrays, keep two indices i and j initially assigned to 0. Compare the ith index of 1st array and jth index of second, increase the index of the smallest element and increase the count.
- Store (m+n)/2 and (m+n)/2-1 in two variables.
- Check if the count reached (m+n) / 2. If (m+n) is odd return m1, If even return (m1+m2)/2.
Method 1 : Code in Java
Run
class Main{
static int getMedian(int ar1[], int ar2[], int n, int m)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int count;
int m1 = -1, m2 = -1;
if ((m + n) % 2 == 1)
{
for(count = 0;
count <= (n + m) / 2;
count++)
{
if (i != n && j != m)
{
m1 = (ar1[i] > ar2[j]) ?ar2[j++] : ar1[i++];
}
else if (i < n)
{
m1 = ar1[i++];
}
else
{
m1 = ar2[j++];
}
}
return m1;
}
else
{
for(count = 0;
count <= (n + m) / 2;
count++)
{
m2 = m1;
if (i != n && j != m)
{
m1 = (ar1[i] > ar2[j]) ?ar2[j++] : ar1[i++];
}
else if (i < n)
{
m1 = ar1[i++];
}
else
{
m1 = ar2[j++];
}
}
return (m1 + m2) / 2;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int ar1[] = { 900 };
int ar2[] = { 5, 8, 10, 20 };
int n1 = ar1.length;
int n2 = ar2.length;
System.out.println(getMedian(ar1, ar2, n1, n2));
}
}
Output :
10
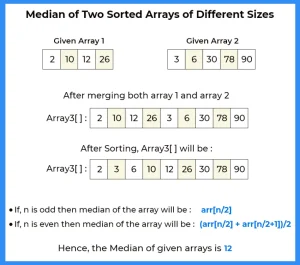
Method 2:
- Create another array say arr3[] of size n+m.
- Now, store the elements of arr1[] and arr2[] in arr3[].
- Sort the arr3[], using sort function
- Now, print the median : if (n+m) is odd then median is arr3[(n+m)/2]
- Otherwise, median is ((arr3[(n+m)/2])+(arr3[(n+m)/2-1]))/2.
Time and Space Complexities :
- Time-Complexity : O((n+m)log(n+m))
- Space-Complexity : O(n+m)
Method 2 : Code in Java
Run
import java.util.Arrays;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr1[] = { 900 };
int arr2[] = { 5, 8, 10, 20 };
int n = arr1.length;
int m = arr2.length;
int[] arr3;
arr3 = new int[n+m];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
arr3[i]=arr1[i];
int j=n;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
arr3[j++]=arr2[i];
Arrays.sort(arr3);
int median;
if((n+m)%2==0)
median = (arr3[(n+m)/2] + arr3[(n+m)/2-1])/2;
else
median = arr3[(n+m)/2];
System.out.println(median);
}
}
Output :
10
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription



Login/Signup to comment