Searching In A Binary Tree In C++
Searching In A Binary Tree
When working with tree data structures, searching for a specific element is one of the most common operations. Unlike arrays or linked lists, trees organize data hierarchically, which can make searches more efficient if implemented properly.
This blog explains how to search in a binary tree using C++, step by step. We’ll cover the concept, algorithm, recursive and iterative implementations, and complexity.
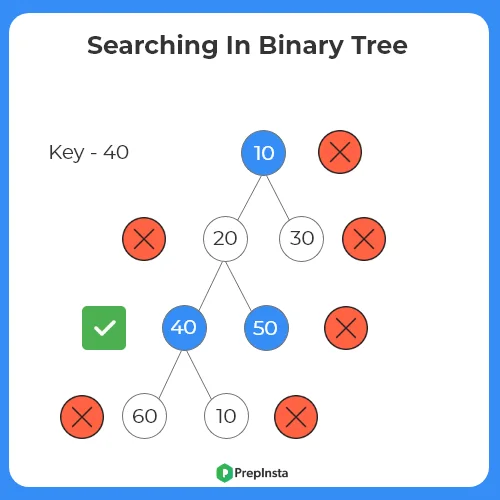
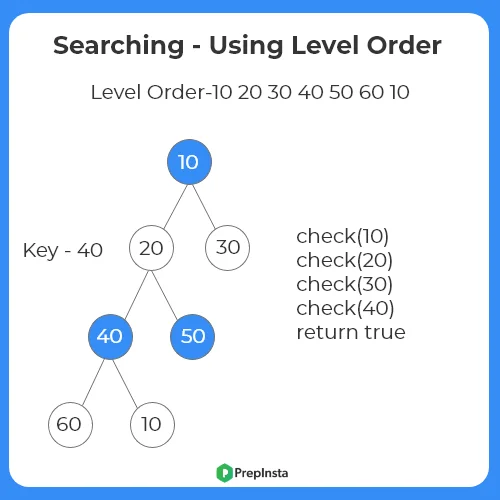
Algorithm Using Level Order Traversal
- Initialize the queue.
- Add root to the queue.
- Until the queue is empty, add the left child and the right child of the current node.
- Pop the node.
- Traverse the queue, check whether key is equal to the value of node.
- If found return true otherwise false.
Algorithm Using Recursion:
- If root is null, return.
- Else Recursively check for the left subtree and the right subtree.
- Return true if found.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Approaches to Search in a Binary Tree
There are two common ways to search in a binary tree:
- Recursive Search (Depth-First Search – DFS)
- Visit nodes in preorder, inorder, or postorder traversal.
- Check each node against the target value.
2. Iterative Search (Level-Order Traversal – BFS)
- Use a queue to traverse level by level.
- Check each node until the value is found or the tree ends.
Algorithm (Recursive DFS Search)
- If the current node is NULL, return false.
- If the current node’s value matches the key, return true.
- Recursively search in the left subtree.
- If not found, recursively search in the right subtree.
- If neither subtree has the key, return false.
C++ Implementation – Recursive DFS
Define the Node Structure
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int val) {
data = val;
left = right = nullptr;
}
};
Recursive Search Function
bool searchDFS(Node* root, int key) {
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->data == key)
return true;
bool leftSearch = searchDFS(root->left, key);
if (leftSearch) return true;
return searchDFS(root->right, key);
}
Helper to Build a Sample Tree
Node* buildSampleTree() {
Node* root = new Node(10);
root->left = new Node(8);
root->right = new Node(15);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(9);
root->right->left = new Node(12);
root->right->right = new Node(20);
return root;
}
Main Function (Testing DFS)
int main() {
Node* root = buildSampleTree();
int key = 12;
if (searchDFS(root, key))
cout << "Key " << key << " found in the tree using DFS." << endl;
else
cout << "Key " << key << " not found in the tree." << endl;
return 0;
}
Algorithm (Iterative BFS Search)
This approach uses a queue to traverse nodes level by level:
- If the root is NULL, return false.
- Push the root into a queue.
- While the queue is not empty:
- Pop the front node.
- If its value matches the key, return true.
- If it has a left child, push it into the queue.
- If it has a right child, push it into the queue.
4. If the loop ends, return false (key not found).
C++ Implementation – Iterative BFS
#include<queue>
bool searchBFS(Node* root, int key) {
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node* current = q.front();
q.pop();
if (current->data == key)
return true;
if (current->left)
q.push(current->left);
if (current->right)
q.push(current->right);
}
return false;
}
int main() {
Node* root = buildSampleTree();
int key = 20;
if (searchBFS(root, key))
cout << "Key " << key << " found in the tree using BFS." << endl;
else
cout << "Key " << key << " not found in the tree." << endl;
return 0;
}Output
For DFS search (key = 12):
Key 12 found in the tree using DFS.
For BFS search (key = 20):
Key 20 found in the tree using BFS.
If the key is not present (e.g., key = 30):
Key 30 not found in the tree.
Time and Space Complexity
Time Complexity (DFS and BFS):
- Worst Case: O(n) (all nodes must be visited)
- Best Case: O(1) (if the key is at the root)
Space Complexity:
- DFS recursion: O(h) (stack space, h = height of tree)
- BFS queue: O(w) (w = maximum width of tree)
Final Thoughts
Searching in a binary tree is fundamental to tree-based programming. Whether you use DFS (recursive) or BFS (iterative) depends on your use case:
- Use DFS for simplicity and when tree depth is manageable.
- Use BFS when you want to find nodes closer to the root first or avoid recursion limits.
With this knowledge, you’re ready to explore binary search trees (BSTs) where searching can be much faster — O(log n) in balanced trees.
FAQs - Searching in a Binary Tree In C++
FAQs - Searching in a Binary Tree In C++
- In a binary tree, nodes can have any value arrangement, so you must check every node — resulting in O(n) time complexity.
- In a binary search tree (BST), the left child is always smaller and the right child larger, allowing you to skip entire subtrees — resulting in O(log n) time complexity for balanced BSTs.
- DFS (Depth-First Search) is simpler to write using recursion and works well for deep trees.
- BFS (Breadth-First Search) uses a queue and is iterative, making it safer for very deep trees where recursion might cause a stack overflow.
- Both have O(n) time complexity in a generic binary tree; the choice depends on your application.
Yes. You can use iterative BFS with a queue to search level by level without recursion. This method is particularly useful when recursion depth is a concern or when you need to locate nodes closer to the root first.
In a standard binary tree, duplicate values are allowed. Both DFS and BFS will stop at the first occurrence of the key unless you modify the code to continue searching and collect all matching nodes.
- DFS (recursive): O(h), where h is the height of the tree (stack space).
- BFS (iterative): O(w), where w is the maximum width of the tree (queue size).
In skewed trees, DFS may use less memory, while in very wide trees, BFS might require more space.




Login/Signup to comment