Introduction to Heaps in Python
Introduction to Heaps in Python
Heaps in Python are a fundamental data structure in computer science used for various applications like priority queues, sorting, and graph algorithms. They allow for quick access to the smallest or largest element, depending on the type of heap. This efficiency makes them ideal for scenarios that require frequent insertions and deletions based on priority.
In Python, heaps are commonly implemented using the built-in heapq module, which provides functions for working with heaps.
What are heaps in Python?
In Python, a heap is a specialized tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property. The heap property ensures that the element with the highest (in a max heap) or lowest (in a min heap) value is always at the root of the tree.
This property makes heaps useful for various applications, such as implementing priority queues and solving problems involving finding the smallest or largest elements efficiently.
- Python provides a module called heapq as part of the standard library, which allows you to work with heaps. The heapq module provides functions to create and manipulate heap data structures.
What are the two types of heaps?
Two types of Heap
What are heaps used for?
Introduction to Heaps in Python are data structures commonly used for various applications in computer science and algorithms due to their efficient and specialized properties.
- Here are some common uses of heaps:
Priority Queues: Heaps allow quick access to the highest or lowest priority element, making them ideal for implementing priority queues in algorithms like Dijkstra’s and Prim’s.
Heap Sort: Heap sort uses a binary heap to sort elements in O(n log n) time and is suitable when in-place, non-stable sorting is acceptable.
Graph Algorithms: Heaps help efficiently select minimum-weight nodes or edges in graph algorithms like Dijkstra’s and Prim’s.
Task Scheduling: Heaps are used to manage tasks based on priority or execution time in real-time systems and scheduling algorithms.
Memory Management: Heaps support efficient memory allocation and deallocation, helping reduce fragmentation in memory management systems.
Recommended for you
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
What are three main properties of heap?
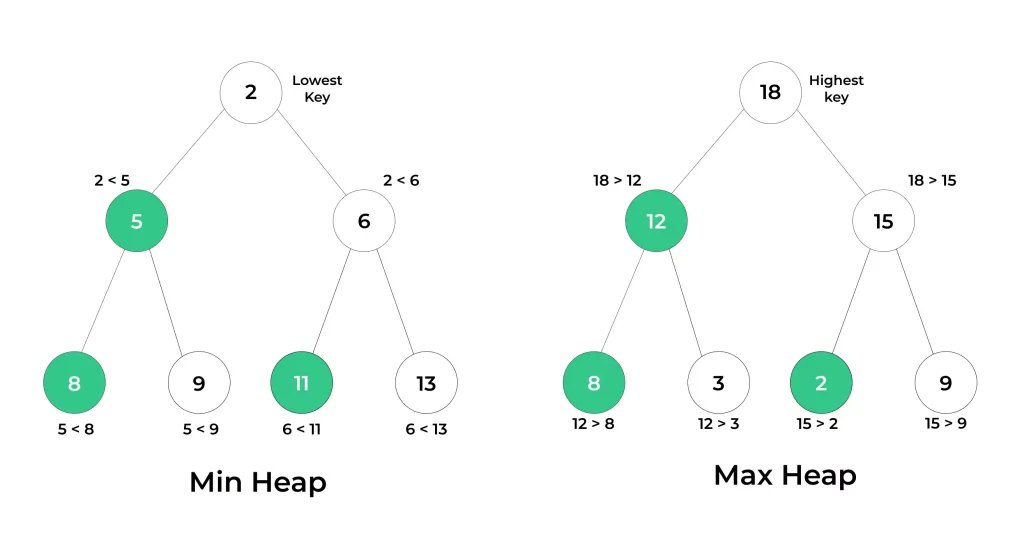
- Min Heap: In a min heap, for any given node 'A,' the value of 'A' is less than or equal to the values of its children. This property ensures that the minimum element is at the root, and all parent nodes have smaller or equal values compared to their children.
- Max Heap: In a max heap, for any given node 'A,' the value of 'A' is greater than or equal to the values of its children. This property ensures that the maximum element is at the root, and all parent nodes have larger or equal values compared to their children.
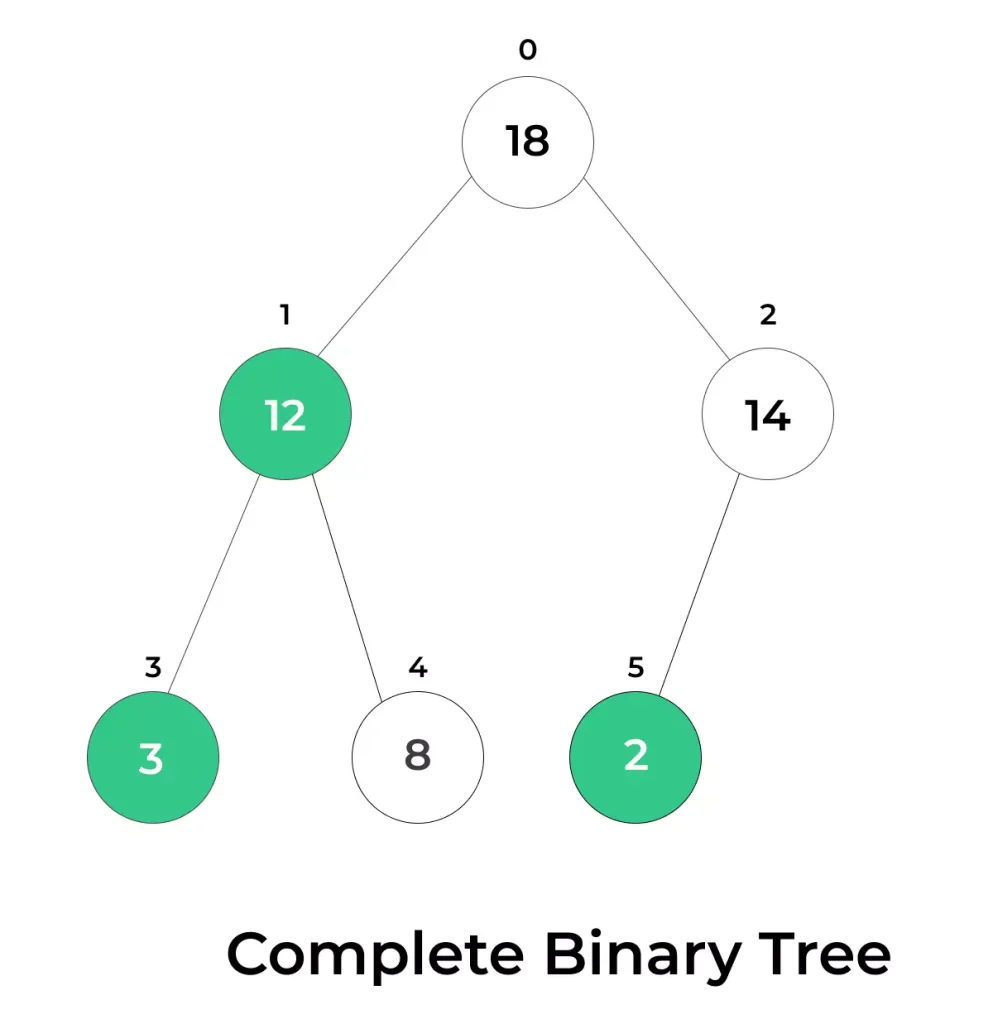
- A heap is implemented as a complete binary tree, where every level is fully filled except possibly the last.
- The last level is filled from left to right, maintaining compact structure.
- This layout makes heaps space-efficient and allows for easy array representation.
- Heaps efficiently support insertion and deletion operations.
- Both operations have a time complexity of O(log n), where n is the number of elements.
- Insertion and deletion maintain the heap property throughout the process.
Introduction to Heaps in Python Example:
A heap is a special tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property — in a min-heap, the parent node is always smaller than its children. Python provides the heapq module to work with heaps efficiently, making it easy to perform operations like insertion, deletion, and finding the smallest element.
Code:
import heapq
# Create an empty heap
heap = []
# Insert elements into the heap
heapq.heappush(heap, 20)
heapq.heappush(heap, 10)
heapq.heappush(heap, 30)
heapq.heappush(heap, 5)
# Remove and return the smallest element
smallest = heapq.heappop(heap)
# Display the heap and the popped element
print("Current Heap:", heap)
print("Smallest Element Removed:", smallest)
Output:
Current Heap: [10, 20, 30] Smallest Element Removed: 5
Explanation:
- We use heapq.heappush() to insert elements into the heap while maintaining the min-heap property.
- heapq.heappop() removes the smallest element (the root).
- Internally, Python uses a list to represent the heap and keeps it in a valid heap order.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion (heappush) | O(log n) | O(n) |
| Deletion (heappop) | O(log n) | O(n) |
| Access Min Element | O(1) | O(n) |
Heappush in python
In Python, the heappush function is part of the heapq module, which is a built-in module used for working with heap data structures.
- A heap is a specialized tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property, which is a specific ordering of elements that makes it efficient to find and remove the smallest (or largest) element.
- The heappush function is used to push elements onto a heap while maintaining the heap property. It takes two arguments: the heap itself and the element you want to insert into the heap.
import heapq # Create an empty heap heap = [] # Push elements onto the heap heapq.heappush(heap, 5) heapq.heappush(heap, 2) heapq.heappush(heap, 8) heapq.heappush(heap, 1) print(heap) # Output: [1, 2, 8, 5]
- In this example, we created an empty heap, and then we used heappush to insert four elements into the heap while maintaining the heap property.
- The result is a list that represents a valid min-heap, with the smallest element (1) at the root.
Wrapping Up:
Introduction to Heap in Python is a highly efficient in-place sorting algorithm with an average and worst-case time complexity of O(n log n). It is particularly advantageous for sorting large datasets due to its memory efficiency, as it doesn’t require additional memory beyond the input array.
- However, it is important to note that heap sort is not a stable sorting algorithm, which means it may change the relative order of equal elements in the sorted output. This property should be considered when sorting data with multiple attributes or when stability is a requirement.
FAQs
A heap is a special tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property either min-heap or max-heap. In Python, it is implemented using the heapq module which supports min-heap by default.
You can insert elements using heapq.heappush(heap, item), which maintains the heap property after insertion. This operation has a time complexity of O(log n).
Use heapq.heappop(heap) to remove and return the smallest element from the heap. It reorders the remaining elements to maintain the heap structure.
Yes, by inserting negative values (e.g., -item) into the heap and reversing the sign when retrieving, we can simulate a max-heap with heapq.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment