Introduction to Circular Queues in Python
Introduction to Circular Queues in Python
Get concept of introduction to Circular Queues in Python. Circular queues are a variation of traditional queues that offer efficient data management in a circular, ring-like structure.
In this page, we’ll delve into the concept of circular queues, their implementation in Python, and their relevance in data structure and algorithm (DSA) practices.
What is Circular Queue
A circular queue, also known as a ring buffer, is a linear data structure that operates on the principles of a regular queue but with a twist. Unlike a traditional queue, where elements are enqueued and dequeued from opposite ends, a circular queue operates within a fixed-size buffer. Once the buffer is full, new elements start overwriting the oldest ones, creating a circular behavior.
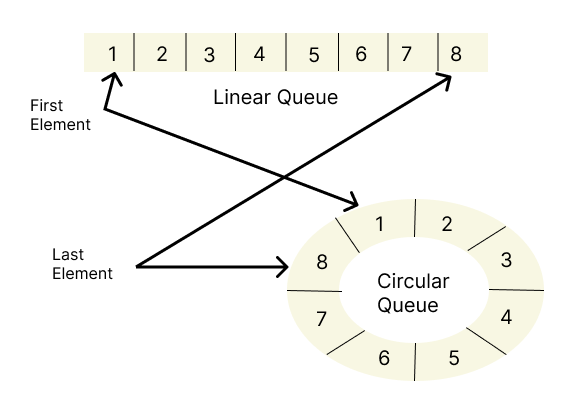
How Circular Queue Works
Circular Queue works by the process of circular increment, you’ll need two pointers: a front pointer and a rear pointer. Initially, both pointers point to the same location in the array.
Here, the circular increment is shown :
# Initialize variables
REAR = 0
# Check for overflow condition
if REAR + 1 == 5:
# Set REAR to the start of the queue
REAR = (REAR + 1) % 5
# Print the updated value of REAR
print("Updated REAR:", REAR)
The following are the operations that can be performed on a circular queue:
- Front : It is used to get the front item from the queue.
- Rear : It is used to get the last element from the queue.
- enQueue(value): This function is used to insert the new value in the queue . The new element is always inserted at the rear end.
- deQueue() : This function deletes an element from the queue. The deletion in queue always takes place from the front end.
Steps for performing enQueue and deQueue operation in Circular Queue:
- Initially queue has a single value 1 and front and rear are set to 1.
- Then insert the value 2 after incrementing the rear.
- Similarly insert the value 3 by incrementing the rear.
- Again insert the value 4 by incrementing the rear.
- Again insert the value 5 by incrementing the rear.
- Now our queue becomes full so delete the element from the front and increment the front .So our front will set at value 2.
- Now Again insert the value 6 by incrementing the rear.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Implementation of Circular Queue in Python
A Circular Queue is a linear data structure that follows the FIFO (First In First Out) principle but connects the end back to the front, forming a circle. It solves the problem of unused space in a normal queue when elements are dequeued from the front.
Code:
class CircularQueue:
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
self.queue = [None] * size
self.front = -1
self.rear = -1
def enqueue(self, data):
# Check if the queue is full
if ((self.rear + 1) % self.size == self.front):
print("Queue is Full\n")
elif (self.front == -1): # First element
self.front = 0
self.rear = 0
self.queue[self.rear] = data
else:
self.rear = (self.rear + 1) % self.size
self.queue[self.rear] = data
def dequeue(self):
# Check if the queue is empty
if self.front == -1:
print("Queue is Empty\n")
elif self.front == self.rear:
temp = self.queue[self.front]
self.front = -1
self.rear = -1
return temp
else:
temp = self.queue[self.front]
self.front = (self.front + 1) % self.size
return temp
def display(self):
if self.front == -1:
print("Queue is Empty")
else:
print("Elements in the Circular Queue are:", end=" ")
i = self.front
while True:
print(self.queue[i], end=" ")
if i == self.rear:
break
i = (i + 1) % self.size
print()
# ---------- Testing the Circular Queue ----------
cq = CircularQueue(5)
cq.enqueue(10)
cq.enqueue(20)
cq.enqueue(30)
cq.enqueue(40)
cq.enqueue(50) # This should show "Queue is Full" due to circular logic
cq.display()
print("Dequeued:", cq.dequeue())
print("Dequeued:", cq.dequeue())
cq.display()
cq.enqueue(60)
cq.enqueue(70)
cq.display()
Output:
Queue is Full Elements in the Circular Queue are: 10 20 30 40 Dequeued: 10 Dequeued: 20 Elements in the Circular Queue are: 30 40 Elements in the Circular Queue are: 30 40 60 70
Explanation:
- A Circular Queue connects the end back to the front to efficiently utilize space.
- It uses modulo arithmetic to wrap around indices.
- enqueue inserts at the rear; dequeue removes from the front.
- It avoids shifting elements like in a linear queue.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Enqueue | O(1) | O(n) |
| Dequeue | O(1) | O(n) |
| Display | O(n) | O(n) |
Difference between Circular Queue and Linear Queue
| Aspect | Circular Queue | Linear Queue |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Circular arrangement of elements | Linear arrangement of elements |
| Overflow Handling | Reuses vacant spaces, wraps around | Requires resizing or memory reallocation |
| Memory Utilization | Optimized due to circular arrangement | May lead to memory fragmentation |
| Space Efficiency | Higher due to circular structure | Can have wasted space due to dequeued elements |
| Implementation | Simpler due to circular nature | Slightly more complex |
Advantages of Circular Queues in Python
Circular queues offer several distinct advantages that make them a preferred choice in various scenarios:
- Efficient Space Usage: Circular queues use a fixed-size buffer, making them suitable for applications with limited memory resources.
- Constant Time Operations: Enqueue and dequeue operations in a circular queue generally occur in constant time, regardless of the number of elements present.
- Data Streaming: Circular queues are commonly used in scenarios involving data streaming, such as audio and video processing, where continuous data flow needs to be managed effectively.
- Implementation of Buffers: They are often employed to implement buffers for communication between different parts of a system.
Wrapping Up:
Circular queues are a versatile and efficient data structure with a wide range of applications. Their ability to manage elements in a circular fashion while optimizing memory usage and enabling constant-time operations makes them a valuable tool in computer science. Whether you’re working on system programming, real-time data processing, or any application that involves managing a continuous flow of data, circular queues are an essential concept to grasp.
FAQs
A circular queue is a linear data structure that connects the last position back to the first to form a circle. This helps efficiently use memory and avoid shifting elements during enqueue and dequeue operations.
In a regular queue, once the rear reaches the end, no more elements can be added even if there’s space at the front. Circular queues reuse empty spaces by wrapping around the array.
The main operations are enqueue() to add, dequeue() to remove, along with isFull() and isEmpty() to check status. These maintain the circular nature and prevent overflow or underflow.
Circular queues are ideal for memory-constrained environments like buffers, scheduling, or real-time systems where fixed-size queues are needed with constant time operations.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment