Program to find Median of two sorted arrays of equal size in C++
Median of two sorted arrays of equal size in C++
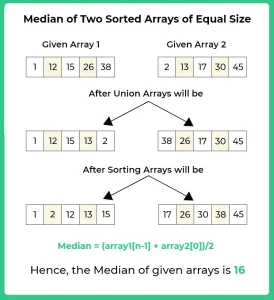
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to find median of two sorted arrays of equal size in C++ programming language. We are given with two arrays say arr1[] and arr2[] of the same size say n . We need to find the median after merging these arrays.

Method 1:
- Find the union of the given two arrays.
- Sort both array 1 and array2 (Using inbuilt sort() function).
- Then the median element will be
Median = (arr1[n-1]+arr2[0])/2
Time and Space Complexities :
- Time-Complexity :O(nlogn)
- Space-Complexity : O(1)
Code for Median of two Sorted arrays of equal size in C++
Run
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int getMedian(int ar1[], int ar2[], int n)
{
int j = 0;
int i = n - 1;
while (ar1[i] > ar2[j] && j < n && i > -1)
swap(ar1[i--], ar2[j++]);
sort(ar1, ar1 + n);
sort(ar2, ar2 + n);
return (ar1[n - 1] + ar2[0]) / 2;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int arr1[n], arr2[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>arr1[i];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>arr2[i];
cout<<getMedian(arr1, arr2, n);
return 0;
}Input :
5
1 12 15 26 38
2 13 17 30 45
Output :
16
Method 2 :
- Take the size of the array from the user and store them in the variables say n.
- Create two arrays of size n and then take elements of the respective arrays from the user.
- Now, create variable count. Keep track of count while comparing elements of two arrays.
- Run a loop that will terminate when count > n.
- If count becomes n(For 2n elements), we have reached the median.
- Take the average of the elements at indexes n-1 and n in the merged array.
Time and Space Complexities :
- Time-Complexity :O(n)
- Space-Complexity : O(1)
Code for Median of two Sorted arrays of equal size in C++
Run
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int getMedian(int ar1[], int ar2[], int n)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int count;
int m1 = -1, m2 = -1;
for (count = 0; count <= n; count++){
if (i == n){
m1 = m2;
m2 = ar2[0];
break;
}
else if (j == n){
m1 = m2;
m2 = ar1[0];
break;
}
if (ar1[i] <= ar2[j]){
/* Store the prev median */
m1 = m2;
m2 = ar1[i];
i++;
}
else{
/* Store the prev median */
m1 = m2;
m2 = ar2[j];
j++;
}
}
return (m1 + m2)/2;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int arr1[n], arr2[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>arr1[i];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>arr2[i];
getMedian(arr1, arr2, n);
return 0;
}
Input :
5
1 12 15 26 38
2 13 17 30 45
Output :
16
Method 3 (By comparing the median of the two arrays-Divide and Conquer) :
- Find the medians of the given two arrays and store them in variable say m1 and m2.
- Now, if m1=m2, then that will be the required output.
- If m1>m2, then we check in the subarrays, arr1[0 – middle element] and in arr2[middle element – last].
- If m2>m1, then we check in the subarrays, arr1[middle element – last] and in arr2[0-middle element ].
- This will be the recursive process and repeat this till size of both the arrays become 2.
- As, when the size will be 2 , we can use the formula :
Median = (max(ar1[0], ar2[0]) + min(ar1[1], ar2[1]))/2
Time and Space Complexities :
- Time-Complexity :O(logn)
- Space-Complexity : O(1)
Code for Median of two Sorted arrays of equal size in C++
Run
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Function to get median of a sorted array */
int median(int arr[], int n)
{
if (n%2 == 0)
return (arr[n/2] + arr[n/2-1])/2;
else
return arr[n/2];
}
int getMedian(int ar1[], int ar2[], int n)
{
if (n == 1)
return (ar1[0] + ar2[0])/2;
if (n == 2)
return (max(ar1[0], ar2[0]) + min(ar1[1], ar2[1])) / 2;
int m1 = median(ar1, n);
int m2 = median(ar2, n);
if (m1 == m2)
return m1;
if (m1 < m2)
{
if (n % 2 == 0)
return getMedian(ar1 + n/2 - 1, ar2, n - n/2 +1);
return getMedian(ar1 + n/2, ar2, n - n/2);
}
if (n % 2 == 0)
return getMedian(ar2 + n/2 - 1, ar1, n - n/2 + 1);
return getMedian(ar2 + n/2, ar1, n - n/2);
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int arr1[n], arr2[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>arr1[i];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>arr2[i];
cout<<getMedian(arr1, arr2, n);
return 0;
}Input :
5
1 12 15 26 38
2 13 17 30 45
Output :
16
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription



