C++ Program to Find Factorial of a Large Number
Factorial of a Large Number in C++
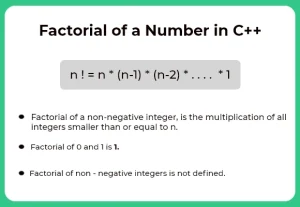
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to find the Factorial of a Large Number in C++ . Factorial of a number means multiply of all below number with each other till 1. If user enter 0 or 1 , then factorial of both numbers will be 1 only. Or If user enters negative numbers then it’s factorial is not defined.

Method 1 :
The logic behind this algorithm is to use the mathematical concept for finding the product of two number. We do multiplication digit by digit from the right hand side of the number and maintain the carry in each multiplication of the digits and finally we reverse the result array.
- Initialize carry as 0.
- Do following for i = 0 to res_size – 1
a) Find value of res[i] * x + carry. Let this value be prod.
b) Update res[i] by storing last digit of prod in it.
c) Update carry by storing remaining digits in carry. - Put all digits of carry in res[] and increase res_size by number of digits in carry.
In the above approach we use extra space to store the result.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 500
int multiply(int x, int res[], int res_size);
void factorial(int n)
{
int res[MAX];
// Initialize result
res[0] = 1;
int res_size = 1;
// Apply simple factorial formula n! = 1 * 2 * 3 * 4...*n
for (int x=2; x<=n; x++)
res_size = multiply(x, res, res_size);
cout << "Factorial of given number is \n"; for (int i=res_size-1; i>=0; i--)
cout << res[i];
}
int multiply(int x, int res[], int res_size)
{
int carry = 0; // Initialize carry
// One by one multiply n with individual digits of res[]
for (int i=0; i<res_size; i++)
{
int prod = res[i] * x + carry;
// Store last digit of 'prod' in res[]
res[i] = prod % 10;
// Put rest in carry
carry = prod/10;
}
// Put carry in res and increase result size
while (carry)
{
res[res_size] = carry%10;
carry = carry/10;
res_size++;
}
return res_size;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
int n=100;
factorial(n);
return 0;
}
Output :
93326215443944152681699238856266700490715968264381621468592963895217599993229915608941463976156518286253697208272237582511852109168640000000000 00000000000000
Method 2 :
In this approach we will use linked list instead of using arrays.
Method 2 : Code in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i <= b; i++)
using namespace std;
// Made a class node containing data and previous pointer as
// we are using tail pointer
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* prev;
Node(int n){
data = n;
prev = NULL;
}
};
void Multiply(Node* tail, int n) {
Node *temp = tail, *prevNode = tail;
// Temp variable for keeping tail
int carry = 0;
while (temp != NULL) {
int data = temp->data * n + carry;
temp->data = data % 10; // stores the last digit
carry = data / 10;
prevNode = temp;
temp = temp->prev; // Moving temp by 1 prevNode will
// now denote temp
}
// If carry is greater than 0 then we create another
// node for it.
while (carry != 0) {
prevNode->prev = new Node((int)(carry % 10));
carry /= 10;
prevNode = prevNode->prev;
}
}
void print(Node* tail)
{
if (tail == NULL) // Using tail recursion
return;
print(tail->prev);
cout<< tail->data; // Print linked list in reverse order
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 20;
Node tail(1); // Create a node and initialise it by 1
rep(i, 2, n)
Multiply(&tail, i); // Run a loop from 2 to n and
// multiply with tail's i
print(&tail); // Print the linked list
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Output :
2432902008176640000
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription





Login/Signup to comment