C++ Program to find all the elements that appear more than ” n/k ” times.
Elements that appear more than “n/k” times in C++
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to find all the elements that appear more than “n/k” times in C++ . We are given with an array of size n, find all elements in array that appear more than n/k times.
Example :
- Input : arr[ ] : {3, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 3, 3} and k = 4,
- Output : 2, 3
- Explanation : As, size of array i.e, n = 8 so, n/k => 2 and in the given input array 2 and 3 occurs 3 and 3 times respectively.

Method 1 (Brute force Approach) :
In this approach we will discuss the naive approach to solve this problem.
- Iterate over the array and count its frequency.
- If count is more than n/k times then print that element.
- Now, here we need to handle the duplicate printing, so for that make every j-th element to -1 (Here, we are assuming that array will contain only positive elements).
Time and Space complexity of above approach :
- Time – complexity : O(n^2)
- Space-complexity – O(1)
Code to find all Elements that appear more than " n/k " times in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int arr[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>arr[i];
int k;
cin>>k;
int x = n/k;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int count = 1;
if(arr[i] != -1){
for(int j=i+1; j<n; j++){
if(arr[i]==arr[j]){
count++;
arr[j] = -1; //set that visited element to -1 to avoid repetition
}
}
}
if(count > x) cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
}
Input :
9
1 2 2 6 6 6 6 7 9
4
Output :
6
Method 2 :
In this approach we will discuss the efficient approach than the above approach to solve this problem .
- Sort the array.
- Iterate over the array and count the frequency of every distinct array element by checking if adjacent elements are equal or not.
- If frequency of the array element is found to be greater than n / k, then print the array element.
Time and Space complexity of above approach :
- Time – complexity : O(n logn)
- Space-complexity – O(1)
Code to find all Elements that appear more than " n/k " times in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int arr[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>arr[i];
int k;
cin>>k;
int x = n/k;
sort(arr, arr + n);
for(int i = 0; i < n;) {
int count = 1;
while ((i + 1) < n && arr[i] == arr[i + 1]) {
count++;
i++;
}
if (count > x) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
i++;
}
}
Input :
9
1 2 2 6 6 6 6 7 9
4
Output :
6
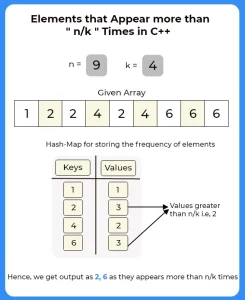
Method 3 (Using Hash-map) :
In this approach we will discuss the efficient approach . We will use map to store the frequency of the element.
- Declare a hash map.
- Iterate over the array and increase that value in map by 1.
- Now, iterate over the map and check if frequency is found to be greater than n / k, then print that key value.
Time and Space complexity of above approach :
- Time – complexity : O(n )
- Space-complexity – O(n)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int arr[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>arr[i];
int k;
cin>>k;
int x = n/k;
unordered_map<int, int>mp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
mp[arr[i]]++;
}
for(auto it=mp.begin(); it!=mp.end(); it++){
if(it->second>x)
cout<first<<" ";
}
}
Input :
9
1 2 2 6 6 6 6 7 9
4
Output :
6
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription




Login/Signup to comment